Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
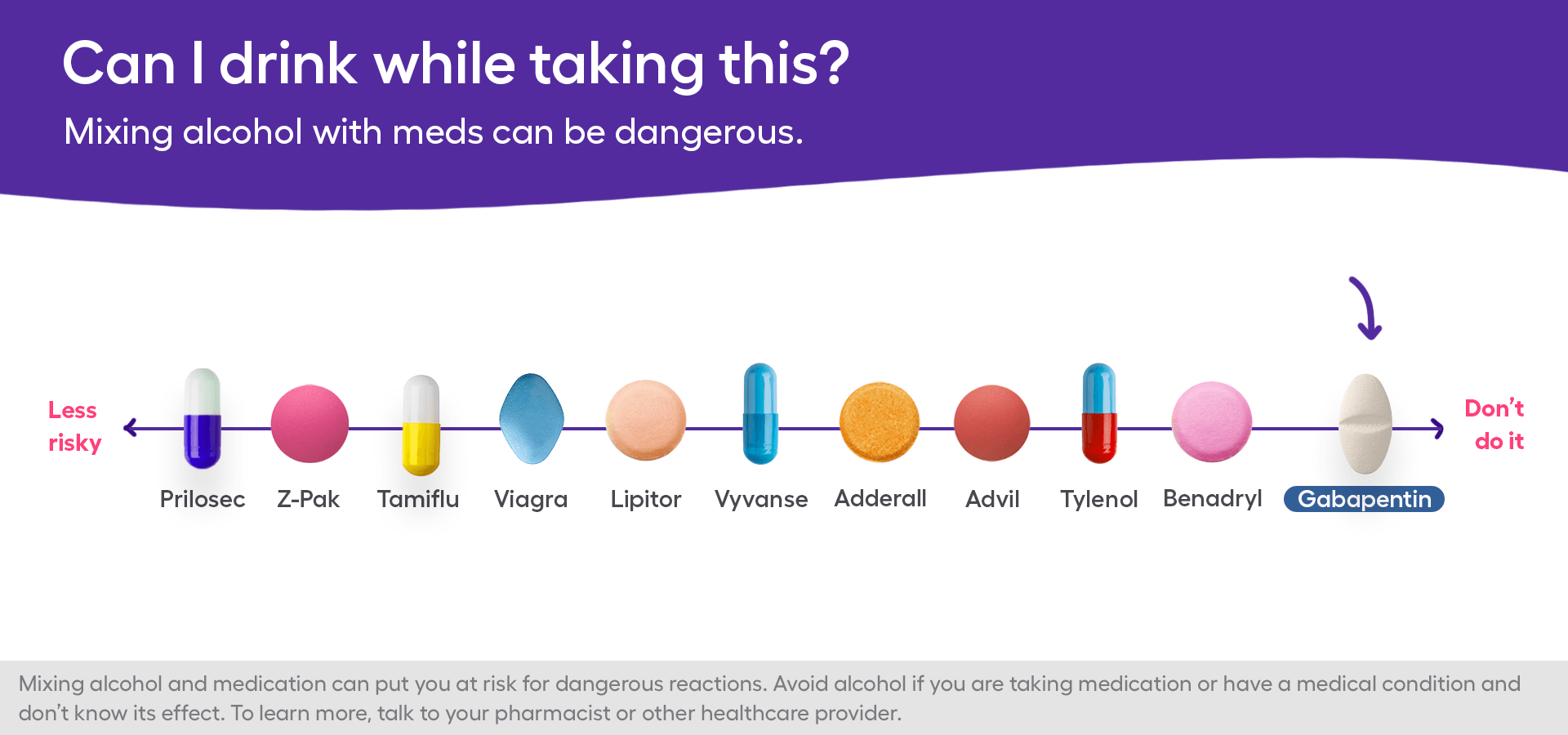
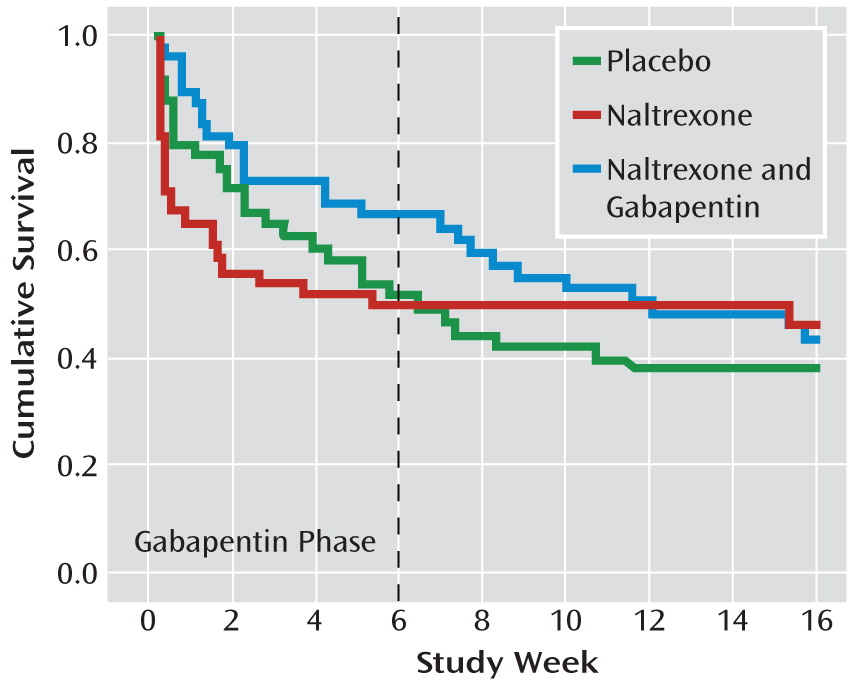
Doctors don’t recommend drinking alcohol while taking gabapentin, especially for those who have just started taking it. However, you may talk to your doctor about drinking in moderation after you’ve reached a stable dose. Mason and coauthors determine if gabapentin increases rates of sustained abstinence and no heavy drinking and decreases alcohol-related insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, in a dose-dependent manner. See the Invited Commentary by Nunes. Clinical studies suggest that gabapentin can reduce symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, including anxiety, insomnia, and tremors. Gabapentin with alcohol dependence treatment can provide a smoother transition during detoxification. The medication may also help reduce alcohol cravings and support abstinence in alcohol dependence. Gabapentin, which is safe for patients who are still drinking, should be prescribed for those with AUD to decrease heavy-drinking days.12,19 Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Results are statistically significant unless indicated. Gabapentin is a common prescription drug used to relieve nerve pain, restless leg syndrome, and other conditions. Consuming alcohol while taking gabapentin can be dangerous. This article will explore the risks of mixing alcohol and gabapentin. You will learn: If you or someone you love struggles with drug or alcohol abuse, you are not alone. Gabapentin isn’t FDA-approved for alcohol treatment, but it has shown promise. Research has found that higher doses (up to 1800mg daily) significantly reduced drinking quantity, cravings, and improved sleep. The prestudy high–alcohol withdrawal group had positive gabapentin effects on no heavy drinking days (P < .02; NNT, 3.1) and total abstinence (P = .003; NNT, 2.7) compared with placebo, while within the low–alcohol withdrawal group, there were no significant differences. In this context, a recent, large RCT found that gabapentin reduced heavy drinking and increased abstinence, and that these findings were apparent only in patients with higher levels of AWS during the 2 weeks before randomization; disconcertingly, gabapentin appeared to worsen drinking outcomes in the patients with low AWS. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol intensifies central nervous system depression, increasing risks of drowsiness, dizziness, and respiratory depression. Consuming alcohol while on gabapentin can lead to severe side effects, including increased risk of seizures, overdose, and death. Gabapentin has shown efficacy in preventing relapse to heavy drinking, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 5.4 for preventing relapse and 7.2 for promoting abstinence in individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD) who have a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Strong evidence shows that naltrexone and gabapentin reduce heavy-drinking days and that acamprosate prevents return-to-use in patients who are currently abstinent; moderate evidence supports the In contrast, the meta-analysis reported here showed an effect of gabapentin only on percent heavy drinking days, though the effect size for that measure exceeded 0.6, a medium effect size, with smaller, non-significant effect on abstinence, relapse to heavy drinking, percent abstinent days, the mean number of drinks/day, and GGT concentration. Patients taking gabapentin had better rates of abstinence and cessation of heavy drinking than those taking placebo. During the 12-week study, the 1,800-mg daily dose showed a substantially higher abstinence rate (17%) than either 900 mg (11%) or placebo (4%). These findings were similar for other drinking variables, where gabapentin was more efficacious than placebo in the high-alcohol withdrawal group only. Gabapentin caused more dizziness, but this did not affect efficacy. OBJECTIVE The main objective was to determine if gabapentin increases rates of sustained abstinence and no heavy drinking and decreases alcohol-related insomnia, dysphoria and craving, in a dose-dependent manner. If you drink while you’re on gabapentin, you may trigger an interaction that amplifies gabapentin’s sedative effects and creates serious health risks. This dangerous combination can lead to respiratory depression and impaired cognitive function. Main Outcomes and MeasuresPercentage of heavy drinking days; secondary efficacy outcomes included drinks per day, drinks per drinking day, and percentage of days abstinent. Registered exploratory analyses tested whether the effects of ibudilast of drinking outcomes were moderated by baseline depressive symptomatology. Gabapentin was associated with significant linear dose-related reductions in drinking quantity and frequency, GGT, alcohol craving, sleep and negative affect, as well as increased rates of abstinence and no heavy drinking over the 12-week study period.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |