Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
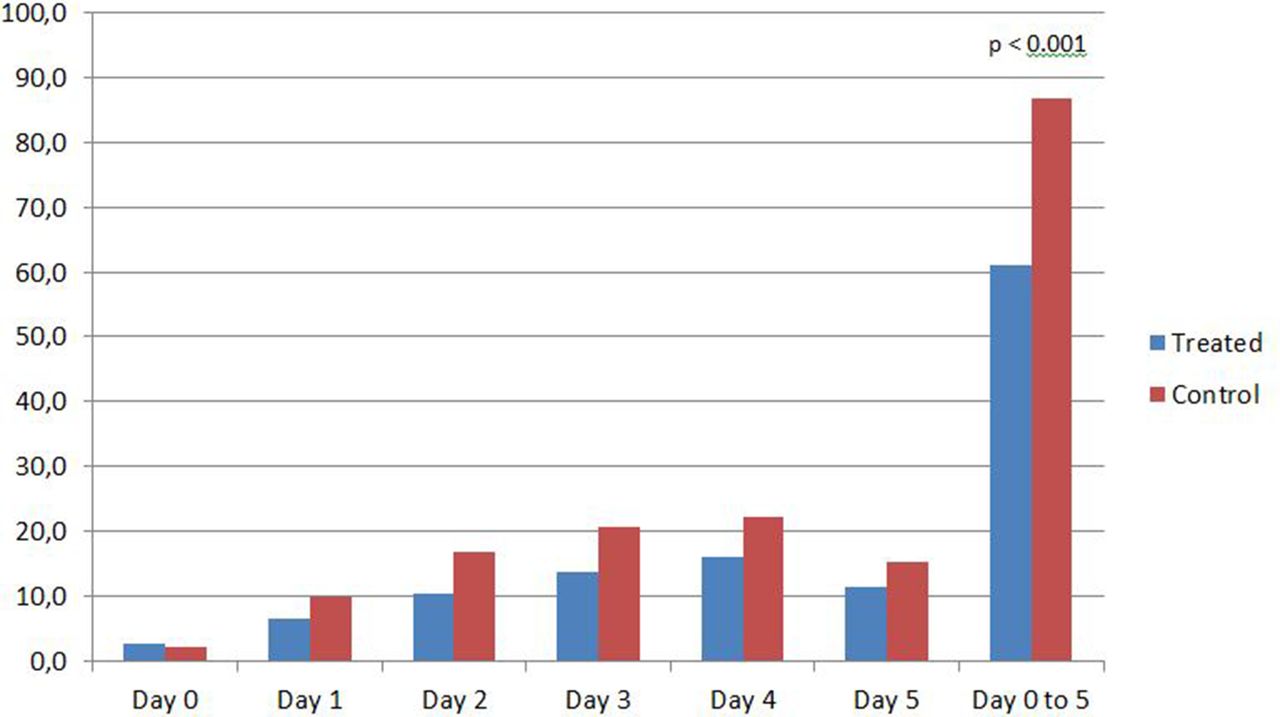
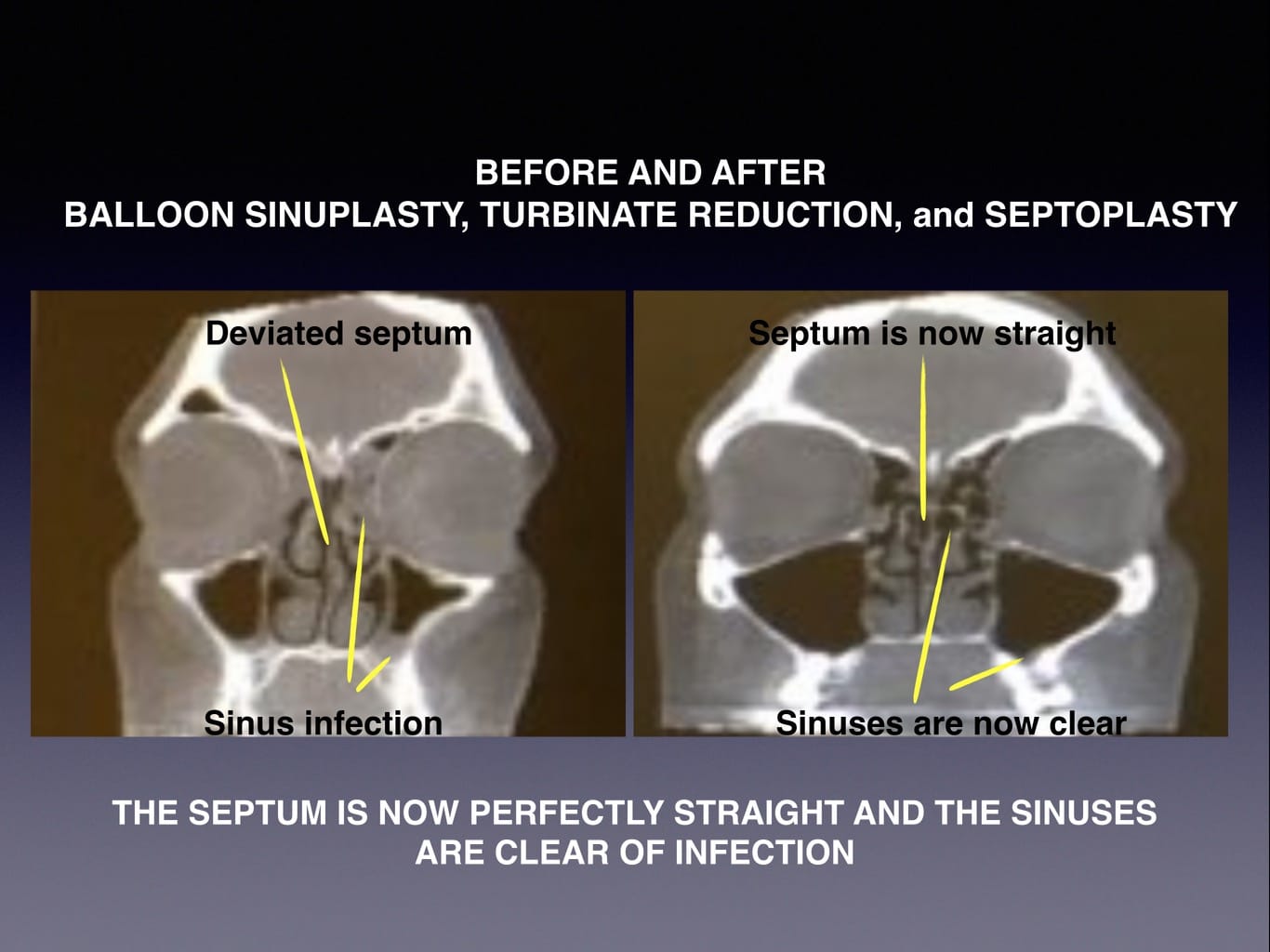
Abstract Purpose of review: Gabapentinoid use has increased substantially in the past several years after initial promising data with regard to acute perioperative pain control. The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication. Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. Objective To determine the efficacy of preoperative gabapentin on patient-reported pain levels and postoperative opioid requirements following sinonasal surgery. Study Design Retrospective review. This randomized clinical trial investigates the effect of perioperative gabapentin treatment vs placebo on postsurgical pain in patients undergoing head and neck mucosal surgery. Abstract Objective: This study investigates the impact of postoperative gabapentin on opioid consumption and pain control following endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) and/or septoplasty. Methods: Patients who underwent ESS and/or septoplasty at a single institution from 2021 to 2022 were enrolled. In this randomized controlled trial, patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery with or without septoplasty at MH-TMC main operating rooms and ambulatory surgery center, were assigned to receiving diclofenac sodium (non-narcotic pain medicine) three times daily as needed, or hydrocodone acetaminophen (narcotic) every 4-6 hours as needed. Within the Otolaryngology literature, administration of a single preoperative gabapentin dose has been associated with decreased post-operative pain or narcotic consumption after tonsillectomy, thyroidectomy, and sinus surgery [12, [18], [19], [20]]. There is evidence supporting the use of NSAIDs and gabapentin for the control of pain after endoscopic sinus surgery. Acetaminophen, α-agonists, and local anesthetics are also viable options for postoperative analgesia. Familiarity with these data is essential to facilitate the use of opioid alterna Objective This study investigates the impact of postoperative gabapentin on opioid consumption and pain control following endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) and/or septoplasty. Methods Patients who und The shift towards multimodal pain regimens, including gabapentin, has taken place without attention to ensuring that they, like opioids, are appropriately discontinued soon after surgery. The prevalence of prolonged use of post-operative gabapentin among older adults is unknown, as are the factors associated with prolonged use. Methods: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with or without septoplasty were randomized to receive a 7-day pre- and post-operative course of placebo or gabapentin, starting at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg three times daily, in a double-blind fashion. This randomized clinical trial investigates the effect of perioperative gabapentin treatment vs placebo on postsurgical pain in patients undergoing head and neck mucosal surgery.Can perioperative pain control be improved with the addition of gabapentin A typical dose range for perioperative gabapentin is 200-300 mg and 25-50 mg for pregabalin. These studies have largely demonstrated that postoperative pain after septorhinoplasty and rhinologic surgery is mild, with pain peaking in the first 1 to 3 days after surgery and steadily declining afterward. Gabapentin may be prescribed either before or after surgery to help with postsurgical pain. However, it should be used with caution due to the high risk of abuse. Methods Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with or without septoplasty were randomized to receive a 7-day pre- and post-operative course of placebo or gabapentin, starting at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg three times daily, in a double-blind fashion. They showed that oral gabapentin was efficacious in the management of postoperative pain at every time point during the first day after surgery and therefore is efficacious in reducing postoperative pain and narcotic requirements after lumbar spinal surgery [49]. Perioperative gabapentin upped the risk of delirium, new antipsychotic use, and pneumonia in older adults after major surgery, a retrospective study showed. Risk of delirium -- the primary outcome I had sinus surgery almost one year ago on my frontal sinuses (above my eyes). The surgery was very successful, in that it has eliminated my chronic sinus infections. I can even breathe better. However, I have had headaches/pain in my forehead off and on since the surgery. At my follow-up appointments, my doctors have said that everything looks great, and the sinuses are clear. Has anyone
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |