Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
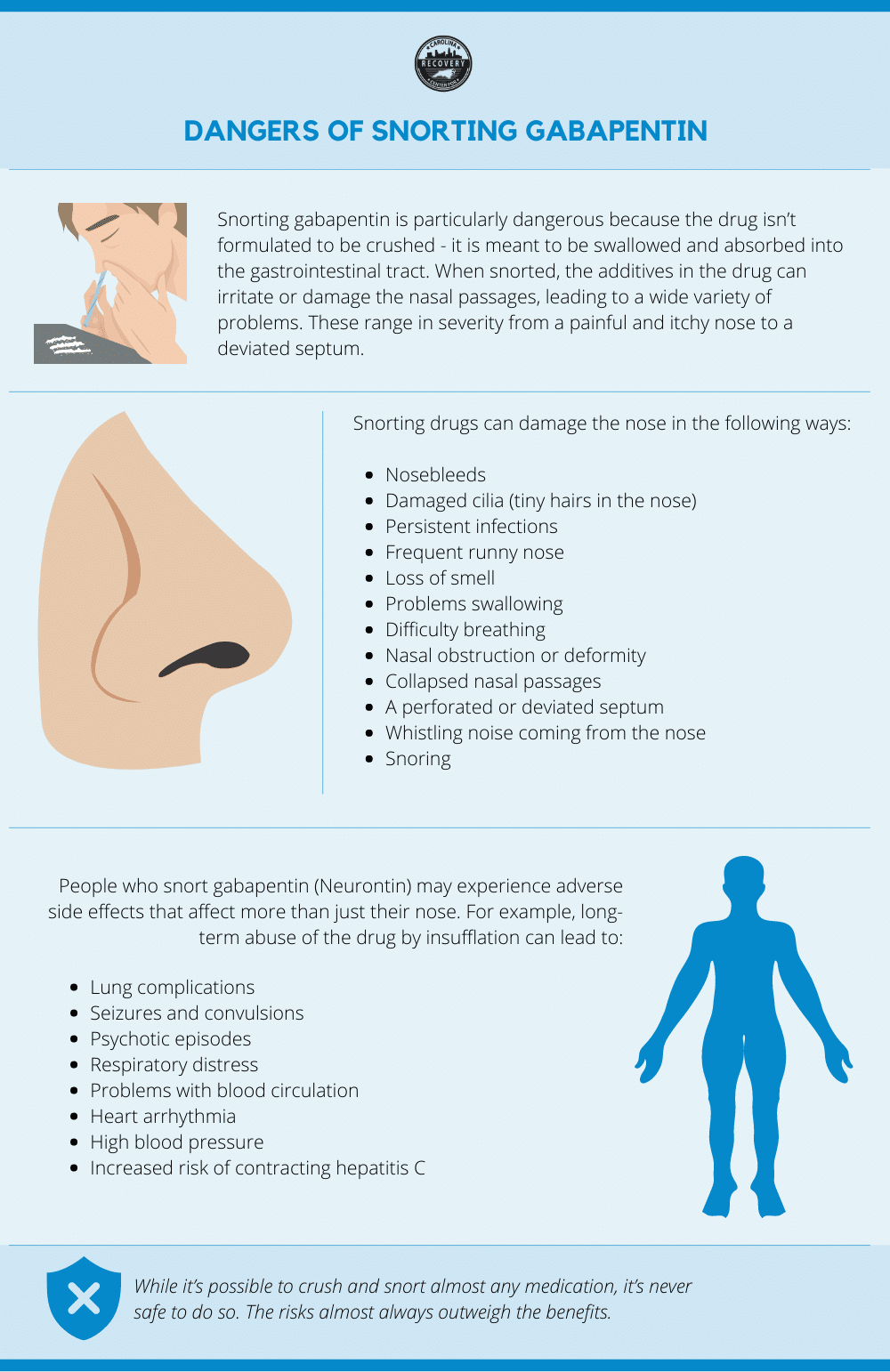 |  |
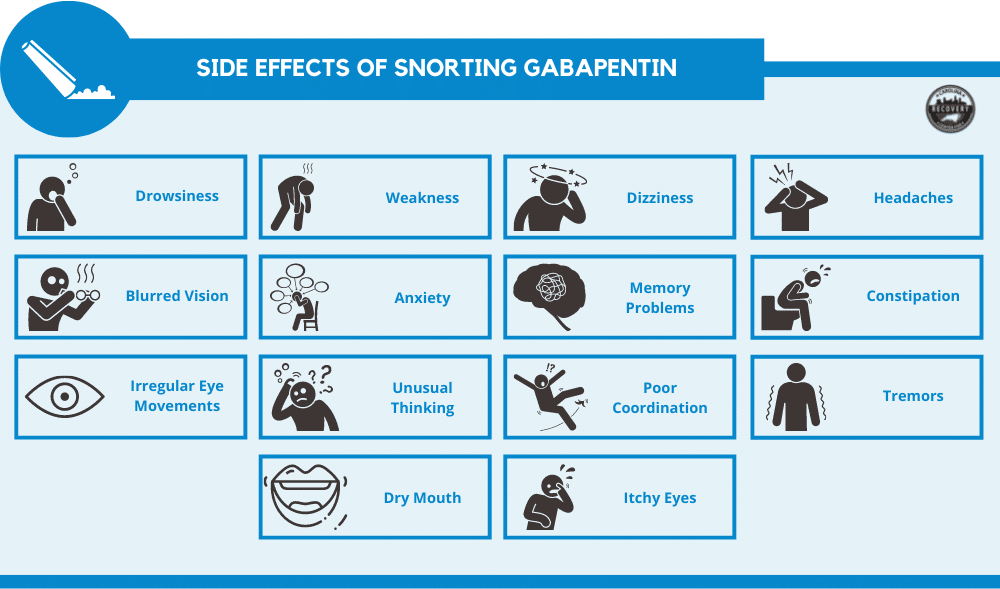
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that’s used to treat certain types of nerve pain and seizures. Gabapentin is generally safe, but it has a potential for misuse or abuse. Withdrawal from gabapentin can have severe symptoms, including rebound seizures. Gabapentin has been shown to lead to dependence, addiction and withdrawal in some people, although when it was first approved in 1993 this risk was thought to be minimal. Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to be an important part of a patient’s medical history when evaluating their risk for addiction and dependence behaviors. When discontinuing gabapentin due to a change in the treatment plan or as a result of gabapentin abuse, gabapentin dose should be tapered slowly rather than stopped abruptly, as significant withdrawal effects may otherwise occur. Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Gabapentin withdrawal treatment typically encompasses a combination of medical interventions, therapeutic approaches, and support systems. Counseling and behavioral therapies can help individuals address the underlying reasons for gabapentin abuse, develop coping strategies, and make positive behavioral changes. Gabapentin Withdrawal Prevalence It is rare to experience withdrawal symptoms from gabapentin, but it does happen. A review of medical journals published between 1993, when gabapentin was approved, and 2015 found 18 case reports of gabapentin addiction, dependence, or withdrawal. Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to be an important part of a patient's medical history when evaluating their risk for addiction and dependence behaviors. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal. Gabapentin is a medication used for seizures and nerve pain. Learn about Gabapentin addiction, including its side effects, signs of abuse, treatment options and more. Gabapentin addiction is the one of the new opiate addictions. Learn how you can recognize the signs, symptoms, and consequences of abusing Gabapentin here. Gabapentin – another drug of misuse? Janet Webb, BSc (Pharm), MSc Queries about the abuse potential of medications are among the many types of calls DPIC receives from health professionals. Gabapentin has recently come under suspicion by attentive pharmacists who have received dubious requests for the drug. Although evidence is currently scarce, anecdotal reports indicate that gabapentin Gabapentin withdrawal can happen in people who suddenly stop taking a high dose of the drug. Tapering off the drug slowly can help avoid withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is a common drug that is FDA-approved to treat seizures and a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug for seizures and nerve pain. Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms and how to safely stop taking the medication. Furthermore, patients with a history of substance abuse are at greater risk during withdrawal, necessitating closer monitoring for potential complications. In summary, professional supervision provides a safeguard against severe withdrawal symptoms and greatly enhances the overall safety and experience of stopping gabapentin. Severe gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can arise when quitting the drug. Learn more about withdrawal from this drug, the signs, and its timeline. People who struggle with alcohol abuse and addiction have frequently been prescribed gabapentin to treat withdrawal symptoms. Learn the facts about abuse. This page will discuss what gabapentin is, side effects of the drug, its misuse liability, symptoms of gabapentin addiction, gabapentin withdrawal, and how a gabapentin rehab program can help with addiction recovery.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |