Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
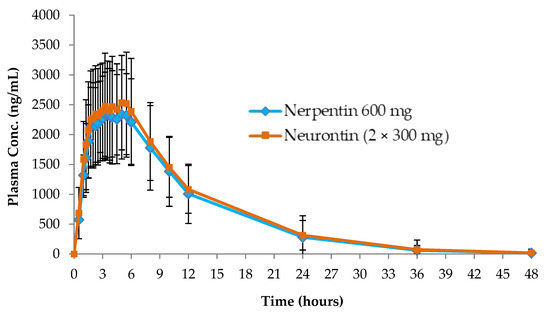 |  |
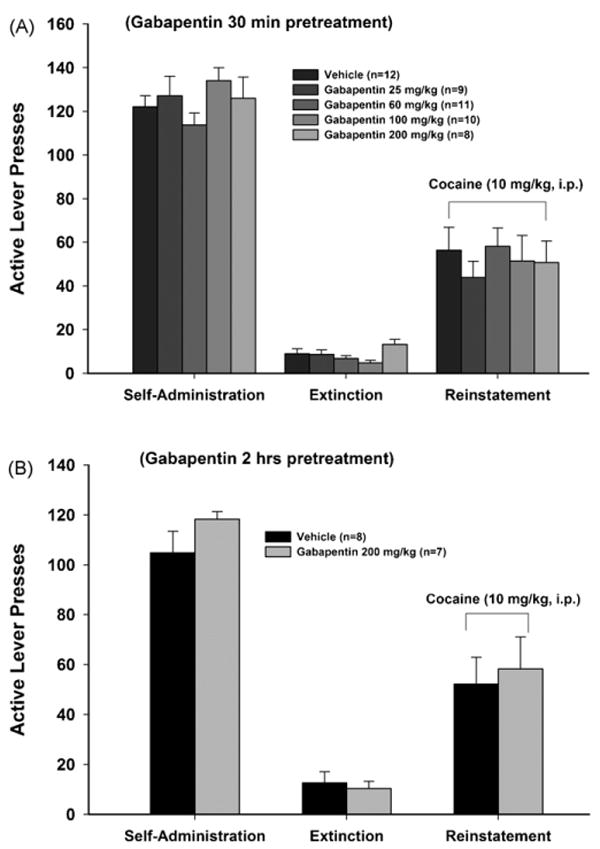
Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to induce addiction. Gabapentinoid prescription has tripled in the USA over the past 15 years [6], in part owing to patent expiration of the parent drug, gabapentin. The majority of these prescriptions are written for ‘off-label’ (non-Food and Drug Administration [FDA]-approved) indications, and this phenomenon may be driven by increasing awareness of the need for non-opioid pharmacotherapeutics. Recent Gabapentin (GBP) was used to explore the chronic analgesic treatment that could reverse pain-related depression. To investigate the in vivo variations of VTA DA neuron firing and LFP, multichannel acquisition processor system was used. Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). Drugs of abuse represent a growing public health crisis. Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to induce addiction. In this study, we used the condit Though it does not directly act on dopamine or serotonin receptors, studies do show that gabapentin can increase total blood levels of serotonin in some people. Although the cellular mechanisms of pharmacological actions of gabapentin (Neurontin) remain incompletely described, several hypotheses have been proposed. It is possible that different mechanisms account for anticonvulsant, antinociceptive, anxiolytic and neuroprotective activity in animal models. There is evidence supporting GABA’s inhibitory effect on dopamine in certain circumstances. For instance, activation of GABA-A receptors in the VTA has been shown to reduce the firing rate of dopaminergic neurons, leading to decreased dopamine release in projection areas. Drugs like gabapentin can mess with your dopamine levels, and with prolonged use, they may be the only source of dopamine in your body. As a result, it is highly addictive. Gabapentin, also known by the brand name of Neurontin, is a prescription pain medication that belongs to its class of drugs known as gabapentinoids. It is commonly used as an anticonvulsant and is prescribed to treat things Gabapentin (GBP) was used to explore the chronic analgesic treatment that could reverse pain-related depression. To investigate the in vivo variations of VTA DA neuron firing and LFP, multichannel acquisition processor system was used. Results: We used SNI to induce depression-like behaviors. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the Notably, blocking dopamine-1 receptors with SKF-83566 completely prevented pregabalin-induced place preference, thus demonstrating the engagement of the dopaminergic system in pregabalin-induced Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, converted to gabapentin after absorption, and thus avoids the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of gabapentin. It is administered as a single daily dose of 600 mg (300 mg in patients older than 65 years) at 5 pm to target adequate therapeutic levels at bedtime. Doses of 1200 mg have been used. Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. In contrast, the antinociceptive properties of gabapentin were observed in both genotypes. Levels of GABA A receptor No evidence exists for direct action at the serotonin, dopamine, benzodiazepine, or histamine receptors; research has shown gabapentin to increase total blood levels of serotonin in healthy control subjects. [33] GABA’s activity has vital consequences for dopamine function and subsequent behavior, especially those relating to outcomes that are motivationally relevant for the individual. It is suggested The inhibitory action of gabapentin on striatal dopamine release is clearly different from that of the GABA B agonist baclofen (Reimann, 1983). Reduced monoamine release may relate either to an Accumulating evidence indicates that gabapentin (GBP), a prescription drug, is prone to misuse, abuse, withdrawal, and dependence. Commonly, drugs of abuse modulate the dopaminergic system to While some studies suggest that gabapentin may indirectly increase dopamine levels in certain brain regions, others have found no significant effect or even a potential decrease in dopamine activity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |