Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
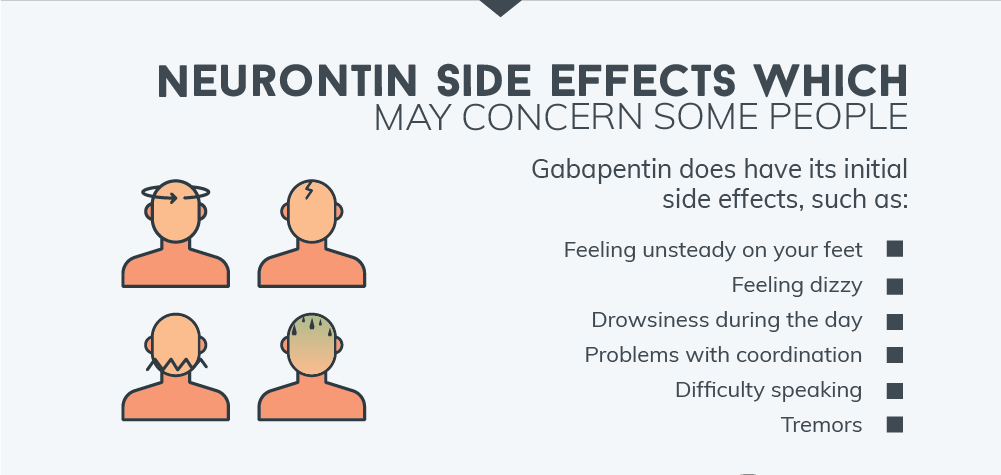
The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Gabapentin works by altering electrical activity in the brain, calming overactive nerve signals. It’s primarily prescribed for seizures and nerve-related pain, but doctors often recommend it for off-label uses such as anxiety and insomnia. Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX national database of de-identified patient records from 2004 to 2024 Gabapentin is often prescribed for nerve pain and seizures, but some users report memory loss as a side effect. This post explores the connection between gabapentin and memory issues, possible risks, and how to manage them. Learn what to watch for and when to consult your doctor for advice. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Explore the link between gabapentin and memory loss. Learn what research and patients reveal about cognitive side effects and how to manage them safely. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is used to treat nerve pain, epilepsy after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting the chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. With every Gabapentin alone may not commonly cause memory loss. It becomes more likely under these conditions: Combination therapy. The probability of gabapentin side effects like memory loss increases when this drug is combined with other medications. Long-term use. Studies claim a connection between cognitive decline and long-term use of this medicine. A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. A recent study has linked gabapentin, a popular painkiller for lower back pain, to increased risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in some adults. Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog in some individuals. Cognitive issues, such as a decrease in alertness, may occur as side effects, often accompanied by dizziness and drowsiness, affecting about 10% of users. While gabapentin is used to manage conditions like nerve pain and menopause symptoms, its impact on cognitive function is a concern for some patients Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Those with 12 or more gabapentin prescriptions were 40% more likely to develop dementia and 65% more likely to develop MCI than those prescribed the drug three to 11 times. Researchers noted that because this is an observational study, it cannot draw a direct cause-and-effect association between gabapentin and brain decline. Gabapentin has been associated with cognitive side effects in some individuals, including memory loss, although these effects are not universally experienced. The drug works by altering nerve activity in the brain, which can sometimes impact cognitive functions like memory, attention, and concentration. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. Gabapentin is widely used to treat seizures and shingles, but its effect on memory has been a topic of ongoing debate. While some patients may experience brain fog or slight confusion, studies have shown that gabapentin alone does not cause long-term memory loss. Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. Gabapentin, which is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |