Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Prophylactic+treatment+(to+prevent+new+attacks):+It+is+indicated+if+the+patient+have+3+or+more+attacks+per+months+or+if+there+is+C.I+to+acute+phase+therapy..jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
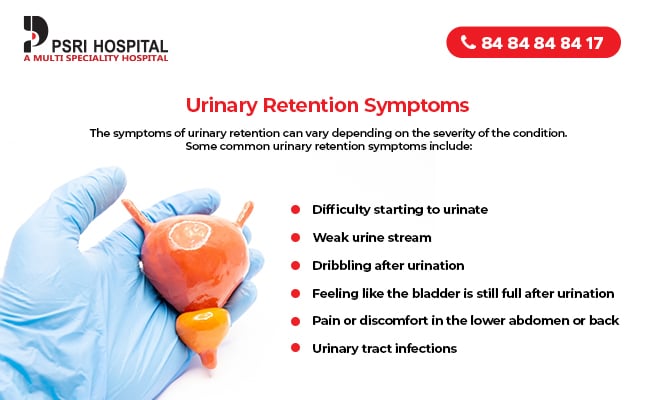
The literature includes a few cases suggesting an association between gabapentin use and urinary incontinence. This case focuses on a previously unrecorded association between gabapentin and increased urinary frequency, which was dose dependent. Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Gabapentin and Urinary retention - a phase IV clinical study of FDA data Summary: Urinary retention is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have Multiple sclerosis. Urinary retention is a condition in which impaired emptying of the bladder results in postvoidal residual urine. It is generally classified into 'acute' or 'chronic' urinary retention. Because of the complex mechanism of micturition, many drugs can interact with the micturition pathway, all via diff Abstract Gabapentin (GBP) is a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that is commonly used in palliative care for symptom management indications including neuropathic pain syndromes, hiccups, cough, and anxiety. An uncommon adverse effect of GBP is urinary incontinence (UI). We report the case of a 61-year-old male with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer who developed probable Gabapentin can cause urinary problems as a side effect. Learn about the connection between gabapentin and urination issues, including symptoms and management strategies. Explore the potential link between gabapentin usage and urinary incontinence risk. Learn about side effects and considerations for Singapore residents. Learn how gabapentin is used to treat urinary retention, a condition where youre unable to fully empty your bladder, and its potential benefits and risks. Gabapentin, is now being prescribed for over active bladder, I sends messages from the brain to the bladder to slow down the muscles, so yes it can reduce how often you go to the toilet, cause fluid retention, and make it difficult to start a flow. Due to fluid retention it can also cause bladder infections. Gabapentin can affect the nerves that signal the bladder to contract, leading to difficulties in urination. Additionally, it may cause relaxation of the bladder muscles or alter the perception of bladder fullness, which can contribute to retention issues. Gabapentin urinary retention occurs when the medication gabapentin, used to treat pain and epilepsy, impairs bladder function. This can lead to difficulty urinating or an inability to empty the bladder completely. Medical conditions like prostate enlargement and neurological disorders can contribute to urinary retention, which causes symptoms such as frequent urination and pain. Diagnosis Only a few cases with GBP-associated urinary incontinence have been reported in the literature. To the authors' knowledge, these cases described individuals with only 1 attempt of the use of GBP. In this way, the present case was the first to describe a subject with the recurrence of urinary inconti Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. The literature includes a few cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, and most of them involved patients with epilepsy who were between the ages of 12 and 43 years. Herein, we present three patient We study how severe was Urinary retention, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) - The drug gabapentin could decrease detrusor activity by inhibiting micturition reflex through brain centers that regulate bladder capacity and by coordinating bladder and external urethral sphincter activity [21]; it could activate posterior and medial hypothalamic regions as well, thus inhibiting bladder activity [21]. Gabapentin is widely used in veterinary medicine to manage pain, anxiety, and seizures in dogs. While it is generally safe, its effects on urination and the urinary system raise questions that pet owners and veterinarians should address. Let’s delve into these effects and provide actionable tips to ensure your furry companion stays healthy and comfortable. Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. The literature includes a few cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, and most of them Gabapentin is a first-line agent for neuropathic pain management and has a favorable safety profile. The literature includes a few cases of gabapentin-induced incontinence, and most of them involved patients with epilepsy who were between the ages Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Abstract Gabapentin (GBP) is a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that is commonly used in palliative care for symptom management indications including neuropathic pain syndromes, hiccups, cough, and anxiety. An uncommon adverse effect of GBP is urinary incontinence (UI). We report the case of a 61-year-old male with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer who developed probable
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Prophylactic+treatment+(to+prevent+new+attacks):+It+is+indicated+if+the+patient+have+3+or+more+attacks+per+months+or+if+there+is+C.I+to+acute+phase+therapy..jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |