Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
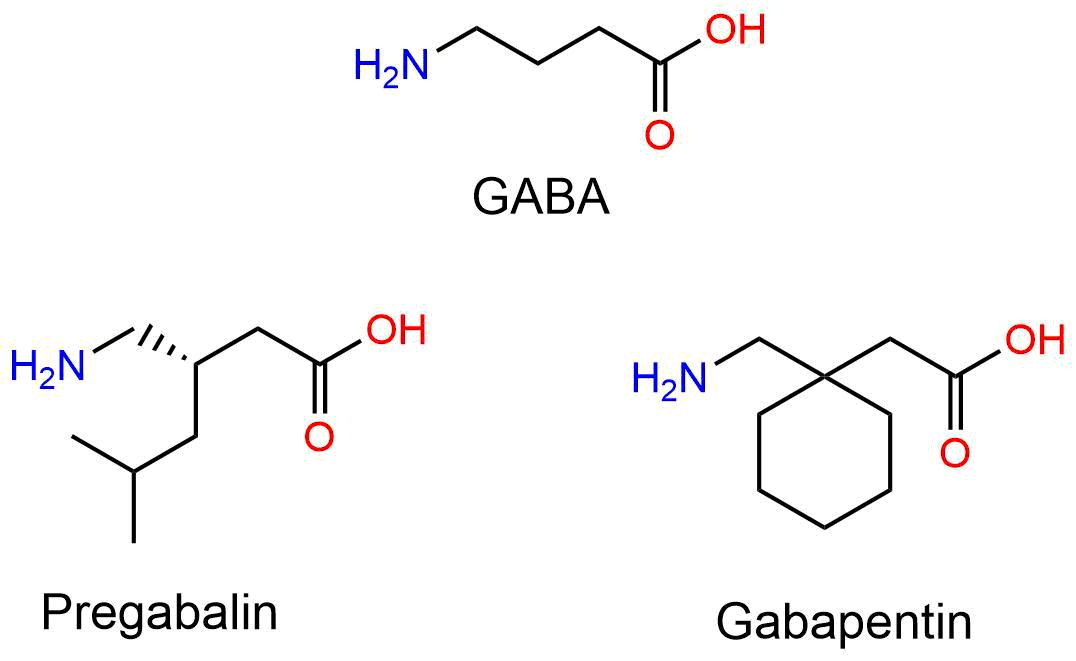
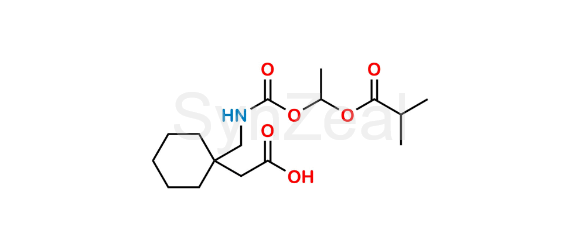
Mechanism of Action Gabapentin Enacarbil is a prodrug that is converted to gabapentin, which binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, decreasing excitatory neurotransmitter release and calming nerve overactivity. Cautions for Gabapentin Contraindications Gabapentin: Known hypersensitivity to gabapentin or any ingredient in the formulation. Gabapentin enacarbil: Manufacturer states none known. Warnings/Precautions Sensitivity Reactions Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), also known as multiorgan Horizant may also be used for other conditions as determined by your healthcare provider. How does Horizant work (mechanism of action)? Horizant is broken down by your body to make gabapentin. The Gabapentin enacarbil is used for treating restless leg syndrome (RLS) and postherpetic neuralgia. It is a prodrug of the anticonvulsant gabapentin, which means it is first converted to gabapentin in the body before it can have its effects. The mechanism of action of gabapentin in treating restless leg syndrome (RLS) or postherpatic neuralgia is not known. Gabapentin structurally resembles the 12.1 Mechanism of Action - Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin and, accordingly, its therapeutic effects in RLS and PHN are attributable to gabapentin. The precise mechanism by which Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) is an extended release tablet used to treat restless legs syndrome and for the pain from having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older Warnings Chemical structure of Gabapentin (A) and Gabapentin Enacarbil (B). Adler 4 administered open-label GBP (average 1163 mg daily) to eight idiopathic RLS sufferers for seven days. Four responded favourably and three others experienced nearly full symptom eradication continuing for six months. Dizziness, sickness and sedation were predominantly encountered resulting in two patients withdrawing Gabapentin enacarbil was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April of 2011. This article reviews clinically significant aspects of this new drug including: the FDA-approved indications, mechanism of action, administration, drug interactions, adverse effects, clinical trial evidence, innovative properties and place in therapy. Objective: Gabapentin immediate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil extended release formulation (GEn) have been approved for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. This is the first pharmacokinetic (PK) comparison of all three formulations using FDA-recommended doses for PHN. Includes Gabapentin Enacarbil indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Pharmacodynamics Since gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, it's physiological effects are the same as gabapentin. Concerning PHN, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Mechanism of action Although the exact mechanism of action of gabapentin in RLS and PHN is unknown, it is presumed to involve the descending noradrenergic system, resulting in the activation of spinal Horizant (Gabapentin Enacarbil Extended-Release Tablets) may treat, side effects, dosage, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and related medications including drug comparison and health resources. Gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant (ER) (U.S.), Regnite (in Japan)) is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug of the gabapentinoid class, and a prodrug to gabapentin. [1] It was designed for increased oral bioavailability over gabapentin, [2][3] and human trials showed it to produce extended release of gabapentin with almost twice the overall bioavailability, [4] especially when taken with a fatty The mechanism of action by which gabapentin is efficacious in PHN is unknown but in animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia (pain-related behavior in response to a normally innocuous stimulus) and hyperalgesia (exaggerated response to painful stimuli). Pregabalin is a gabapentin analog and is virtually identical to it in terms of its mechanism of action therapeutic profile (Sills, 2006). A prodrug of gabapentin, gabapentin enacarbil, is designed to display greater bioavailability and a better pharmacokinetic profile than gabapentin (Cundy et al., 2008). Gabapentin enacarbil is licensed for restless leg syndrome in the United States. 17 GBP-GR is administered once daily and gabapentin enacarbil is administered in two divided doses. 18 GBP-GR exhibits saturable absorption similar to immediate-release gabapentin but this is enhanced by high-fat content in meals. 18 Pharmacokinetic comparisons Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Easy-to-read patient leaflet for Gabapentin Enacarbil. Includes indications, proper use, special instructions, precautions, and possible side effects. Description Gabapentin enacarbil is used to treat moderate-to-severe primary Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). RLS is a neurologic disorder that makes the legs feel uncomfortable. This results in an irresistible feeling of wanting to move your legs to make them comfortable. Gabapentin enacarbil is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |