Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
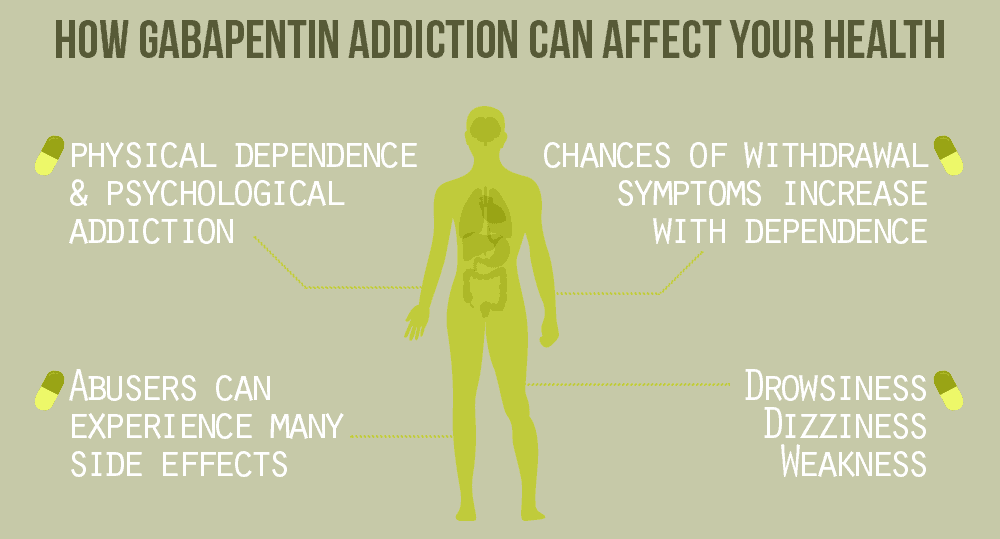 |  |
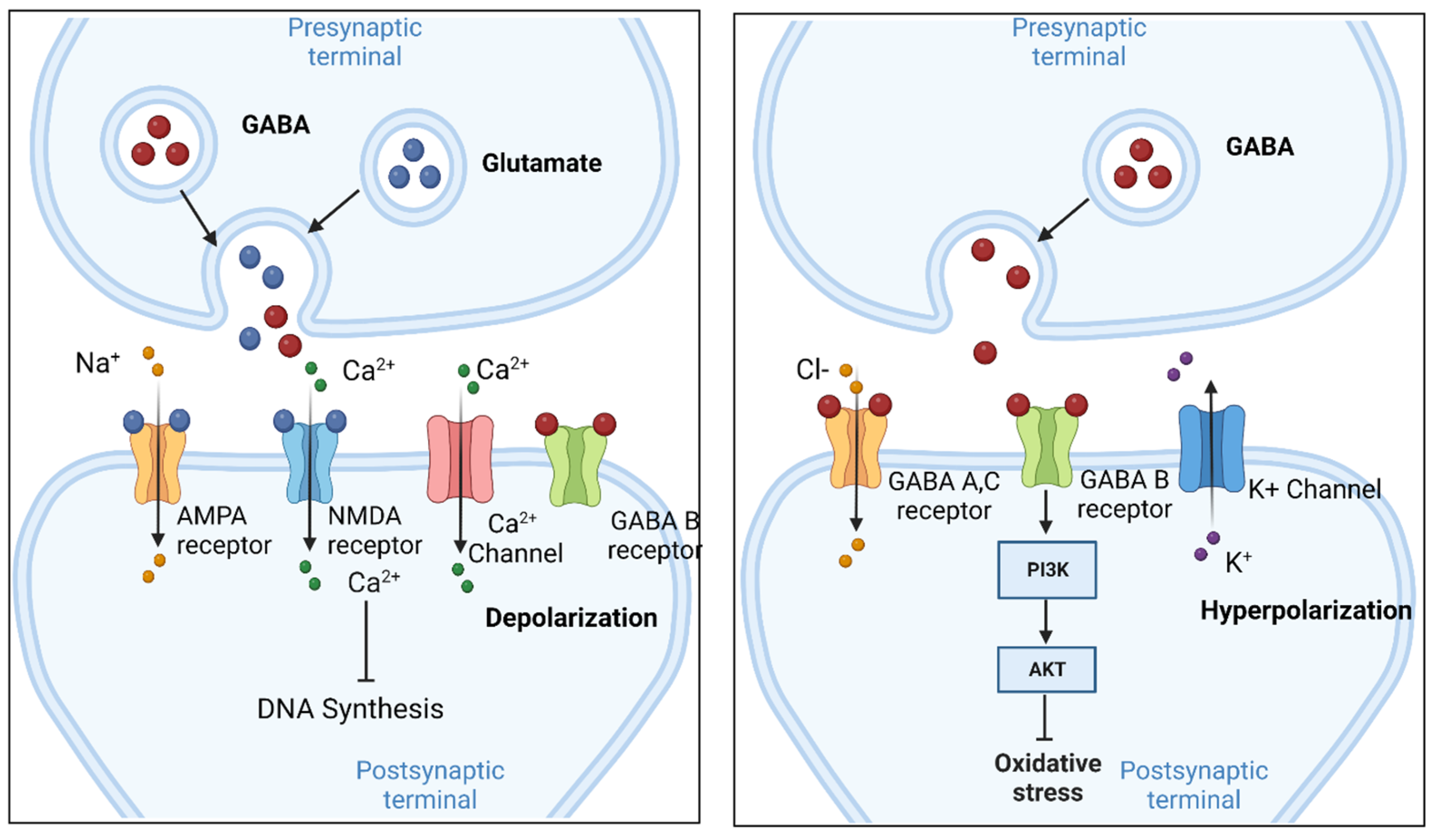
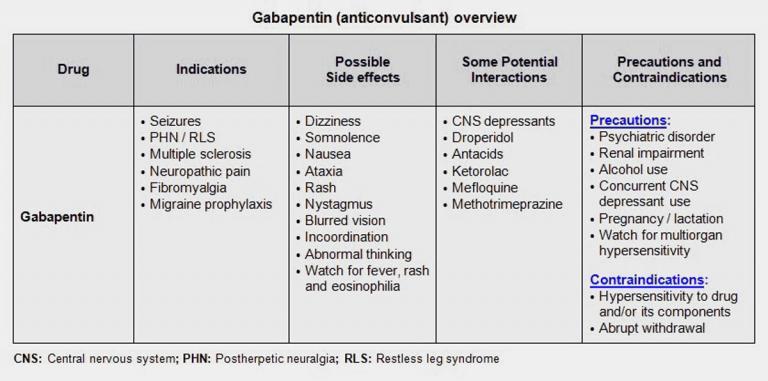
Gabapentin works by altering electrical activity in the brain, calming overactive nerve signals. It’s primarily prescribed for seizures and nerve-related pain, but doctors often recommend it for off-label uses such as anxiety and insomnia. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Thanks to its low addictive potential, gabapentin is usually seen as a safer option to opioids, however, the new findings raise concerns on its potential side effects on brain health. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. Gabapentin is often prescribed for nerve pain and seizures, but some users report memory loss as a side effect. This post explores the connection between gabapentin and memory issues, possible risks, and how to manage them. Learn what to watch for and when to consult your doctor for advice. Does your mind get a bit cloudy when you take gabapentin? It could be gabapentin brain fog. Discover its causes, side effects, and prevention here! Gabapentin is a medication that works on the brain’s neurotransmitters to help control certain conditions. It’s often known by brand names like Neurontin and Horizant in the pharmacy world. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. What’s more, the risk was more than doubled in people normally considered too young to suffer from brain aging, those 18 to 64, results show. Explore the link between gabapentin and memory loss. Learn what research and patients reveal about cognitive side effects and how to manage them safely. Investigation of acute and chronic effects of gabapentin on both GABA and glutamate, particularly in brain regions typically implicated in seizure disorders, would be required to further examine gabapentin's anti-seizure effects in human subjects. Gabapentin works its magic by calming overactive nerves in the brain. It’s like a gentle hand soothing a frazzled mind, bringing relief to those who’ve long suffered. But here’s the rub: our brains are intricate machines, and tinkering with one part can have unexpected effects on others. Gabapentin works by altering the way nerve impulses work in your brain to help treat different conditions. Such as seizures, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, depression, neuropathic pain associated with other health conditions such as diabetic neuropathy. It’s essential to continue following the prescribed dosage and administration schedule. Gabapentin works by changing brain electrical activity and the functioning of neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. The medication is available in pill, tablet, and liquid form. Brand names for gabapentin include Horizant, Gralise, and Neurontin. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |