Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-480792463-59e11be8aad52b00118a3af4.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
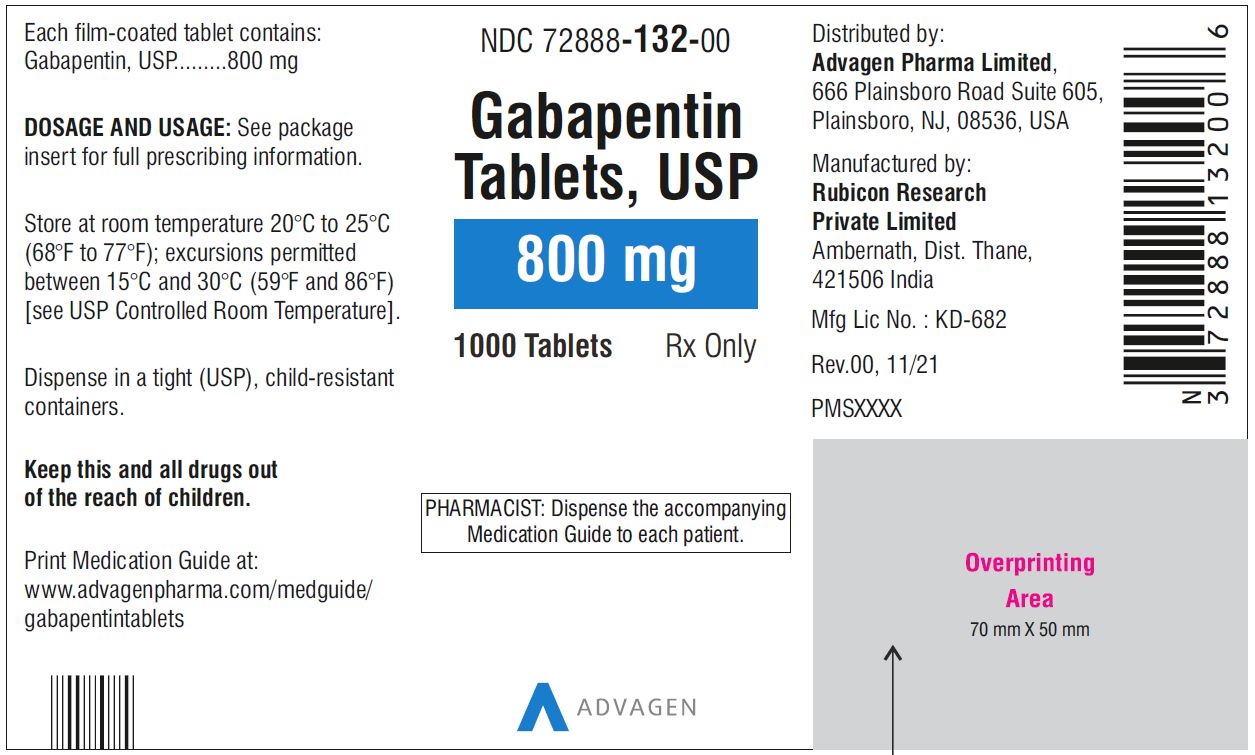
Each of us needs to be wary of prescribing for renal patients and this handbook provides a highly practical, user-friendly method of ensuring that appropriate prescriptions are given to patients, whether they have normal renal function, renal impairment, transplants or are receiving renal replacement therapy. Pricing and pack information for Oral tablet, Oral capsule and Oral solution forms of Gabapentin Renal clearance (CLr) and CLr adjusted for body surface area also declined with age; however, the decline in the renal clearance of gabapentin with age can largely be explained by the decline in renal function. [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate. Prescribing advice for patients with renal impairment including those with AKI or CKD. Read about dose adjustment and estimating renal function using eGFR and creatinine clearance. Ensure the following higher risk groups have a recorded renal function in the last 15 months: Patients prescribed gabapentinoids aged >65 years. Patients prescribed gabapentinoids aged >65 and co-prescribed a strong opioid (see BNF for information on strong opioids Analgesics | Treatment summaries | BNF | NICE). Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis Gabapentin is a medication used to manage nerve pain (e.g., postherpetic neuralgia), restless leg syndrome, and seizures. Available as gabapentin capsules or extended-release tablets, it calms overactive nerves. Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of View pregabalin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. The Renal Drug Handbookhas developed into an essential resource for nephrologists, specialist nurses and pharmacists engaged in the care of these patients. As the field moves forward so also do the therapeutic opportunities, and pitfalls. Fortunately successive editions of the handbook have kept pace with these advances - the present Fifth Edition includes over 900 drug monographs, each Gabapentin can also be used in patients with renal function below 20 mg/dl (although a dosing adjustment is needed). A 2018 clinical review examined gabapentin and other drugs as anti-craving therapy in alcohol use disorder. Neuropathic pain **Patients with renal impairment are more sensitive to neurological side effects of these drugs and should be carefully monitored** Gabapentin HD: 100mg after each dialysis session. If required the dose may be titrated in 100mg increments every 7 days to 300mg post HD, according to response and tolerability. PD and CrCl <30mL/min: Cimetidine impairs the renal excretion of gabapentin but not to a clinically important extent. It does not interact with anti-retroviral antibiotics. Gabapentin is widely used for neuropathic pain.3–12 However, there is no evidence that it is more effective than older anti-epileptics.14 Although in an open study in diabetic neuropathy, gabapentin Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-480792463-59e11be8aad52b00118a3af4.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |