Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
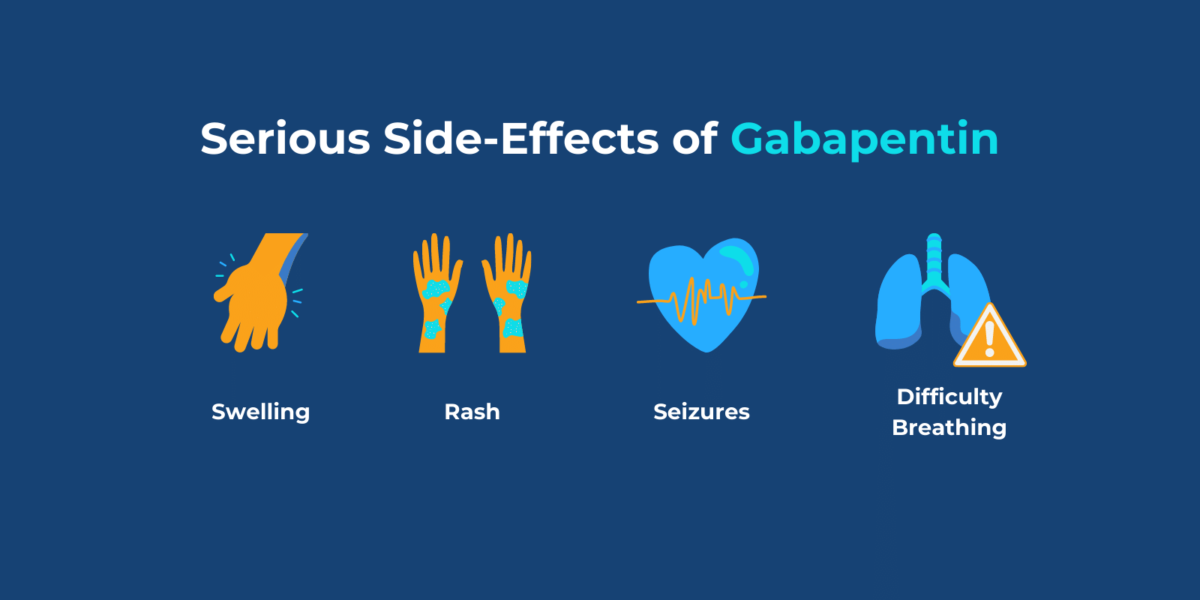 |  |
Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Gabapentin can be used by kidney disease patients, but dosage adjustments are critical. Learn how to safely use gabapentin with kidney issues and discover alternative medications. When kidney function declines, the clearance of Gabapentin can be affected, leading to increased levels in the bloodstream. For patients with normal kidney function, Gabapentin's half-life—approximately 5 to 7 hours—allows for effective dosing without significant accumulation. Gabapentin and Blood creatinine increased - a phase IV clinical study of FDA data Summary: Blood creatinine increased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Enbrel, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Gabapentin, a medication frequently prescribed for managing neuropathic pain and seizures, impacts kidney function, necessitating careful consideration of creatinine levels. Creatinine, a waste product generated by muscle metabolism, serves as a key indic Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, can potentially cause kidney problems. Prolonged use, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney dysfunction or advanced age, increases the risk. Gabapentin impacts kidney function by reducing its ability to clear the drug, leading to its accumulation and potential damage. Clinical manifestations include increased creatinine levels, swelling The FDA drug label does not directly answer whether gabapentin worsens renal function. However, it does indicate that gabapentin is substantially excreted by the kidney and that patients with impaired renal function are at a greater risk of toxic reactions. Information on drugs that elevate serum creatinine concentration, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis. Gabapentin affects kidney function as it is primarily eliminated by the kidneys and its clearance is directly proportional to creatinine clearance. This means that patients with impaired renal function may have reduced gabapentin clearance, leading to increased drug levels and potential Laboratory tests revealed extreme elevations of muscle enzymes, increased creatinine and potassium levels. She required hemodialysis as a result of anuria. Investigation confirmed the diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis, and discontinuation of GBP resulted in resolution of clinical and biochemical features of rhabdomyolysis. In addition, we excluded those who started both gabapentin and pregabalin on the cohort entry date, and we excluded patients with no serum creatinine measurements in the year before cohort entry. When starting gabapentin, your prescriber will typically initiate a lower dose and then increase your dose over a few days to weeks. This helps your body get used to gabapentin, and minimizes the risk of side effects. Gabapentin, a home medication, was increased from 600 mg TID to 800 mg TID. Unfortunately, patient experienced acute kidney injury in setting of IV contrast administration; her creatinine increased from 0.72 to 3.2 over 5 days. On day 4, patient developed depressed mental status with myoclonus. Elevated creatinine levels can be a sign of kidney problems, but sometimes certain medications can increase creatinine. Learn about creatinine levels in blood tests. Cats with CKD had significantly higher dose-normalized serum gabapentin concentrations than normal cats for both doses at both time points. Dose-normalized gabapentin serum concentrations at 3h and 8h were significantly correlated with serum Creatinine and SDMA, measures of kidney function used in IRIS staging. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |