Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
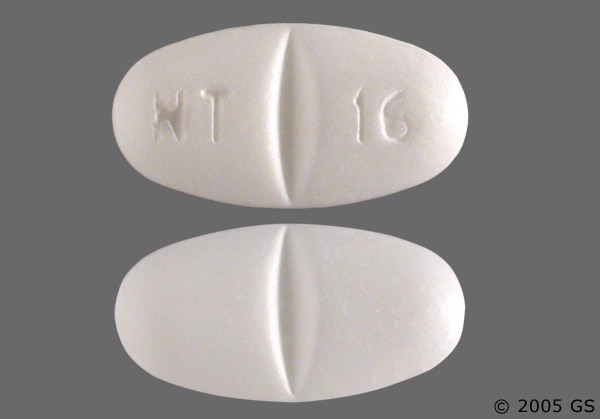
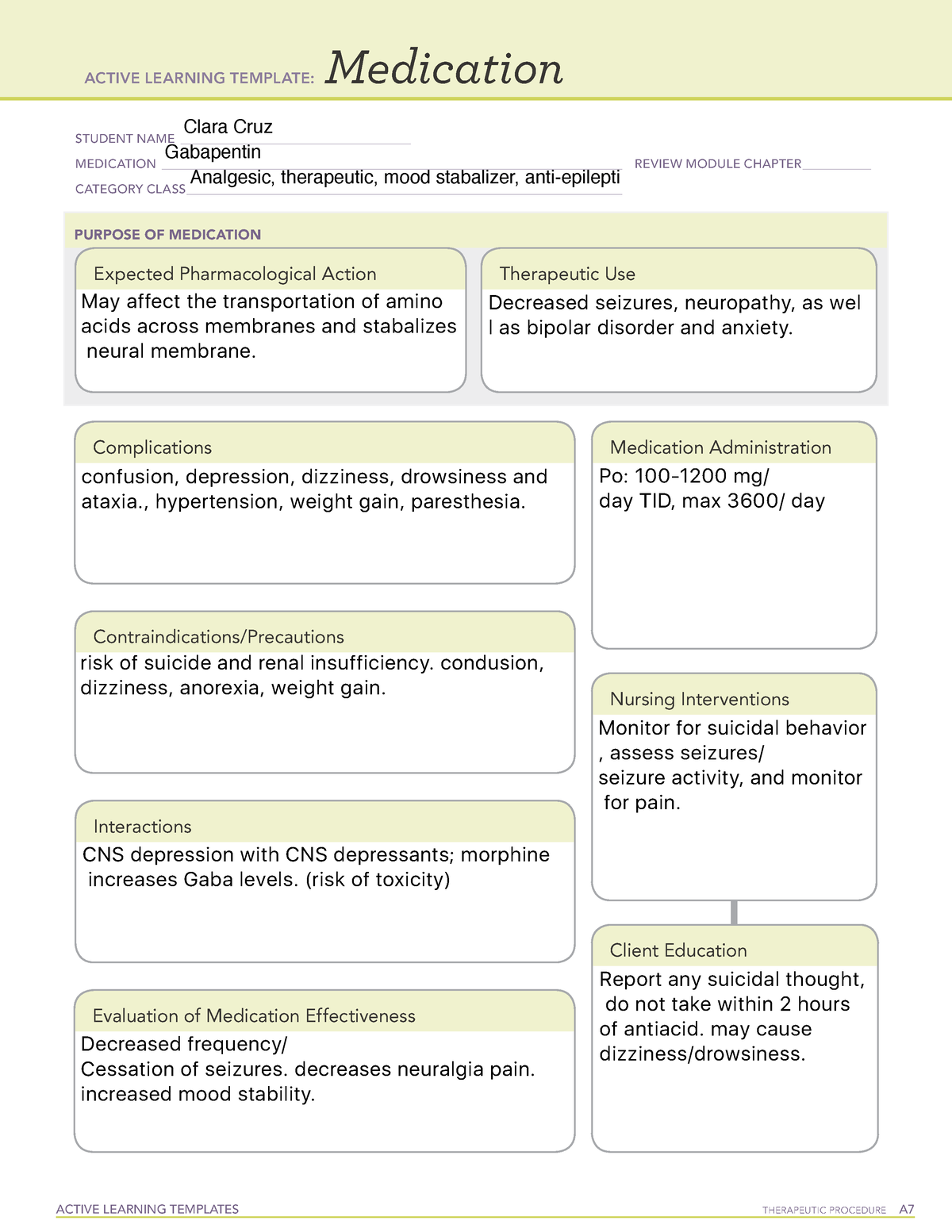
Find detailed information on Gabapentin including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half-life, administration, and more. The Classification of Gabapentin Gabapentin belongs to a class of medications known as anticonvulsants or antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Within this category, it stands out due to its unique mechanism of action compared to other traditional AEDs like phenytoin or carbamazepine. While those medications primarily work by enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission or blocking sodium channels, gabapentin Gabapentin (Neurontin) is not a narcotic or federally controlled substance by the DEA as of November 2022, but it is classified as a Schedule V controlled substance in certain states. In general, medications classified as Schedule V (Schedule 5) controlled substances are considered to have the lowest potential for abuse compared to other controlled schedules, but may still pose a risk of Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), restless legs syndrome (RLS), a painful movement disorder in the legs partial seizures in adults and children Gabapentin is a medicine from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. It is used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and restless leg syndrome. Learn about its dosage forms, warnings, interactions, and more. Gabapentin is a controlled substance in states like Michigan and Kentucky, while others have mandated reporting rules. Learn about its risk for abuse here. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat neuropathic pain and partial seizures of epilepsy. It belongs to a class of drugs called gabapentinoids, which act by binding to a protein involved in calcium channel function. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more. Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which bind selectively to the α 2 δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). [1][2][3][4][5] Clinically used gabapentinoids include gabapentin View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants. It is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless legs syndrome. Learn how to take gabapentin, what side effects to watch for and what drugs to avoid while taking it. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. It belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants that decrease abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants, which can be used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and restless leg syndrome. Learn how it works, what side effects it may have, and how it is regulated by the FDA. Brand names: Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin Drug class: GABA-mediated Anticonvulsants Medically reviewed by Drugs.com on Jun 10, 2024. Written by ASHP. Introduction Uses Dosage Warnings Interactions Stability FAQ Introduction Anticonvulsant; structurally related to the inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter GABA; also possesses analgesic activity. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin. Uses Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin isn't a narcotic, but it is a controlled substance in some states. Here's what you should know before using it.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |