Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 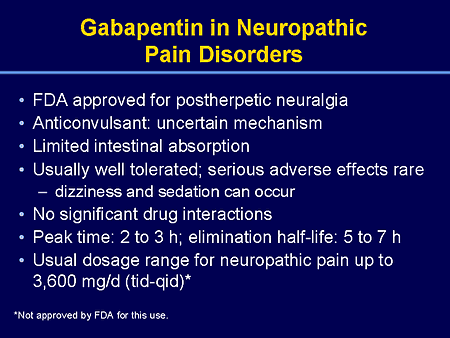 |
Uses Warnings Before taking Dosage Side effects Interactions FAQ What is gabapentin? Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. There are rare postmarketing reports of individuals experiencing withdrawal symptoms shortly after discontinuing higher than recommended doses of gabapentin used to treat illnesses for which the drug is not approved. NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. Gabapentin is approved for the former indication in the US. [7] In addition to these two neuropathies, European Federation of Neurological Societies guideline notes gabapentin effectiveness for central pain. [11] A combination of gabapentin with an opioid or nortriptyline may work better than either drug alone. [11][32] Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Introduction: Gabapentin is a prescription medication approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuropathic pain and epileptic disorders. This drug is currently marketed in capsule, tablet, and oral solution formulations. In recent years, however, gabapentin has been increasingly encountered by law enforcement, documented in national crime lab NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 5.1 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including gabapentin, the active ingredient in GRALISE, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more What are the approved indications for gabapentin and pregabalin? What is the evidence for and against their use in various off-label indications, and how can doctors help limit gabapentinoid-related harms? Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. What Are the Uses of Gabapentin? The uses of Gabapentin are primarily for treating seizures and nerve pain, with additional off-label applications for anxiety, insomnia, and withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is an FDA-approved drug for epilepsy and postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated Medical Indications In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal Overview of FDA-approved uses for pregabalin and gabapentin, highlighting their indications and clinical applications in medical practice.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |