Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
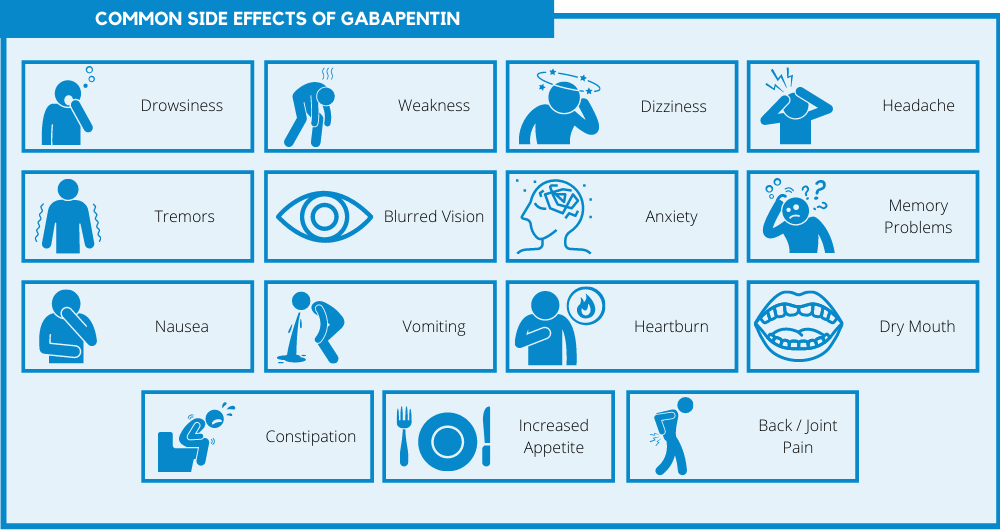 |  |
It is crucial for healthcare providers to be attentive to any signs of depression or worsening emotional symptoms in patients prescribed gabapentin, as these issues can impact overall treatment outcomes and quality of life. The relationship between gabapentin and depression is complex and not yet fully understood. While gabapentin is not typically indicated as a primary treatment for depression, some studies and anecdotal reports have suggested a potential association between gabapentin use and the development or worsening of depressive symptoms. While gabapentin isn’t typically used as a standalone treatment for depression, some studies suggest it may have a role as an adjunct therapy, particularly in bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has gained attention for its use in managing depression, especially in individuals who have treatment-resistant depressive disorders. It is not an FDA-approved indication, but physicians may prescribe it off-label based on clinical judgment. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Understanding Gabapentin Use Gabapentin is a medication primarily utilized for its antiepileptic properties. While its primary use is for the treatment of seizures, this versatile drug has a variety of therapeutic benefits and is also employed for off-label uses. Therapeutic Benefits Gabapentin serves a vital role in managing various conditions related to the nervous system. In addition to its Gapentin is not typically used to treat anxiety alone, but some recent studies suggest it may be effective in easing anxiety symptoms in individuals with depression or bipolar disorder. Gabapentin is not commonly used to treat depression, but some recent studies indicate it may treat anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. A normal dose of gabapentin for adults can be anywhere from 100 mg to 3600 mg each day. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin is primarily prescribed as an anticonvulsant for seizures and neuropathic pain, but its role in treating depression remains unclear. Despite being used off-label for mood disorders, significant evidence directly linking gabapentin to effective treatment of depression is lacking. Research into whether gabapentin can effectively treat depression has produced mixed results. Some studies suggest that gabapentin may have antidepressant properties due to its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity. Gabapentin may serve various therapeutic roles, but careful consideration of its psychiatric implications is vital for effective treatment. Users are encouraged to remain vigilant regarding their mental health while under gabapentin treatment. Uncovering Evidence: Gabapentin and Depression Case studies linking gabapentin to depression Numerous case studies illustrate the potential psychiatric Scientific evidence does not support gabapentin as effective for depression, but some patients report improvement. It may help to manage related symptoms of anxiety, insomnia, or nerve pain, but it is not a replacement for antidepressants. Therapy is widely delivered to treat anxiety and depression for those prescribed gabapentin, and it’s highly effective. Although there are many types of depression and anxiety therapy, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Neurontin Drug Usage Information Neurontin is not your traditional anxiety treatment. It was originally created as an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy though for some people who anxiety, it may be an effective treatment. Doctors that prescribe Neurontin for anxiety often only do so if the patient has been diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Neurontin is used as a supplementary drug for those Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog in some individuals. Cognitive issues, such as a decrease in alertness, may occur as side effects, often accompanied by dizziness and drowsiness, affecting about 10% of users. While gabapentin is used to manage conditions like nerve pain and menopause symptoms, its impact on cognitive function is a concern for some patients
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |