Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
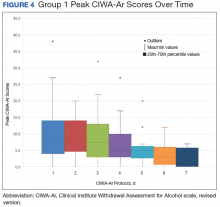
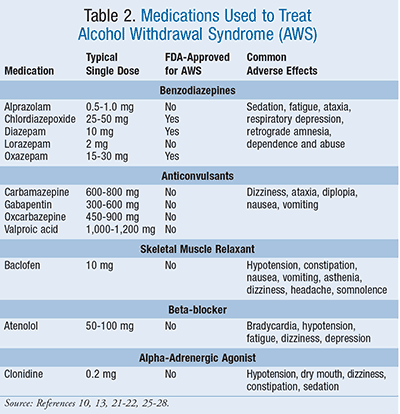
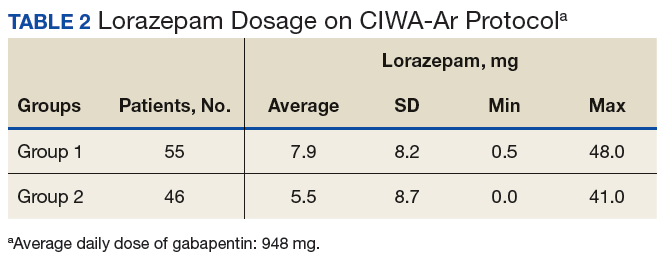
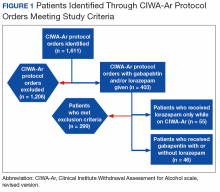
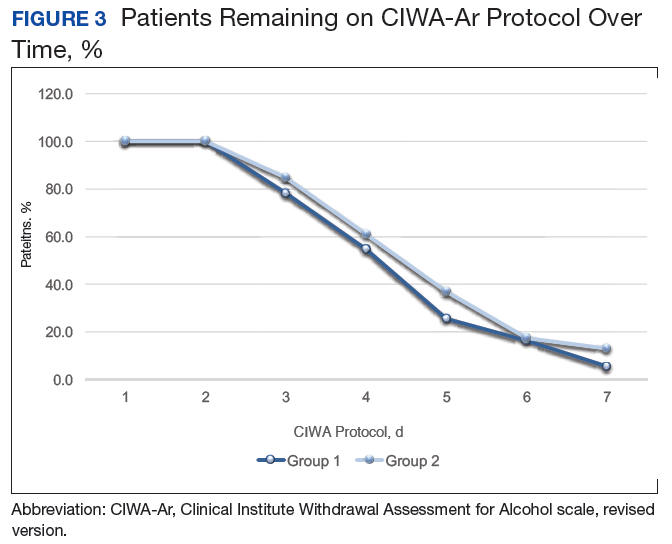
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine if gabapentin can effectively replace/reduce the use of benzodiazepines for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms in hospitalized patients. Time to alcohol withdrawal symptom resolution, amount of benzodiazepines administered, rate of resolution of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, serious withdrawal-related complications Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Gabapentin is typically used for the acute phase of alcohol withdrawal, often lasting from a few days to several weeks. The exact duration depends on the severity of the withdrawal symptoms and the individual’s response to the medication. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: A clinical trial showed that people with Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is an antiepileptic medication with evidence of benefit in alcohol use disorder patients. The mechanism of action of gabapentin may also benefit patients suffering from acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Gabapentin’s anxiolytic and sedative properties along with its overall safety profile suggest that it may be a viable adjuvant to lorazepam in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal. Abstract Study Objective Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Alcohol withdrawal is a set of symptoms that can develop if you stop or significantly reduce alcohol intake after long-term use. It ranges from mild to severe. Gabapentin 1800 mg/day used during first 2 days of hospital admission significantly lowered total dose of benzodiazepines. Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. Gabapentin shows promise in treating mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), either alone or alongside traditional therapies. Studies over the last two decades indicate it effectively reduces withdrawal symptoms and improves patient comfort. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Background Gabapentin is an antiepileptic medication with evidence of benefit in alcohol use disorder patients. The mechanism of action of gabapentin may also benefit patients suffering from acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Introduction Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) is an acute and life-threatening complication of alcohol use disorder (AUD) that is common among emergency department (ED) patients. 1 Nearly one-third of patients presenting primarily for alcohol use disorder will experience moderate to severe withdrawal during the course of their ED stay. 2 Alcohol withdrawal in the ED is associated with Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Conclusion On average, total benzodiazepine requirement was less with concomitant use of gabapentin in acute alcohol withdrawal management. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |