Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
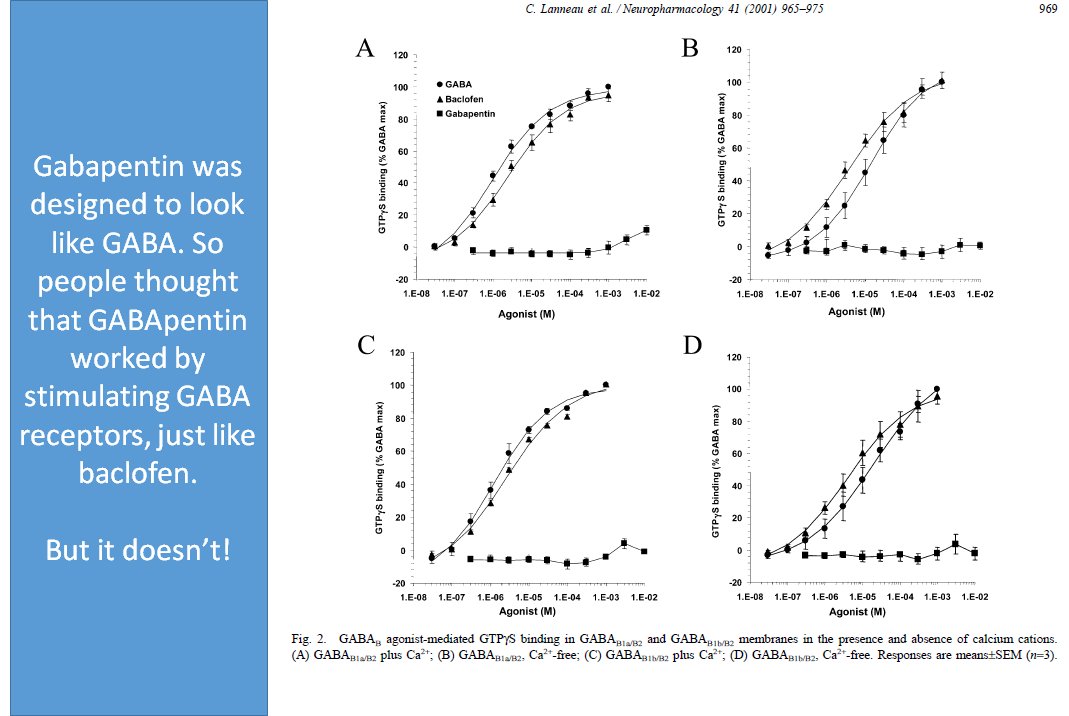
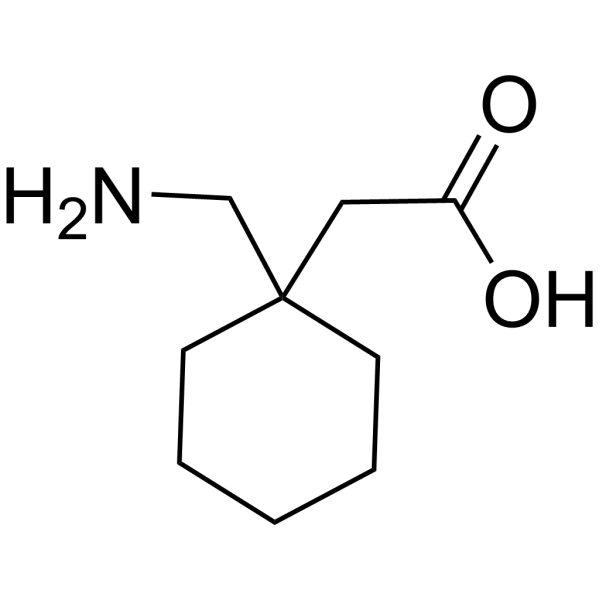
Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Ativan, a benzodiazepine that enhances GABA activity, can influence dopamine release and contribute to its addictive potential. Similarly, gabapentin and dopamine interactions highlight how drugs designed to mimic GABA can have complex effects on other neurotransmitter systems. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions including the cerebellum and hippocampus. Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium It is structurally related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). However, does not modify GABA binding, is not converted into a GABA agonist, and does not inhibit GABA uptake/degradation By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions including the cerebellum and hippocampus. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits Gabapentin is structurally similar to GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, but it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it binds to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from neuronal tissues in vitro. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. A2δ is expressed in Purkinje cells, which use gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) as a neurotransmitter. The author states that gabapentinoids inhibit the α2δ subunit and reduce neurotransmitter release, resulting in the induction of cerebellar ataxia. 1,2 Gabapentin has been demonstrated to activate gluta- mate decarboxylase (GAD)J31,34] and also weakly inhibit GABA-T activity [1]. Recent studies have also demonstrated that gabapentin alters the metabolism of GABA by enhancing the rate of syn- thesis .of GABA in several regions of the brain [17]. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we GABA - formula, structure, properties, abbreviation, benefits and side effects. Why is alanine important? Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin's binding site is located on the α2 δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. 6 In vitro, gabapentin can inhibit neuronal calcium currents by 35% and decrease neuronal tachykinin-mediated activity. 7,8 It has been suggested that mitigation of hypothalamic tachykinin neurotransmitter activity via a decrease in neuronal calcium GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |