Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
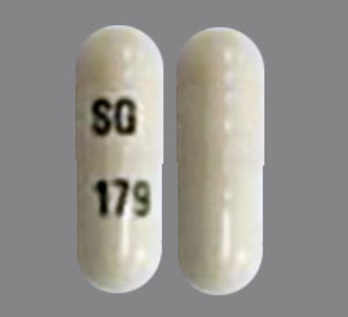
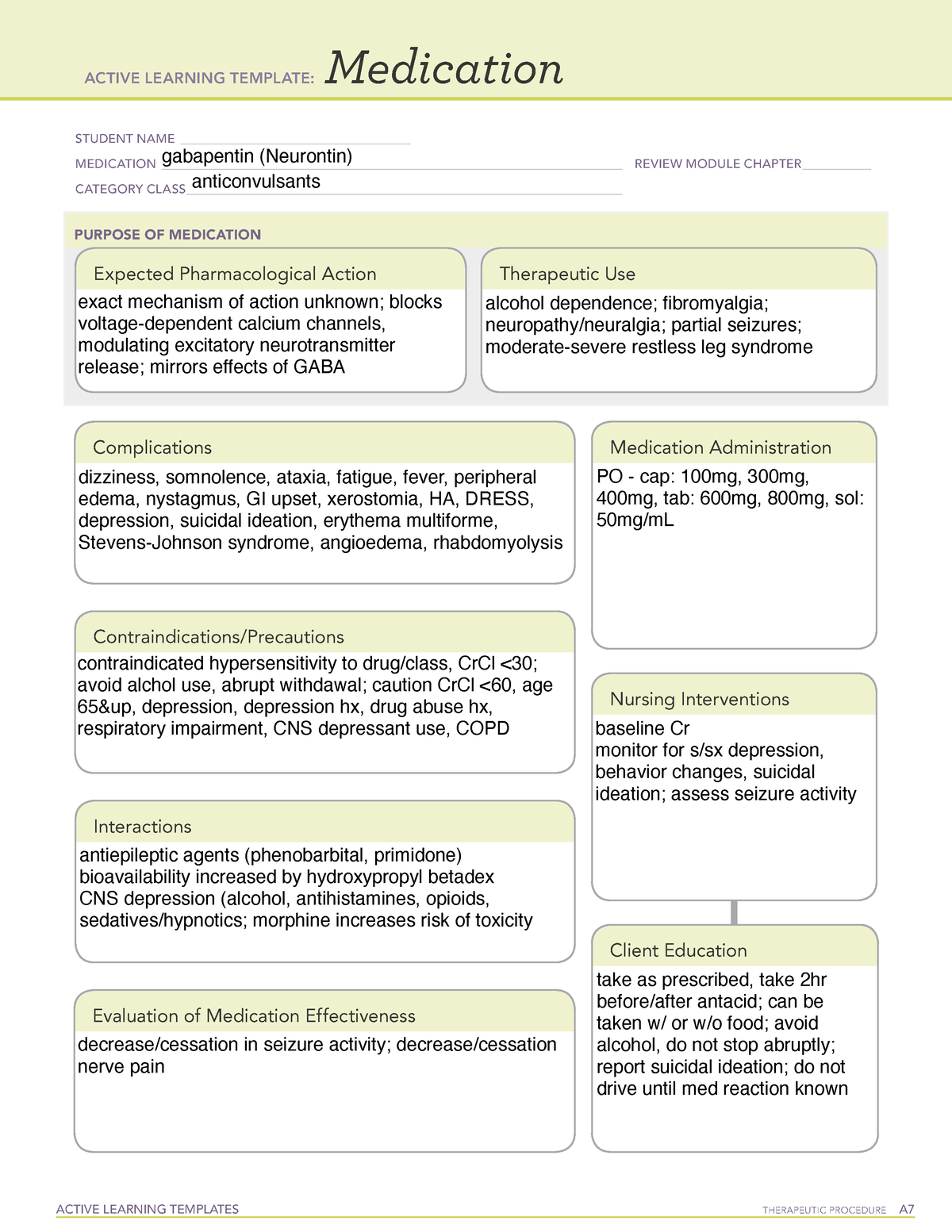
Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (1,2) Gabapentin: is licensed for add-on treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation has no significant interactions with other drugs is widely used in chronic pain conditions has a short half-life and generally needs to be given three times daily does cross the blood-brain Gabapentin, initially developed for epilepsy, is now widely used for nerve pain and other off-label applications. Rising prescription rates have sparked discussions about whether it should be classified as a controlled substance due to concerns over misuse and dependency. The change will take place in April 2019. Class C is the third in the government’s three-tier system for categorising controlled substances. Drugs in class C are associated with the least amount of harm compared with those in classes A or B. Pregabalin and gabapentin are currently used to treat conditions like epilepsy, nerve pain and anxiety. Prescription drugs pregabalin and gabapentin are to be reclassified as class C controlled substances from next April, the government announced today (15 October). See Epilepsy. MHRA/CHM advice: Gabapentin (Neurontin ®) and risk of abuse and dependence: new scheduling requirements from 1 April (April 2019) Following concerns about abuse, gabapentin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Gabapentin is a prescription medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of neuropathic pain (postherpetic neuralgia) and seizure disorders. Why is gabapentin controlled in some states? Gabapentin is structurally and pharmacologically related to pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR), which is a Schedule V drug and controlled federally in all states. ‘In April 2019, following a public consultation, as well as advice from the Advisory Council of the Misuse of Drugs, gabapentinoids were reclassified as Class C controlled substances and scheduled under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001’. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. As of 1 April 2019, pregabalin and gabapentin are controlled under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 as Class C substances and scheduled under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001 as Schedule 3 The ACMD recommended that gabapentin and pregabalin be controlled as Class C drugs under the 1971 Act, and placed in Schedule 3 to the 2001 Regulations. For more information about these compounds Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of From 1 April 2019 pregabalin and gabapentin will be reclassified as class C controlled substances in the UK. The change, announced in October 2018, is expected to prompt a decline in the use of the drugs as prescribing, dispensing, and collecting them becomes more onerous for doctors, pharmacists, and patients. The reclassification will make it illegal to supply pregabalin and gabapentin Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin binding at a2d subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels can increase the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and may directly or indirectly effect the dopaminergic reward system associated with addiction. Gabapentin is not currently listed as a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. Section 32B : Class C controlled substances; unlawful manufacturer, distribution, dispensing or possession with intent to manufacture, etc. Section 32C : Class D controlled substances; unlawful manufacture, distribution, dispensing, cultivation or possession with intent to manufacture, etc. Pregabalin and gabapentin are to be reclassified as Class C controlled substances from April 2019, the government has announced. Gabapentin is a controlled substance in states like Michigan and Kentucky, while others have mandated reporting rules. Learn about its risk for abuse here. From midnight on 1st April 2019, gabapentin and pregabalin will be reclassified as Schedule 3 controlled drugs, under the Misuse of Drugs Regulations (2001), and Class C of the Misuse of Drugs Act (1971), as is already the case with Tramadol. Their reclassification follows a Government consultation and recommendations from the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs that additional safeguards Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which bind selectively to the α 2 δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). [1][2][3][4][5] Clinically used gabapentinoids include gabapentin
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |