Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
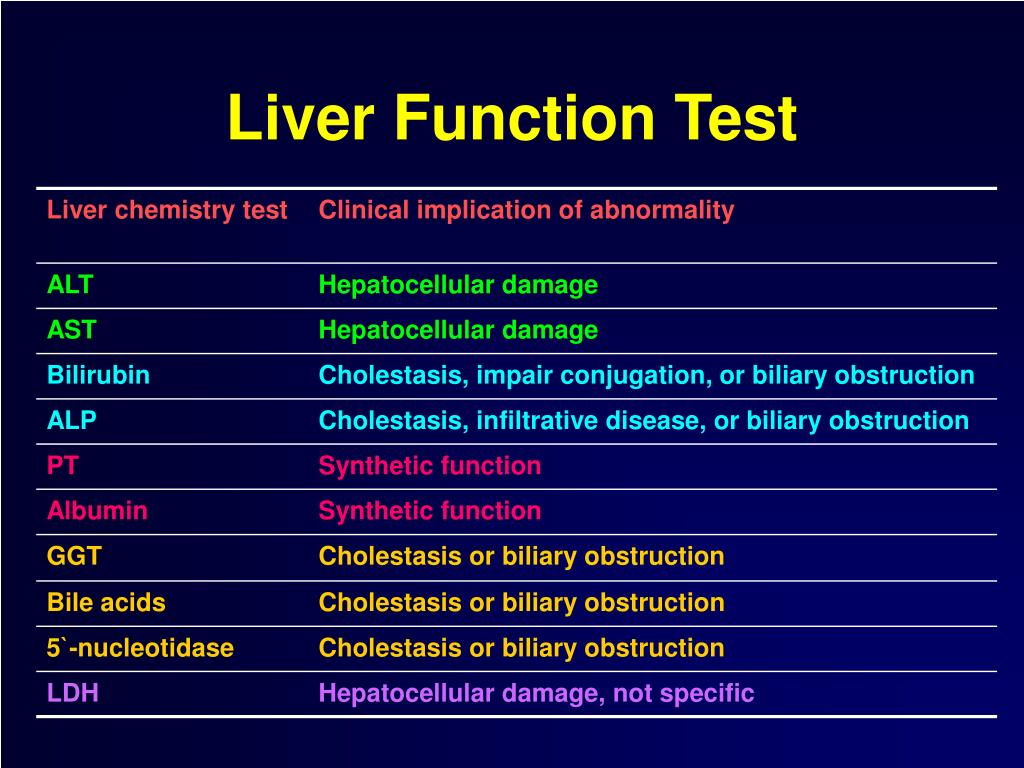
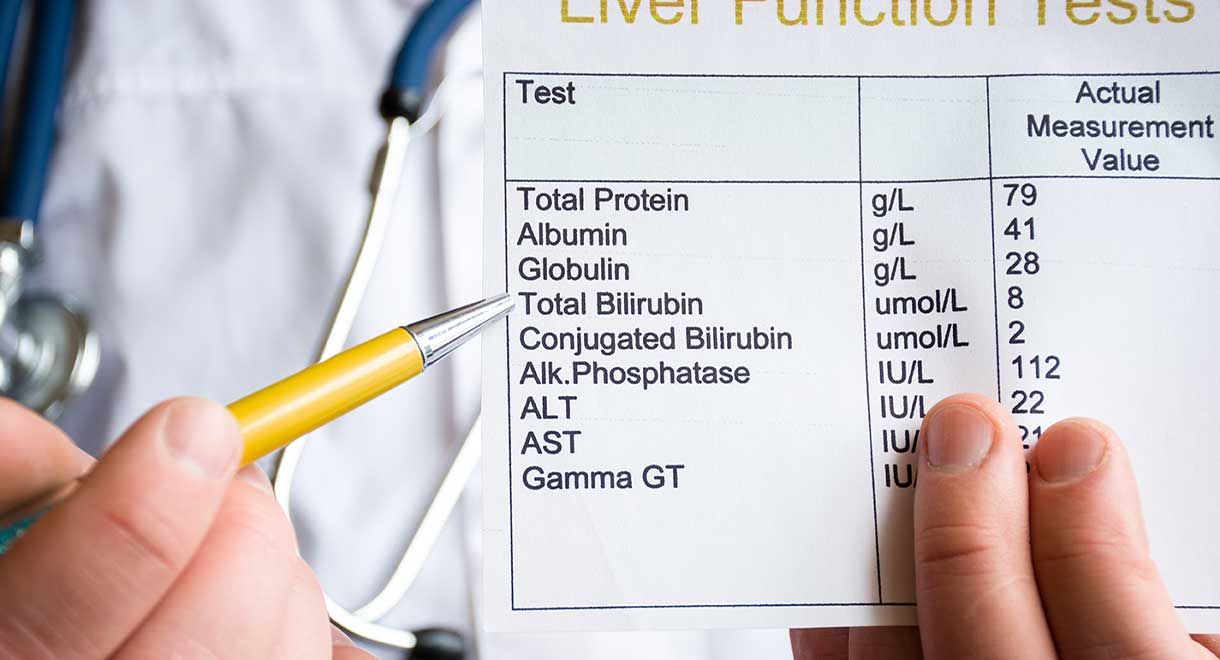
Gabapentin was held. Thereafter, the man's liver function tests improved and remained stable. He discontinued gabapentin. He was advised to follow up outpatient. However, he was lost to follow-up. Based on clinical presentation and investigational findings, he was diagnosed with drug-induced liver injury attributed to gabapentin. Pfizer, the manufacturer of gabapentin, reports abnormal liver function in clinical trials of patients with gabapentin. While there have been some individual reports of liver damage from gabapentin, it is considered extremely rare. Vitamin E protects against gabapentin-induced chronic hepatic and renal damage associated with the inhibition of apoptosis and tissue injury in rats. Liver function test abnormal in Gabapentin - how severe and when it was recovered? (a real world drug study) Summary: We study how severe was Liver function test abnormal, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin). Choosing the most appropriate antiepileptic drug in this setting represents a difficult challenge, as most medications are metabolized by the liver. This article focuses on the acute and chronic treatment of seizures in patients with advanced liver disease and reviews the hepatotoxic potential of specific antiepileptic drugs. Can gabapentin cause liver enzymes to be elevated? Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive therapy in managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain syndromes. It is a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and has been approved for use in the United States in 1993. It is used as an anticonvulsant and neuropathy agent, with over 18 million prescriptions filled Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant drug that’s FDA-approved to treat partial seizures, restless leg syndrome, and nerve pain from shingles, spinal injuries, diabetes, or other conditions. Since the body eliminates gabapentin completely through the kidneys, it’s typically considered safe in patients with pre-existing liver disease. Introduction: Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant that is also used off-label to treat neuropathic pain. It is not metabolized by the liver, and there have been few reports of hepatotoxity associated with it. We present a rare case of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurring in a young male. Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with an extensive past medical history including type 1 Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer. In our review, we analyse the evidence for DILI, severe liver injury leading to death or liver transplantation, abnormalities of liver function tests in clinical trials and hepatotoxicity. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Question I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. Therefore this study was undertaken to find out the possibility of li Valproate massive toxic effects were on the liver as marked by elevated liver function tests and plasma ammonia as well as a deranged redox status. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Therefore, an understanding of liver enzyme levels, often measured via tools such as liver function tests (LFTs), is crucial for patients on gabapentin. The question of whether is gabapentin bad for your liver requires careful evaluation, particularly for individuals with pre-existing hepatic conditions. A full blood count, renal profile, and liver ultrasound scan were also normal. Gabapentin induced cholestasis was thought likely and the drug was stopped. After this, clinical symptoms and liver function tests improved gradually (figure). There are various reports that the elevation of liver enzymes after chronic antiepileptic medication would reflect hepatocellular damage. Our previous and several other studies shows that long term treatment with old or new anti epileptic drugs affect liver function from transient state to a fatal liver damage (1,8-10). As in other cases of DILI, gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurs within the first seven days post exposure to the drug. The discontinuation of gabapentin leads to an improvement in liver test abnormalities. The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Pregabalin is an inhibitor of neuronal activity used for therapy of painful neuropathy and as an anticonvulsant. Therapy with pregabalin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, and clinically apparent liver injury from pregabalin has been reported but appears to be quite rare. The liver plays a vital role in metabolizing medications, including gabapentin. While most individuals tolerate gabapentin without significant issues, there are rare instances where liver function may be compromised. This article delves deep into the relationship between gabapentin and liver health, exploring mechanisms of action, potential side effects, case studies, and recommendations for
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |