Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
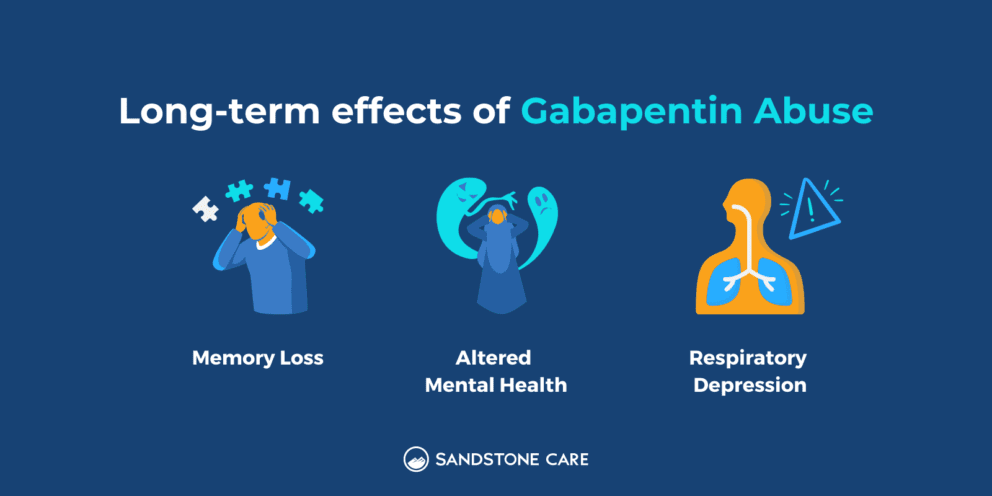
Gabapentin is an emerging drug of misuse Reports of gabapentin misuse are increasing. 3,4 Gabapentin can be misused orally, intranasally and intravenously, with doses ranging from therapeutic (< 3600 mg/d) to supratherapeutic (12 000 mg/d). 2 The exact prevalence of gabapentin misuse is unclear, as the current evidence is of low quality, relies on self-reports or has been derived from selected 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia - In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a Gabapentinoid abuse and adverse events in patients Without controlled pharmacological studies to assess gabapentin's and pregabalin's abuse potential, other available data can be used to estimate the potential risk of misuse. This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified Gabapentin has been shown to lead to dependence, addiction and withdrawal in some people, although when it was first approved in 1993 this risk was thought to be minimal. Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as Gabapentin addiction is caused by its misuse for recreational purposes or to enhance the effects of other substances. Risk factors include a history of substance abuse, mental health disorders, and chronic pain conditions. The drug’s availability and perceived safety also contribute to its misuse. Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects Gabapentin – another drug of misuse? Janet Webb, BSc (Pharm), MSc Queries about the abuse potential of medications are among the many types of calls DPIC receives from health professionals. Gabapentin has recently come under suspicion by attentive pharmacists who have received dubious requests for the drug. Although evidence is currently scarce, anecdotal reports indicate that gabapentin Gabapentin (Neurontin) carries a risk for abuse, can get you high if mixed with drugs, causes adverse side effects, and can lead to overdose. Gabapentin is one of the recommended mainstays of evidence-based treatment. 3 Unfortunately, our clinical experience suggests that gabapentin is now prevalent as a drug of abuse. The drug’s effects vary with the user, dosage, past experience, psychiatric history, and expectations. Gabapentin addiction is the one of the new opiate addictions. Learn how you can recognize the signs, symptoms, and consequences of abusing Gabapentin here. Read on to learn more about Gabapentin, common side effects, symptoms of addiction, and how to treat Gabapentin addiction. The most popular way to abuse gabapentin is by mixing it with alcohol, opioids, or benzodiazepines to increase the effects of the other intoxicant. Some people abuse the drug by taking a high dose of it, crushing and snorting it, or injecting it. Neurotin, the trade name of a drug called gabapentin, is addictive. Learn more about gabapentin uses, side effects, and how to spot abuse. Signs of Gabapentin Abuse Gabapentin can result in physical dependence. 11 When prescribed for medical use, healthcare providers will taper dosage to avoid or ease gabapentin withdrawal symptoms associated with abrupt termination. Can Gabapentin Make You High? In our latest question and answer, the pharmacist discusses the growing trend of abuse and misuse of gabapentin as well as what to watch out for. The gabapentinoid drugs, gabapentin and pregabalin, are first-line treatments for neuropathic pain. The epidemics of chronic pain and opioid misuse have given rise to the widespread use of non-opioid drugs such as the gabapentinoids for treatment. Unfortunately, the widespread use of gabapentinoid drugs has resulted in reports of misuse and abuse. Here we summarize the clinical reports of Gabapentin is a medication that prevents seizures and pain, but like any medicine, it can be misused. Learn what can happen if you misuse gabapentin and have a substance use disorder. While the nation is addressing an opioid crisis, other pain-relieving drugs share the potential for abuse as well. Though gabapentin was initially marketed as a medication with low potential for abuse and is commonly thought to be safe and effective, a growing body of evidence highlights the potential risks of overprescribing the medication. Here are several factors to keep in mind when considering gabapentin for your patients or working with patients who have been prescribed gabapentin by another doctor.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |