Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
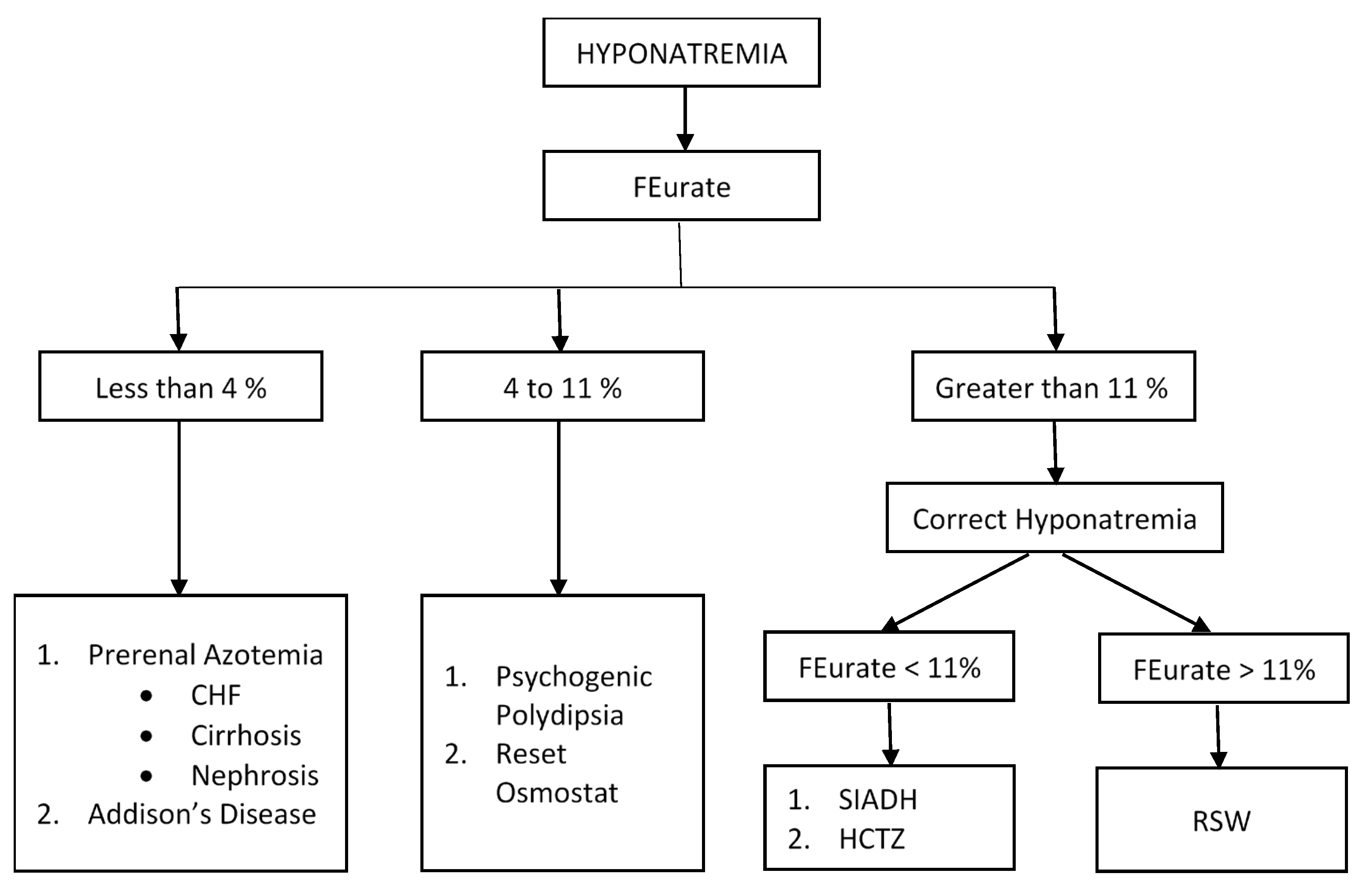 |
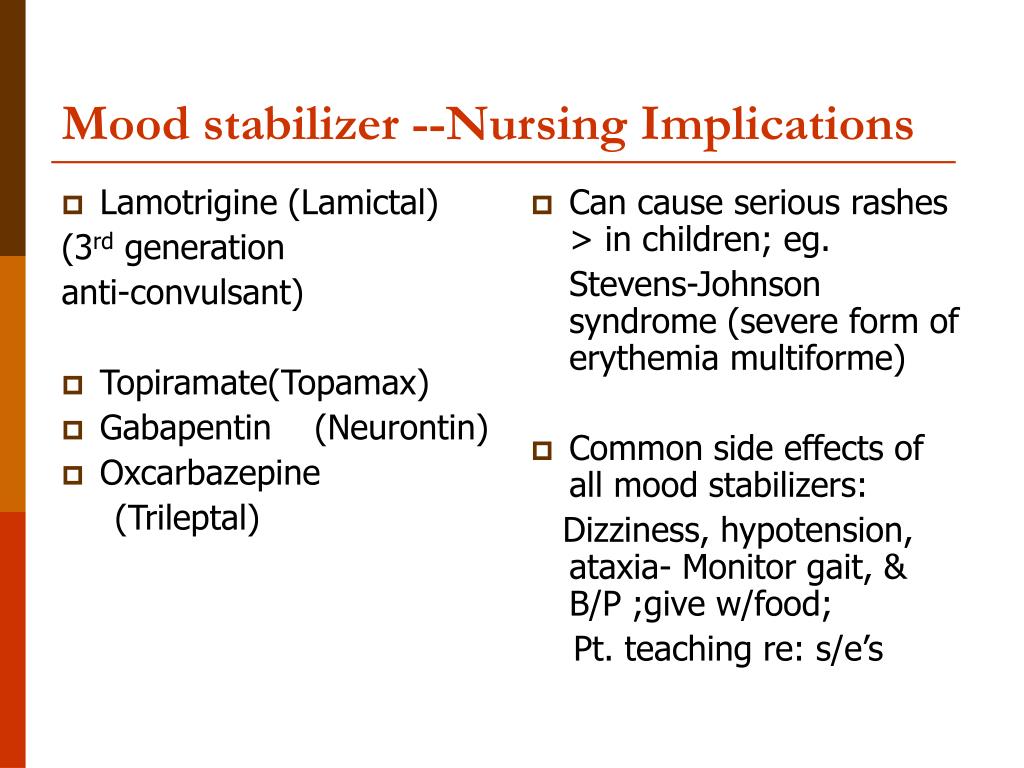
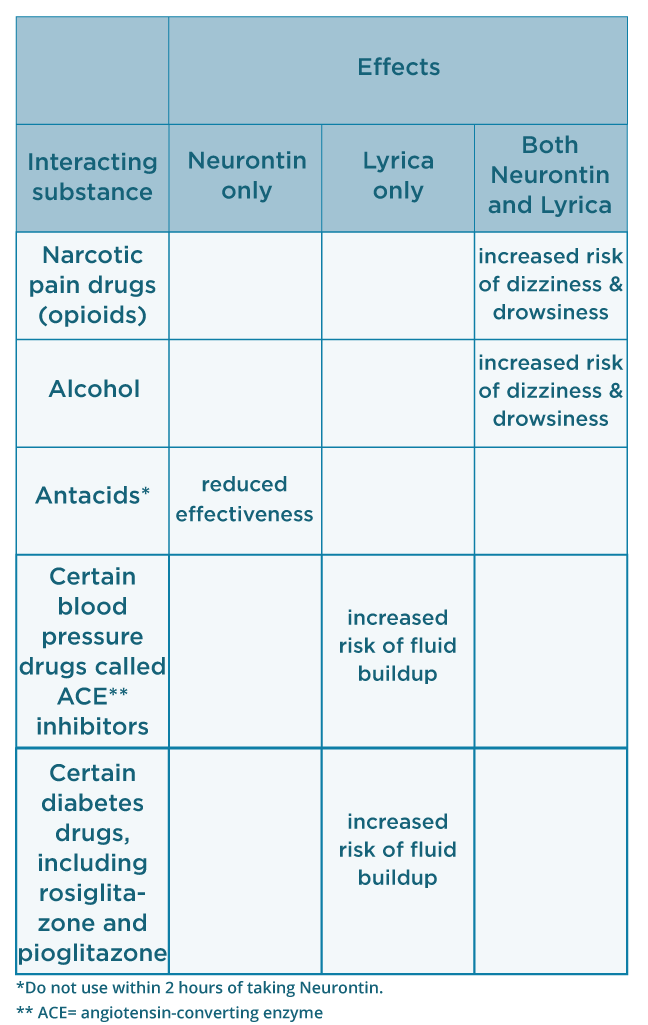
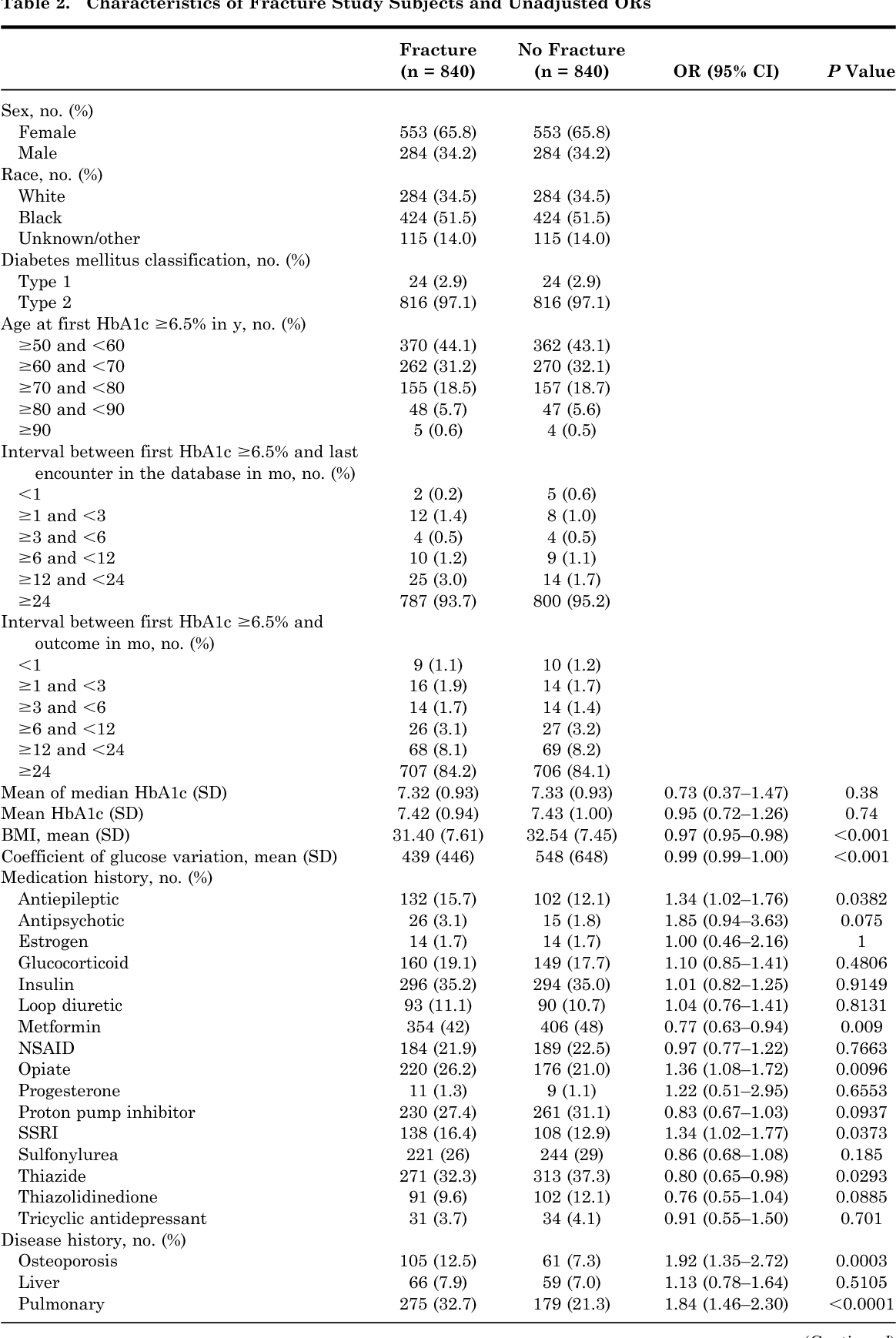
To evaluate the risk factors and prevalence of hyponatremia among epilepsy patients in relation to use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).We retrospectivel Comparisons with earlier studies suggest that although gabapentin-induced hyponatremia is less common than with sodium channel-blocking AEDs, it is still clinically relevant. Conclusion: Gabapentin can cause hyponatremia, especially at higher dosages and in susceptible patients. In the excellent review of drug-induced hyponatremia, Liamis et al1 gave clinical information about the incidence of hyponatremia associated with specific drug treatment and discussed the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. They also presented rare causes of drug-induced hyponatremia derived from occasionally reported cases. However, many drugs were not included in the investigators The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is the most common cause of euvolemic hyponatremia, and many medications have been associated with SIADH. Pregabalin is a drug used for the treatment of neuropathic pain, though Abstract Gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels and is used for a wide variety of on- and off-label indications. Gabapentin is dosed at total daily doses ranging from 300 to 3600 mg/d, which is generally divided into 3 doses. Although gabapentin is generally well tolerated, 1 potential reported adverse effect is peripheral edema. However The corresponding association for phenytoin and valproate was moderate. The risk for hyponatremia was lower during ongoing treatment. Lamotrigine and gabapentin had the lowest risk both during initiation and ongoing treatment and may be advantageous in patients at risk of developing hyponatremia. Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level 134 mmol/L) is the most common electrolyte abnormality in hospitalized patients. Certain drugs (eg, diuretics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics) have been implicated as established causes of either asymptomatic or symptomatic hyponatremia. However, hyponatremia occasionally may develop in the course of treatment with drugs used in everyday Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the anticonvulsants most commonly reported to be associated with hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy, although other anticonvulsants, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and gabapentin, have also been reported to cause hyponatremia [56]. Management of gabapentin-induced hyponatremia typically involves reducing or discontinuing the medication if hyponatremia is confirmed and clinically significant. Fluid restriction may be necessary in symptomatic cases, and severe cases might require hypertonic saline. Gabapentin and Hyponatremia: Risks & Management Understanding Gabapentin and Its Uses Gabapentin and Hyponatremia: Risks & Management Gabapentin is a key medicine used for many health needs. It is best known for helping with anticonvulsant therapy. This means it helps stop seizures in people with epilepsy. It does this by changing how calcium moves in brain cells. Gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels and is used for a wide variety of on- and off-label indications. Gabapentin is dosed at total daily doses ranging from 300 to 3600 mg/d, which is generally Do you take Gabapentin and are concerned about Hyponatremia? eHealthMe's data-driven phase IV clinical trials have been referenced on 800+ peer-reviewed medical publications including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature. Check whether Hyponatremia is associated with a drug or a condition. Hyponatremia induced by antiepileptic drugs is common, but detailed evidence is lacking. This can be problematic for the treating neurologist confronted with a patient with severe hyponatremia in need of an alternative drug. The objective of this study was to examine the association between individual antiepileptic drugs and hospitalization due to hyponatremia. This article explores the relationship between Gabapentin use and the development of hyponatremia, a potentially dangerous condition characterized by low levels of sodium in the blood. Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level < 134 mmol/L) is the most common electrolyte abnormality in hospitalized patients. Certain drugs (eg, diuretics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics) have been implicated as established causes of either asymptomatic or symptomatic hyponatremia. However, hyponatremia occasionally may develop in the course of treatment with drugs used in everyday Drug-induced hyponatremia caused by renal water retention is mainly due to syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD). SIAD can be grouped into syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) and nephrogenic syndrome of In acute symptomatic hyponatremia, hypertonic saline solution (3%) is commonly used to acutely increase serum sodium levels and prevent severe neurologic symptoms (eg, seizures). Hypovolemic hyponatremia is treated with adequate fluid resuscitation to decrease the stimulus for ADH secretion. Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. Understanding the risk associated with AED-induced hyponatremia and taking effective measures to combat serum sodium imbalance induced by AED therapy are necessary. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Hyponatremia is an adverse effect of many antiseizure medications (ASMs). It occurs with interference with the normal balance of electrolytes within the body. Various risk factors associated with the development of hyponatremia in patients taking
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |