Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | /GettyImages-141483002-5bb39d7746e0fb0026439ac9.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 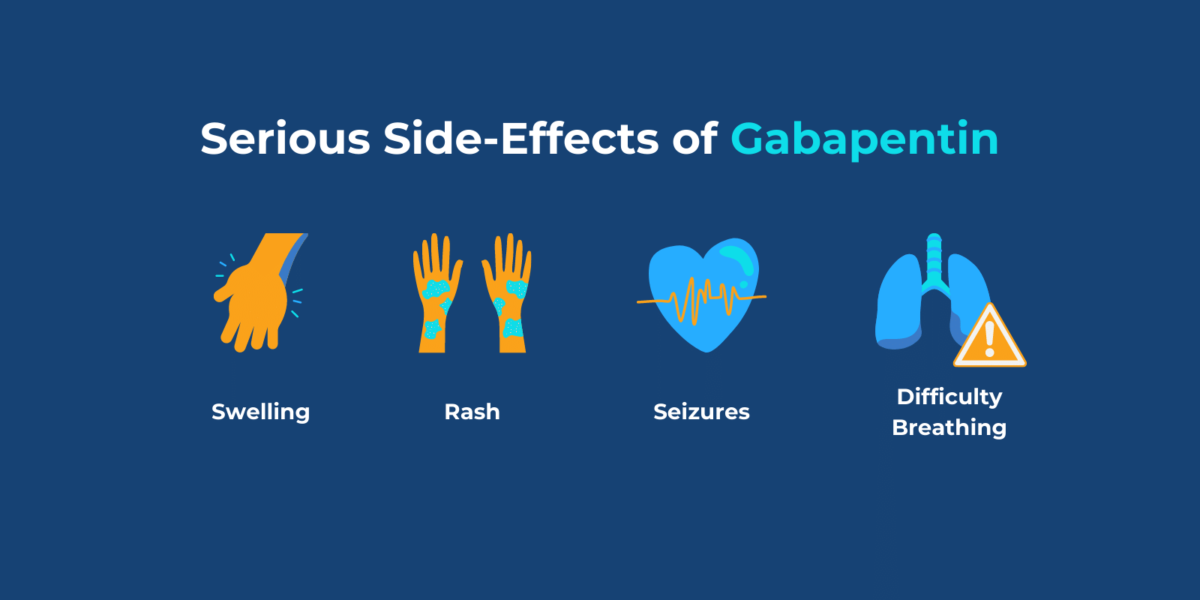 |
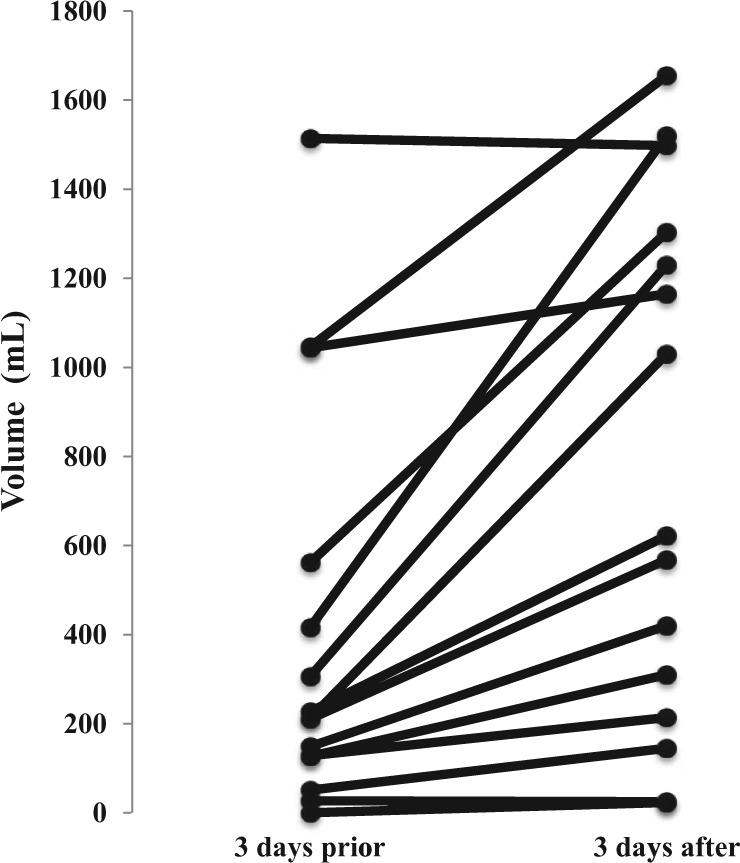
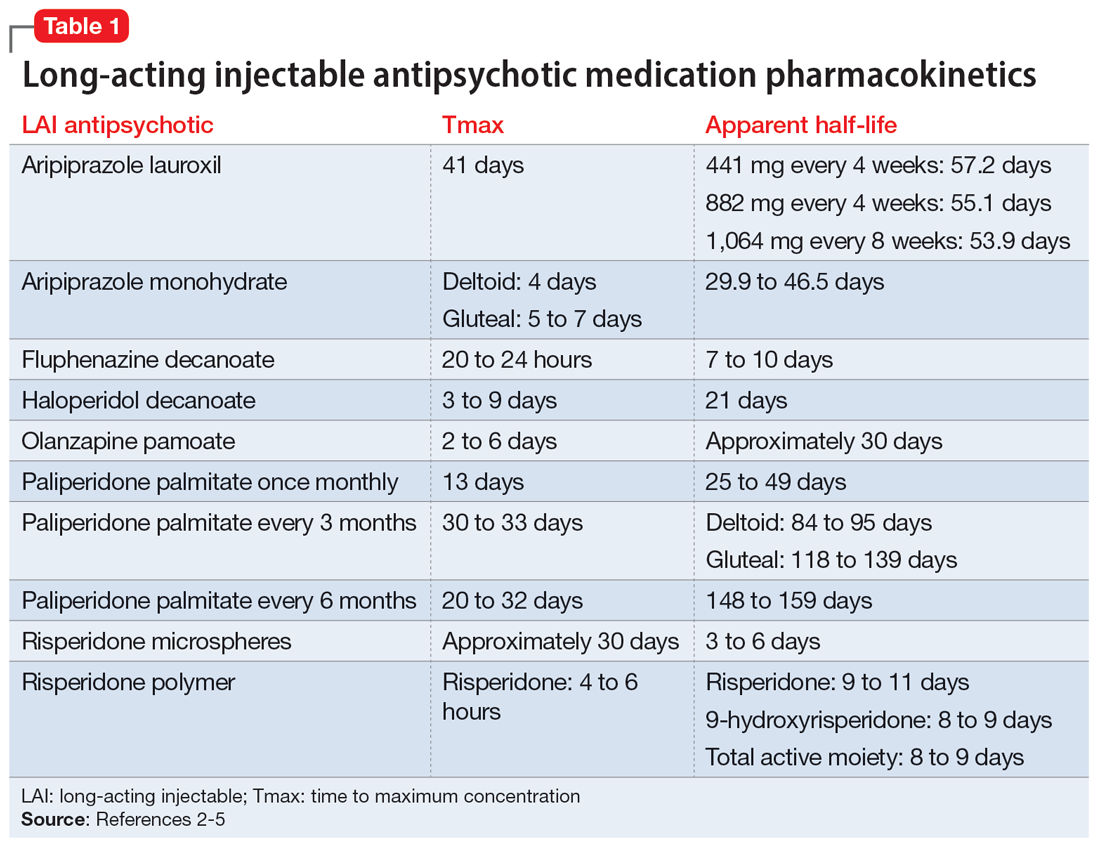
Abstract Background Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic pain, restless leg syndrome, and partial-onset seizures. Although the most frequent side effects of gabapentin are associated with the central nervous system, gabapentin can also affect the cardiovascular system. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. In addition, case reports [10] and post-marketing surveillance [11] have highlighted an underappreciated risk of worsening heart failure with gabapentinoids. Acute heart failure, which may be associated by peripheral edema (i.e., cardiogenic peripheral edema), seems to be a risk specific to pregabalin exposure that is not found with gabapentin The association of widely used neurological agents gabapentin and pregabalin and heart failure (HF) is not widely known, although fluid retention after their use in the form of peripheral edema has been recognized. Meanwhile, some evidence suggests that both drugs may be related to HF, especially to new onset HF. The pharmacokinetics and side effects of pre-gabalin and gabapentin tend to be Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic pain, restless leg syndrome, and partial-onset seizures. Although the most frequent side effects of gabapentin are associated with the central nervous system, gabapentin can also affect the cardiovascular system. Our findings suggest that increased risk for adverse cardiovascular events, along with other side effects, the efficacy of pain control and the degree of tolerance of the patient, should be considered when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin long-term in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Fibromyalgia, a chronic pain disorder, impacts approximately 2% of adults in the US. Gabapentin and pregabalin are common treatments to manage fibromyalgia-related pain. Our recent study showed the risk of adverse cardiovascular events increased in Gabapentin must be prescribed by a doctor and is taken orally via a tablet, a capsule, a solution, or a suspension. The drug has a number of side effects and may affect your heart and cardiovascular system in different ways. There is research to suggest that cardiovascular effects occur after taking gabapentin. Purpose of Review The objective of this manuscript is to describe the cardiovascular effects of the gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin. Recent Findings The most frequent adverse effects of gabapentin and pregabalin affect the central nervous system, such as somnolence and fatigue. Additionally, pregabalin, and a much lesser extent, gabapentin, may adversely affect the cardiovascular Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to This systematic review analysed the cardiovascular safety of gabapentin and pregabalin in clinical practice. Methods Databases were searched for articles examining the occurrence of cardiovascular events with gabapentin and pregabalin in different clinical conditions. Background: Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. We present a case of gabapentin induced CHF with rapid resolution after discontinuing the Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Although evidence suggests pregabalin can cause edema and heart failure, its cardiac safety profile in clinical practice is unknown. We sought to examine the risk of heart failure among older patients receiving pregabalin compared to those receiving gabapentin. Gabapentin modulated the central cardiovascular effect in the NTS We initially investigated the central cardiovascular effects of gabapentin in the SHR rats by microinjection into the NTS. Unilateral microinjection of increasing doses of gabapentin (3.03 to 33 nmol) into the NTS produced dose-dependent depressor and bradycardic effects (Figure 1A). Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate Introduction: Gabapentinoids are ligands of the α2-δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav) that have been associated with a risk of peripheral edema and acute heart failure in connection with a potentially dual mechanism, vascular and cardiac. Objectives & methods: All cases of peripheral edema or heart failure involving gabapentin or pregabalin reported to the French Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | /GettyImages-141483002-5bb39d7746e0fb0026439ac9.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |