Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
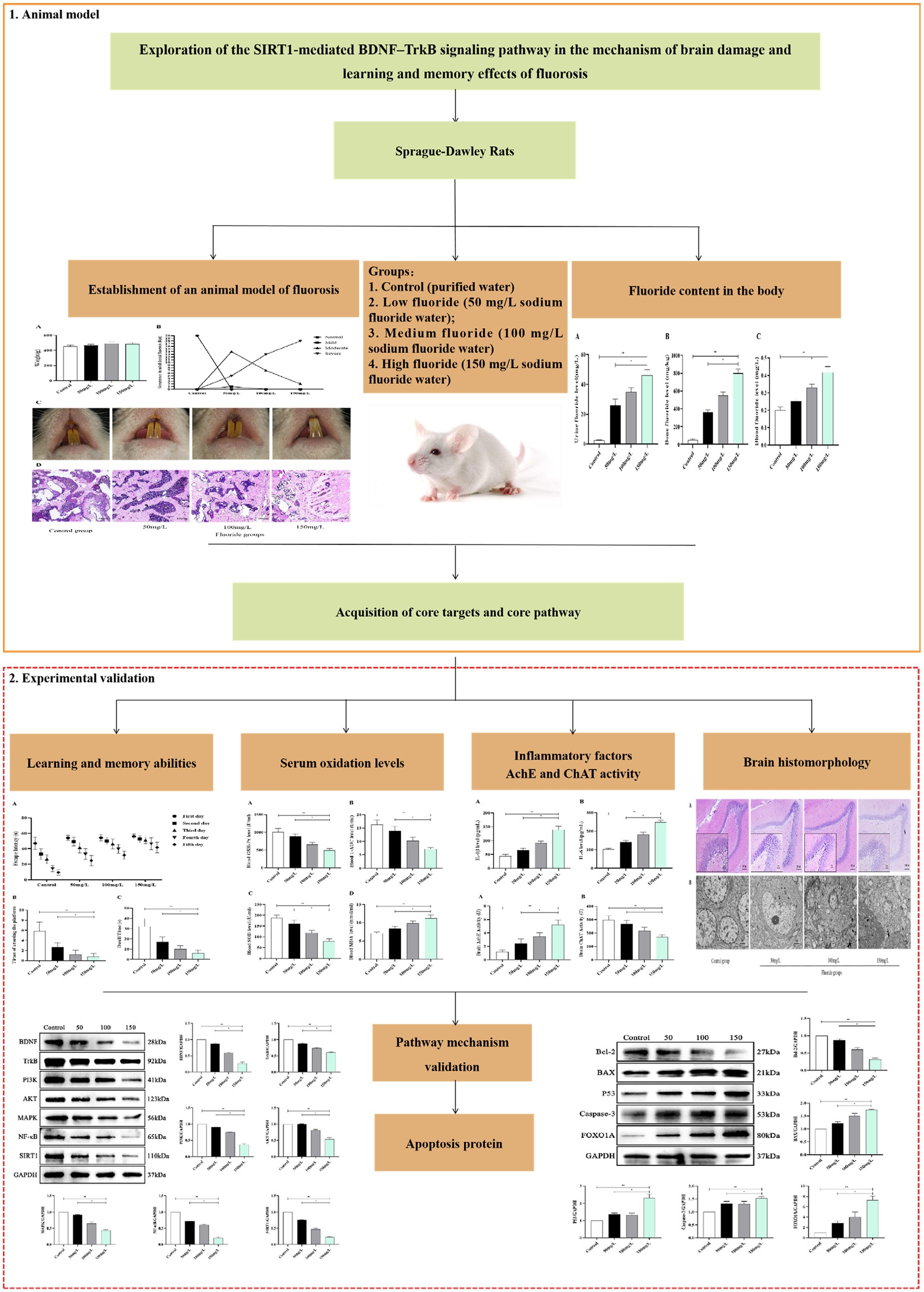
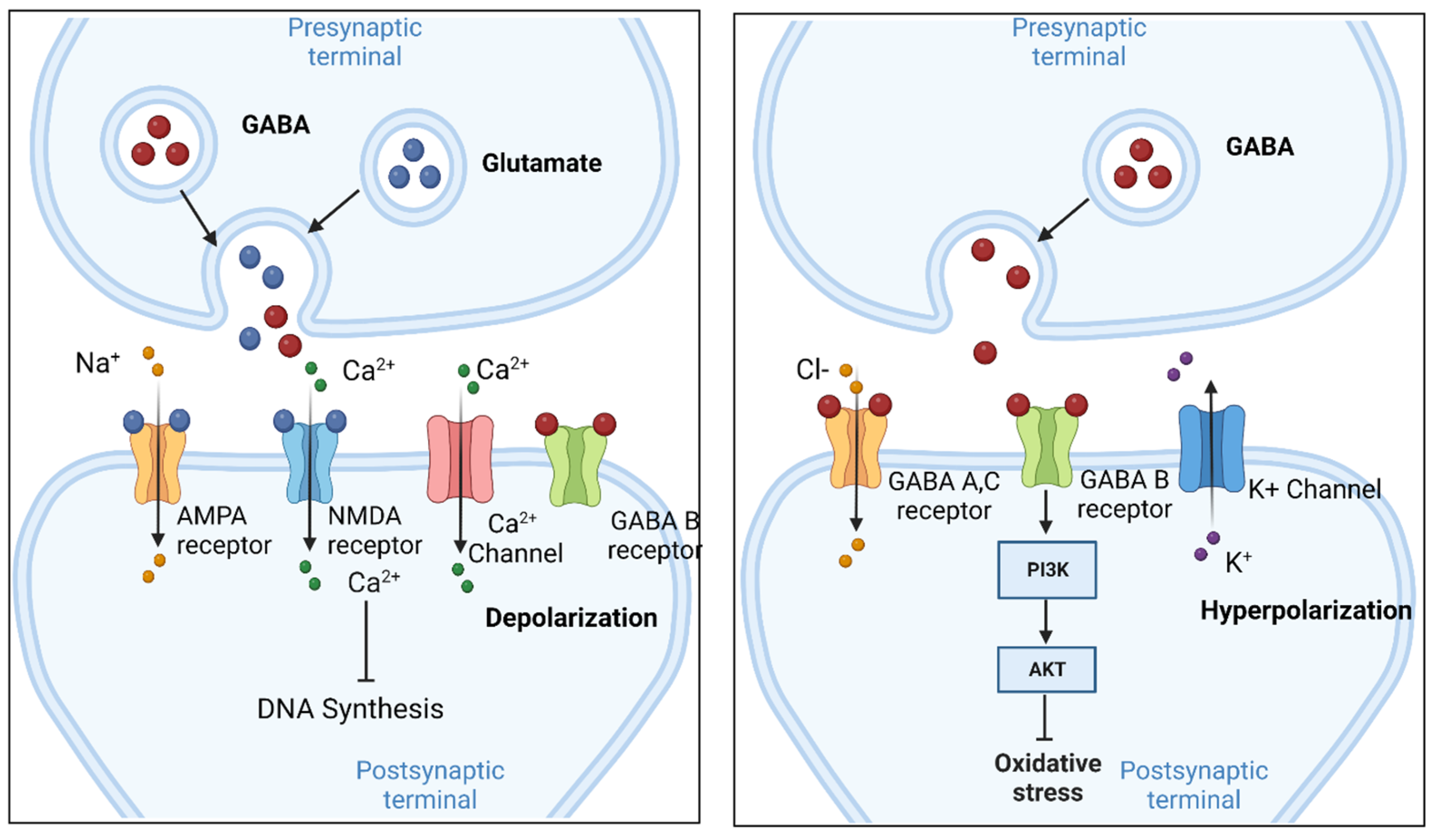
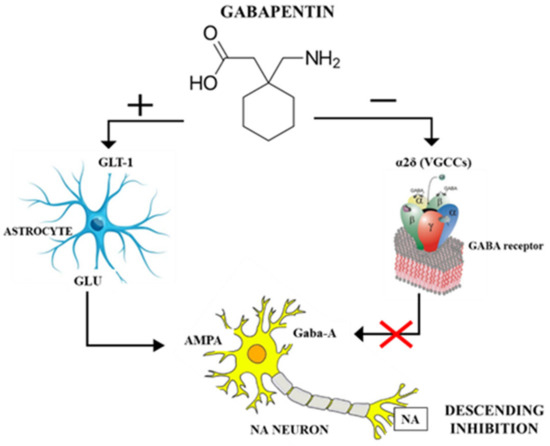
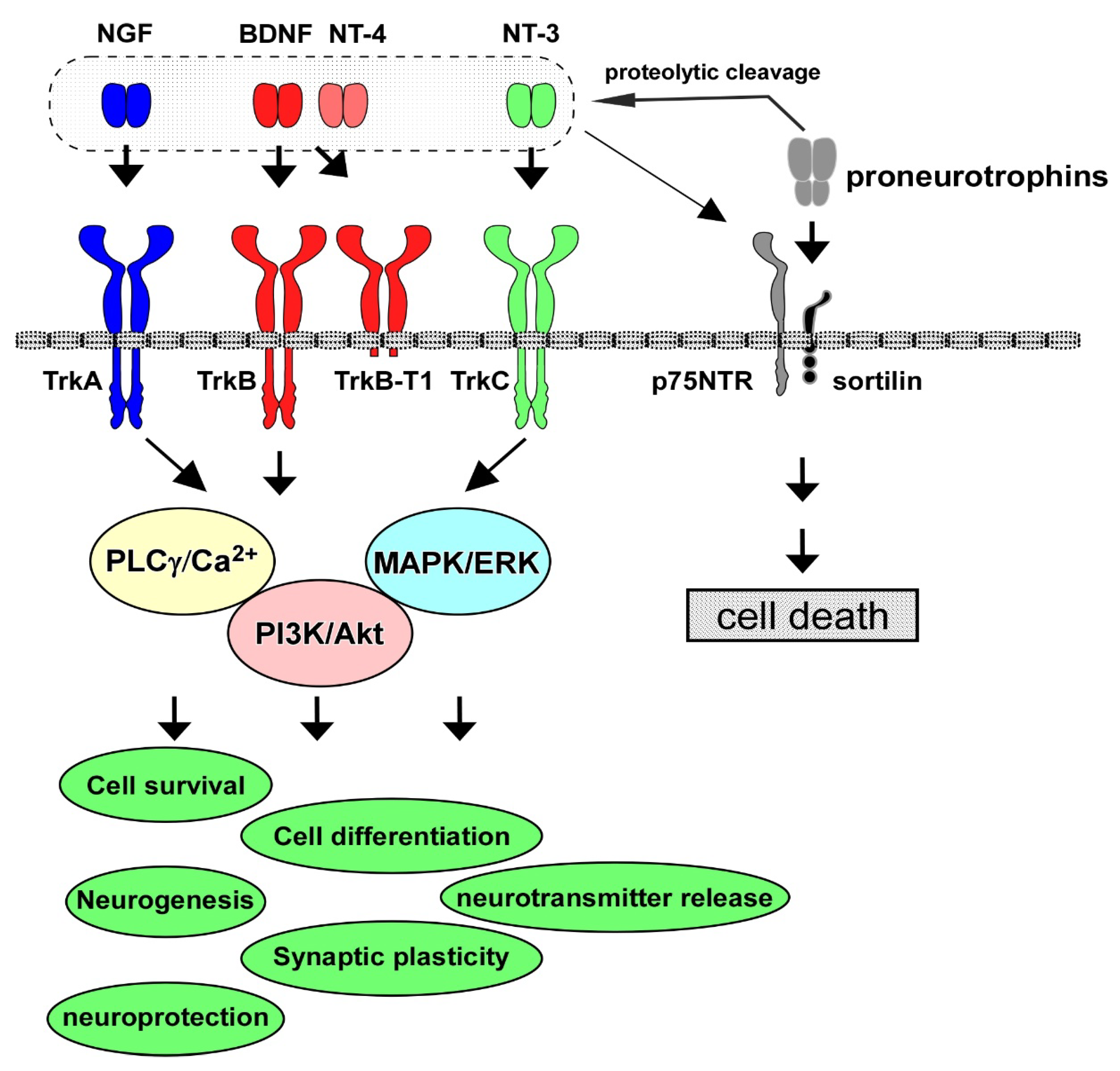
Background In animal models of neuropathic pain (NP), promising results have been reported with the administration of minocycline, possibly through inhibition of spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. No data are available on the effect of amitriptyline and gabapentin on spinal BDNF expression. If the mechanism of action of the latter drugs does not involve brain-derived Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is vital for synaptic plasticity, cell persistence, and neuronal development in peripheral and central nervous systems (CNS). Numerous intracellular signalling pathways involving BDNF are well recognized to affect neurogenesis, synaptic function, cell viability, and cognitive function, which in turn affects pathological and physiological aspects of These results illustrated an increased expression of BDNF and enhanced glutamatergic transmission in rats with oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain, which was markedly attenuated by gabapentin. Accumulated studies have focused on some key molecules that may be involved in these pathological processes, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF is an important member of the neurotrophic factor family. Results: Gabapentin treatment at the therapeutic level interfered with the neurogenesis and morphogenesis of vmDA neurons in the fetal brain by causing changes in morphology and alterations in the expression of key developmental genes, such as Nurr1, Chl1, En1, Bdnf, Drd2, and Pitx3. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin can relieve chronic pain and depression-like behavior in rats with chronic pain and depression, and promote neurogenesis of hippocampal dentate gyrus neurons. Results: Gabapentin treatment at the therapeutic level interfered with the neurogenesis and morphogenesis of vmDA neurons in the fetal brain by causing changes in morphology and alterations in the expression of key developmental genes, such as Nurr1, Chl1, En1, Bdnf, Drd2, and Pitx3. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings These results illustrated an increased expression of BDNF and enhanced glutamatergic transmission in rats with oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain, which was markedly attenuated by gabapentin. Abstract Background: In animal models of neuropathic pain (NP), promising results have been reported with the administration of minocycline, possibly through inhibition of spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. No data are available on the effect of amitriptyline and gabapentin on spinal BDNF expression. If the mechanism of action of the latter drugs does not involve brain 加巴喷丁对慢性疼痛和抑郁共病成年大鼠海马齿状回神经发生的影响 Effect of gabapentin on neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus of adult rats with co-disease of chronic pain and depression Researchers have identified a mechanism by which brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) can suppress GABAergic transmission in hippocampus. In this article, Dr. Rajamani Selvam explains how he and his team achieved these results, and their potential impact on the treatment of neurological disease. Abstract Spinally released brain-derived nerve growth factor (BDNF) after nerve injury is essential to anatomic and functional changes in spinal noradrenergic and cholinergic systems, which are engaged or targeted by commonly used treatments for neuropathic pain. Since BDNF signals via tropomyosine receptor kinases (trks), we tested whether trk blockade by repeated spinal injection of the trk Reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmission co-occur in brain conditions (depression, schizophrenia and age-related disorders) and are High-grade gliomas functionally remodel neural circuits in the human brain, promoting tumour progression and impairing cognition. We investigated the modulation of BDNF by GABA A agonist i.e., gabapentin, indomethacin (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory) and their low-dose combination on adjuvant-induced inflammatory arthritis. In this study we used Gabapentin and indomethacin and their low combination for chronic pain management therapy by targeting brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) associated chronic pain pathway. These include antidepressants (amitriptyline, doxepin, or duloxetine), antiseizure medications (gabapentin, pregabalin, carbamazepine, and valproate), antiinflammatory, opioids and capsaicin. However, tight control of blood sugar (glucose) is important to prevent symptoms and problems from getting worse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |