Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) | 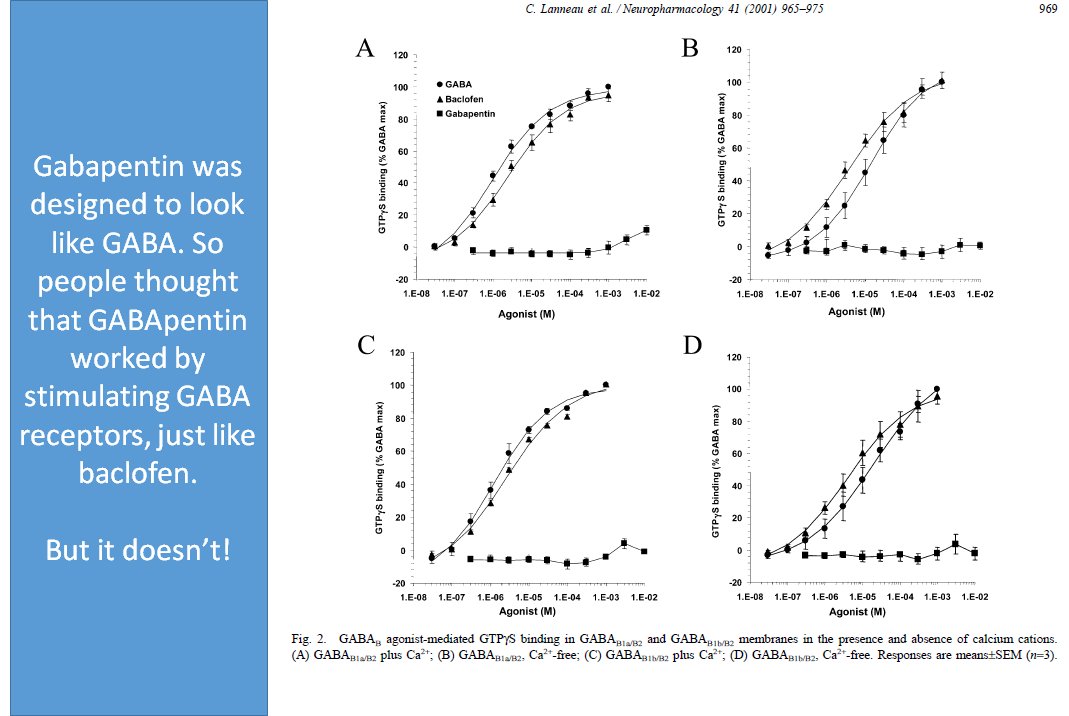 |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at GABAPENTIN (NEURONTIN) One of the most extensively used anticonvulsants in the management of neuropathic pain, gabapentin has proven efficacy in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, phantom limb pain, and pain following spinal cord injury (Fig. 346-4). An analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), gabapentin is thought to exert its analgesic effect by modulating Does gabapentin increase or decrease dopamine? Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, primarily responsible for inhibiting nerve transmission, which helps to reduce neuronal excitability. In contrast, gabapentin is a medication designed to mimic the effects of GABA, used primarily to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) was first synthesized in 1883. It was first identified as a biochemical substance in 1910 by Ackermann and Kutscher who showed that putrefactive bacteria could produce it by decarboxylation of glutamic acid. It was later found in many microorganisms and plant tissues and in 1950; its presence in considerable amounts in mammalian brain What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. So does Gabapentin produce GABA tolerance, and also can you increase GABA tolerance using only artificial indirect GABA increasing drugs? Would this then create cross tolerance for other GABAergic substances? Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the Can Gabapentin Cause Serotonin Syndrome? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and nerve pain medication prescribed to patients with seizure disorders like epilepsy or pain caused by the shingles virus. Common brand names for gabapentin include Gralise, Horizant, Neuraptine, and Neurontin. This drug works by stimulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically GABA and serotonin Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Key Takeaways: GABA is a natural supplement that helps alleviate anxiety and physical tension. Gabapentin is a Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in your brain, meaning it slows your brain’s functions. GABA is known for producing a calming effect. Gabapentin is a prescription medication primarily used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and certain types of chronic pain, but it is sometimes misused recreationally for its sedative effects. When taken in higher doses or used in combination with other substances, gabapentin can produce effects that some may describe as a “high,” although this is not its intended use. What Is Gabapentin Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that Fig. 1 Extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors and their potential modulation by gabapentin. GABA-A receptors, which are GABA-gated chloride channels, are pentameric channels composed of various subunits (α1–6, β1–4, γ1–3, δ, ε, θ, ρ1–3). They are localized at synaptic and extrasynaptic sites. Synaptic (γ-containing) receptors, present ubiquitously within the brain, produce phasic Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Learn about the difference between GABA and gabapentin, a neurotransmitter and an inhibitory medication often used for seizures and neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |