Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
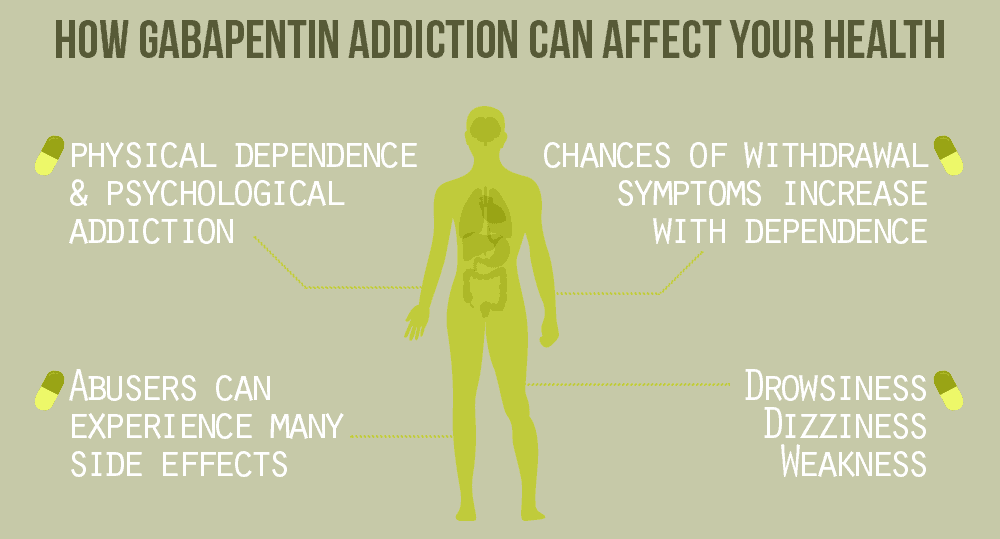
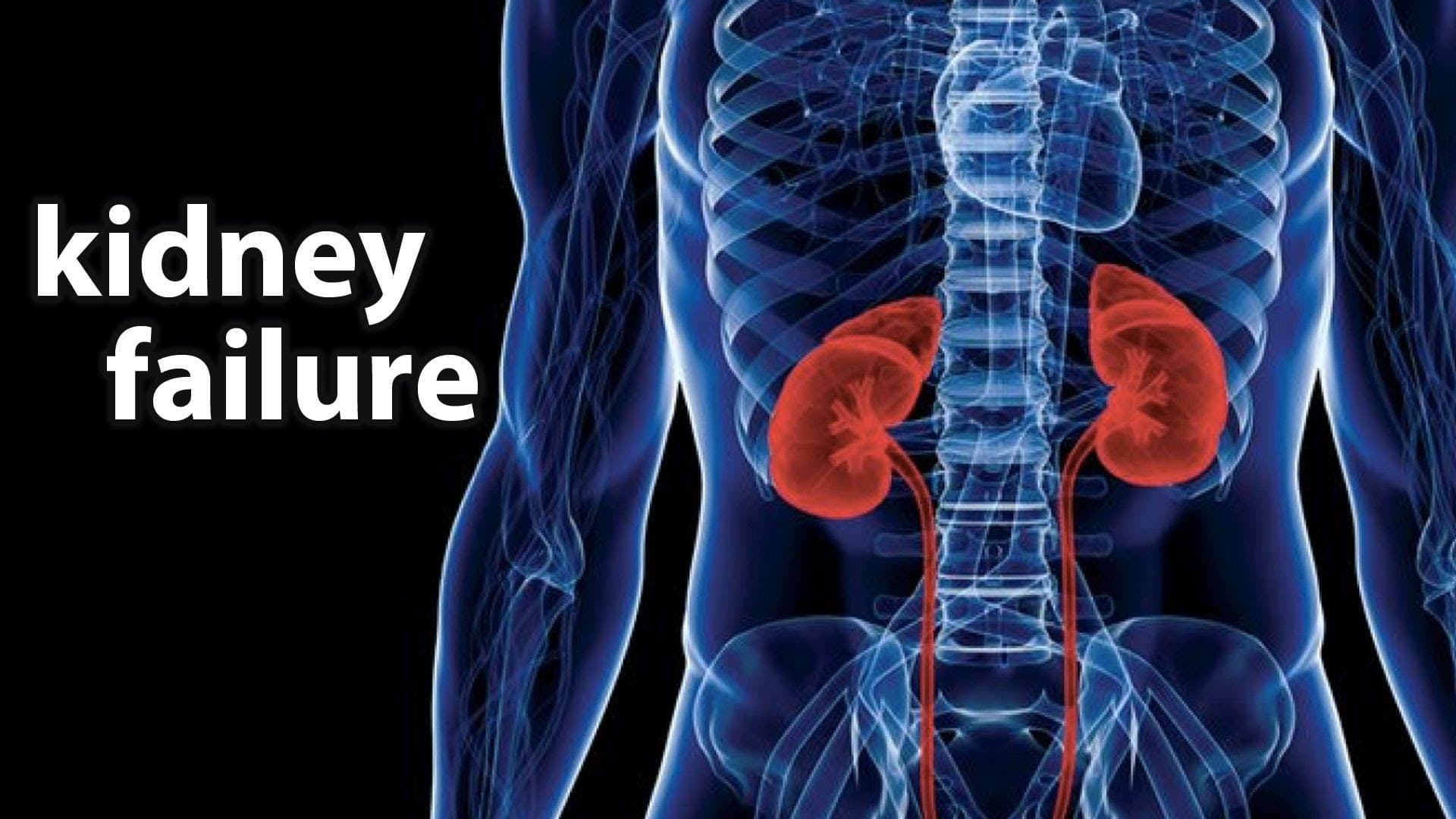
Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. While gabapentin itself doesn't directly damage the kidneys, it can cause side effects like dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema that may be more pronounced in those with kidney disease. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Another similarity was the rapid resolution of the condition and the improvement in Ck values after discontinuing the drug. In summary, we can conclude that although it happens infrequently, gabapentin may cause myotoxicity, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure even in patients whose renal function was previously normal. Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Pharmacology Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors in For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. In people with renal impairment, gabapentin can be harder to clear from the body. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has no harmful effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance.24In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (with-out dialysis),30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Gabapentin does not inherently damage kidneys but requires careful consideration when prescribed to individuals with existing renal impairments. Monitoring kidney function regularly while adjusting dosages based on eGFR levels can help mitigate potential risks associated with this medication. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. For patients with normal kidney function, Gabapentin's half-life—approximately 5 to 7 hours—allows for effective dosing without significant accumulation. However, those with compromised renal function may experience prolonged effects due to slower elimination rates. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, can potentially cause kidney problems. Prolonged use, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney dysfunction or advanced age, increases the risk. Gabapentin impacts kidney function by reducing its ability to clear the drug, leading to its accumulation and potential damage. Abstract Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related adverse events (GRAEs). Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |