Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
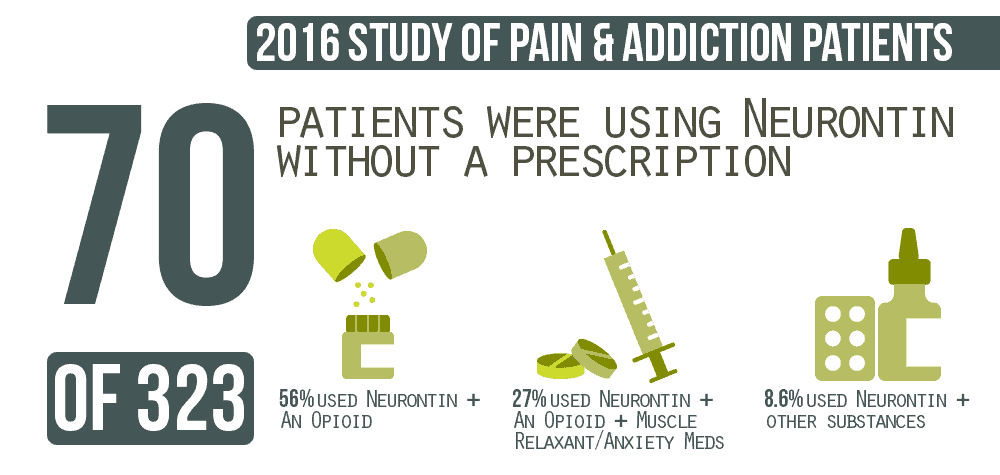
Treating Gabapentin Abuse Gabapentin is not a drug that should be stopped suddenly, and medical detox is often the first line of treatment. During medical detox, gabapentin dosage may be reduced slowly through a drug tapering schedule instead of stopping it “cold turkey.” This can help to minimize the possible withdrawal symptoms. This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified The gabapentinoid drugs, gabapentin and pregabalin, are first-line treatments for neuropathic pain. The epidemics of chronic pain and opioid misuse have given rise to the widespread use of non-opioid drugs such as the gabapentinoids for treatment. Unfortunately, the widespread use of gabapentinoid drugs has resulted in reports of misuse and abuse. Gabapentin, a prescription medication approved for the treatment of seizures and neuralgia, is often prescribed off-label for substance use treatment, mental health problems, and pain. Emerging reports also suggest it is misused for the purpose of Gabapentin addiction is a type of prescription drug use disorder characterized by the compulsive and non-medical use of the medication gabapentin. While gabapentin is not considered highly addictive like some other substances, you can develop dependence in some cases. Gabapentin addiction: Learn about the potential for dependence, recognize withdrawal symptoms, and discover treatment options. The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 biographical references (from the year 1983 to 2016). A Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects Gabapentin addiction is the one of the new opiate addictions. Learn how you can recognize the signs, symptoms, and consequences of abusing Gabapentin here. Gabapentin addiction manifests through various behavioral, physical, and psychological signs. Individuals addicted to gabapentin engage in behaviors such as doctor shopping to obtain multiple prescriptions, lying about symptoms to justify higher doses, and combining gabapentin with other substances for enhanced effects. Gabapentin misuse can lead to addiction, especially among those with a history of substance use, and may require medical supervision for withdrawal. Signs of gabapentin addiction include euphoria, misuse of other substances, and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation. Gabapentin is a prescription Painkiller that is less addictive than Opioids. Still, addiction and abuse occur; overdosing is possible. Gabapentin (Neurontin) carries a risk for abuse, can get you high if mixed with drugs, causes adverse side effects, and can lead to overdose. Learn about gabapentin for alcohol use disorder (AUD). Explore how this medication may help with withdrawal symptoms, cravings, and support recovery. Read on to learn more about Gabapentin, common side effects, symptoms of addiction, and how to treat Gabapentin addiction. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that has been increasingly abused in recent years. Learn more about the effects of gabapentin abuse and addiction treatment options. Gabapentin is one of the recommended mainstays of evidence-based treatment. 3 Unfortunately, our clinical experience suggests that gabapentin is now prevalent as a drug of abuse. The drug’s effects vary with the user, dosage, past experience, psychiatric history, and expectations. Gabapentin misuse of higher than normal dosing can result in a “high.” However, people will not necessarily experience addiction because gabapentin does not activate the typical dopamine-mediated reward pathway in the brain like other addictive drugs. Gabapentin abuse most often occurs supplementary to other substance addictions. Gabapentin is a generic drug used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It's not an opioid but is it addictive? Learn about gabapentin addiction versus dependence and more. Gabapentin has been shown to lead to dependence, addiction and withdrawal in some people, although when it was first approved in 1993 this risk was thought to be minimal. Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |