Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | +Which+one+of+the+following+is+the+best+next+step+in+management+Discontinue+oxycodone..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
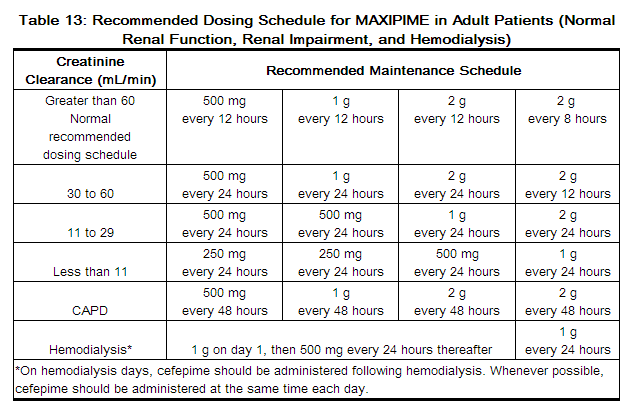
For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Creatinine clearance (CLCr) is difficult to measure in outpatients. In patients with stable renal function, creatinine clearance can be reasonably well estimated using the equation of Cockcroft and Gault: The use of gabapentin in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied. 2.4 Dosage in Elderly Because elderly patients are more likely to have Kidney disease alters the pharmacokinetic disposition of many medications, requiring dosage adjustment to maintain therapeutic serum concentrations. The Cockcroft-Gault (CG) equation is used for pharmacokinetic studies and drug dosage adjustments, but the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study equation is more accurate and more often reported by clinical laboratories than the CG From the Guidelines Gabapentin dosing in patients with renal impairment should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance (CrCl) to minimize the risk of toxicity and optimize efficacy. The dosing recommendations for gabapentin in patients with renal impairment are as follows: For patients with a CrCl of 60 mL/min or greater, the standard dosing of 300-1200 mg three times daily can be used. For CrCl <15 mL/minute: Reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance based on dose for creatinine clearance of 15 mL/minute (eg, reduce dose by one-half [range: 50 to 150 mg/day] for CrCl 7.5 mL/minute) ESRD requiring hemodialysis: Dose based on CrCl plus a single supplemental dose of 125 to 350 mg (given after each 4 hours of hemodialysis For neuropathic pain, a standard dosage pattern is used, typically recommending a dose three times daily. For epilepsy, the tool provides a dosage range within specific limits. Adjustments are made according to kidney function using the patient’s creatinine clearance value. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance (see Special Populations: Patients With Renal Insufficiency, below). Introduction Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Absorption of gabapentin is solely dependent on LAT that are easily saturable, resulting in dose-dependent pharmacokinetics. As the dose of gabapentin increases, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) does not increase proportionally. Dosage adjustment of GRALISE is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. GRALISE should not be administered in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min or in patients undergoing hemodialysis. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Abstract Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are well-tolerated medications primarily cleared by the kidney. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Objective: To determine whether patients with decreased creatinine Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. In elderly patients, and in patients with impaired renal function, gabapentin plasma clearance is reduced. Table 3. Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5; Creatinine Clearance (CrCl) Recommended Dosage Adjustments; Gabap 5. Peadiatric Renal Dosing For Children: Kidney Function: If a child has kidney problems, the dose needs to be lower. Ages ≥12 years: Adjust based on creatinine clearance and weight. Dosage Adjustment: Lower doses required; consult a paediatric specialist. 6. Administration How to Take Gabapentin: Gabapentin Capsules/Extended-Release: Recommended daily dose for gabapentin is in general in a range 900–3600 mg if creatinine clearance is higher than 80 ml/min. We have chosen to show half of the maximum recommended dose in each stratum. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | +Which+one+of+the+following+is+the+best+next+step+in+management+Discontinue+oxycodone..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |