Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 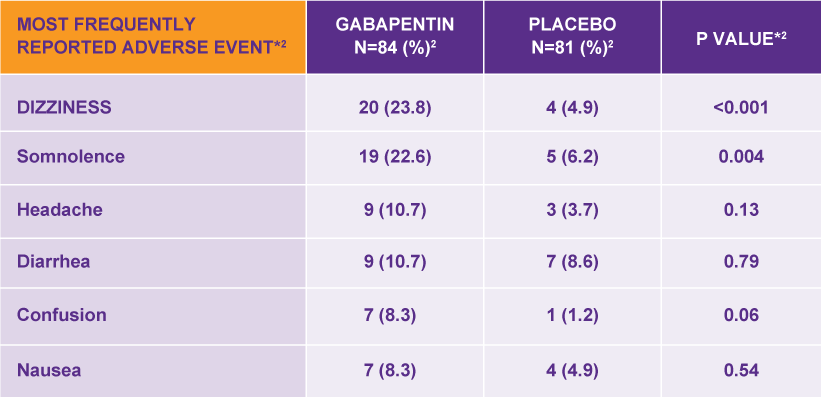 |
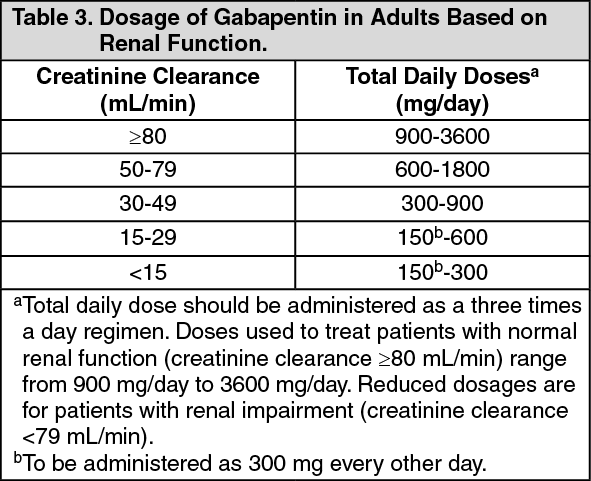
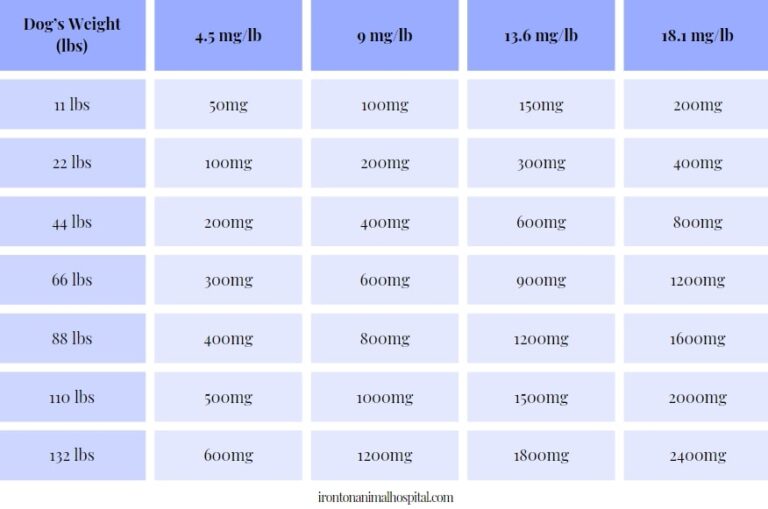
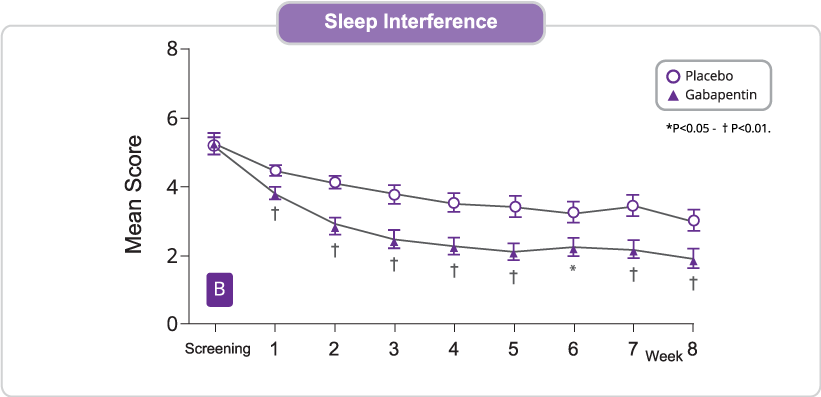
The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin tablets is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin three The dose can be increased further if necessary. Slow titration table for elderly patients or patients who are sensitive to Gabapentin Stay on this dose for a few days and if pain relief is adequate remain at this, but if pain is still a problem, try increasing the tablets as follows (see overleaf). The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin capsules is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2,400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3,600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin Dosage in Elderly Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and lowest doses should be started if therapy is needed, and dose should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance values in these patients. *Some experts recommend avoiding gabapentin in patients who are >65 years of age, however, it remains up to the clinician Key Takeaway Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for various conditions in elderly patients, but requires careful dosing and monitoring due to age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and potential side effects. Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Prescribe gabapentin with caution to people with: A history of substance abuse. A history of psychotic illness. Low body weight (high doses of oral solution). Mixed seizures (including absences). Diabetes mellitus. Renal impairment – dose adjustments are necessary. Also prescribe gabapentin with caution to people who are: Elderly. At risk of suicide. [ABPI, 2020a; Joint Formulary Committee The target gabapentin dose is between 1800 mg to 3600 mg/d [86], but it is necessary to evaluate renal function before increasing the daily dosage. Gabapentinoids may cause dizziness, diplopia, concentration disorders and peripheral edema, including ankle swelling. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Learn about gabapentin dosages based on treatment, medical condition, children, and more with GoodRx. Key Takeaway While gabapentin can be effective for treating certain conditions in elderly patients, it requires careful dosing and monitoring due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Gabapentin is increasingly prescribed to elderly patients for various conditions, but its safety profile in this age group requires special attention. This article explores the benefits, risks, and considerations for gabapentin use in older adults. The study concluded that close monitoring of the resident and low dosing (600 mg/day or less) of gabapentin is most beneficial to the elderly resident if they are receiving the benefits of pain relief including a decreased burning sensation. Physical effects like dizziness and cognitive effects like confusion are common Gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Discover other significant concerns for elderly gabapentin users and the importance of personalized View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |