Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 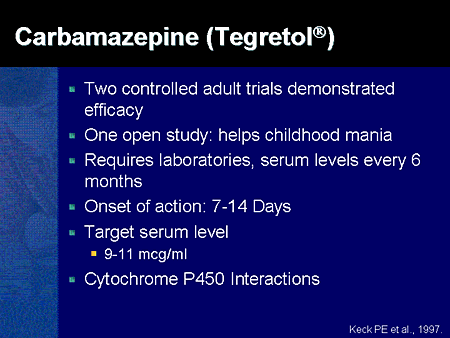 |
In these situations, clinically important drug interactions may occur. Carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital and primidone induce many cytochrome P450 (CYP) and glucuronyl transferase (GT) enzymes, and can reduce drastically the serum concentration of associated drugs which are substrates of the same enzymes. Clinically significant interactions can occasionally occur due to weak inhibitors and inducers (eg, target drug is highly dependent on CYP3A4 metabolism and has a narrow therapeutic index). Accordingly, specific interactions should be checked using a drug interaction program such as the drug interactions program included within UpToDate. On the other hand, pharmacokinetic interactions involve alterations of the drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Most reported drug interactions are pharmacokinetic ones, e.g., through affecting drug metabolism enzymes such as cytochrome P450 (CYP450). Several review articles have been published discussing gastric acid-related drug–drug interactions (DDIs) mediated by coadministration of antacids, histamine H2 receptor antagonists, or proton pump inhibitors, but are not sufficiently comprehensive Mysoline (primidone) Cymbalta (duloxetine) Neurontin (gabapentin) Lion's Mane is not known to alter any of the enzymes in our body that are responsible for metabolizing drugs (e.g., CYP liver metabolizing enzymes) and there have been no specific drug interactions documented with it. CYP3A4 is the most important of the CYP450 enzymes for drug metabolism and for drug interactions. It is not practi- cal to try to memorize the many CYP3A4 substrates, but it would be prudent to be familiar with the most common CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers since such drugs are likely to interact with approximately half of all drugs on the market. Ethosuximide, gabapentin, tiagabine, and vigabatrin are neither inducers nor inhibitors of drug metabolism. Hepatic enzyme inhibition usually occurs because of competition at the enzyme site. Knowledge of the specific metabolic enzymes involved in the metabolism of AEDs allows clinicians to predict potential interactions. Opioid analgesics are commonly prescribed for acute and chronic pain. A better understanding of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters-involved interactions with opioids will provide greater insight into potential DDIs and could help warrant safety and efficacy of opioids. 1 Moreover, opioid pain management involves economic issue. Summers et al observed that chronic pain patients exposed Cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism of diazepam in human and rat: involvement of human CYP2C in N-demethylation in the substrate concentration-dependent manner. The mechanisms of this possible drug interaction are discussed, with emphasis on cytochrome P450 metabolism. CONCLUSION. The present case is a warning of the possible interaction of a drug (gabapentin) not contemplated when starting or when monitoring an antiepileptic treatment. When polypharmacotherapy is used, there is a potential risk of drug interactions (DIs) [1]. A clinically relevant DI occurs when the efficacy or safety of a drug is altered by the concomitant administration of another medication. In a few cases DIs may prove beneficial, resulting in an increased efficacy or reduced risk of adverse drug reactions, and therefore certain drug combinations may be Purpose: Pregabalin, gabapentin, and carbamazepine, a potent inducer of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and P-glycoprotein, are frequently used antiepileptic drugs that are often administered together with factor Xa inhibitors (FXaI). We aimed to investigate whether potentially clinically relevant drug-drug interactions occur with these combinations. Whether you are taking gabapentin for nerve pain, seizures, or other conditions, it is important to be aware of the drugs that should not be taken with this medication. Gabapentin is a common prescription drug that is used to treat a variety of conditions, and it is important to understand the potential interactions with other drugs and what to avoid. In this article, we’ll discuss the drugs Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Because of the enhanced understanding of the mechanisms involved in drug interactions, particularly at the level of induction and inhibition of CYP isoenzymes, a more rational approach to the prediction and management of such interactions is now possible. In these situations, clinically important drug interactions may occur. Carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital and primidone induce many cytochrome P450 (CYP) and glucuronyl transferase (GT) enzymes, and can reduce drastically the serum concentration of associated drugs which are substrates of the same enzymes. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are widely used as long-term adjunctive therapy or as monotherapy in epilepsy and other indications and consist of a group of drugs that are highly susceptible to drug interactions. The purpose of the present review is to In these situations, clinically important drug interactions may occur. Carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital and primidone induce many cyto-chrome P450 (CYP) and glucuronyl transferase (GT) enzymes, and can reduce drastically the serum concentration of associated drugs which are substrates of the same enzymes. Interactions between Antiepileptic and Cardiovas-cular Drugs Due to their predominant hepatic metabolism by cytochrome P450 isoforms, antiepileptic drugs may cause theoretically numerous pharmacokinetic drug in-teractions with cardiovascular drugs. The old anti-epileptics such as phenytoin and carbamazepine are shown to cause most of these interactions. Due to their low potential for drug Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |