Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
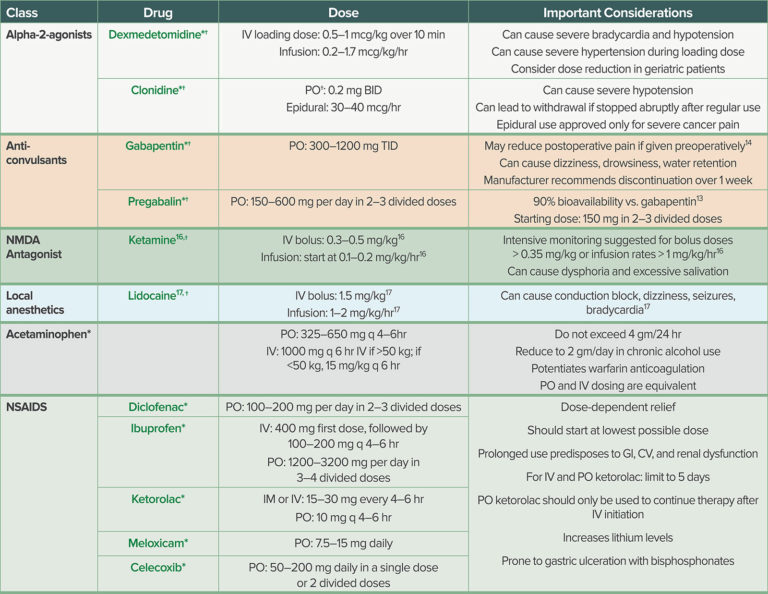
Specific protocols and dosages vary depending by institution. When implementing ERAS protocols, collaborate with informatics to create easily accessible order sets or bundles for the electronic medical record. Evaluate outcome measures, including patient length of stay, total cost, and total number of pills of opioids prescribed at discharge. In recent years, there has been increased interest in using gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) as part of multimodal medication plans or enhanced recovery after surgery protocols to mitigate several perioperative clinical challenges. Reviewer comment: I think if we are going to administer pre‐op drugs the gabapentin dose needs to be considered in renal failure ‐ even celebrex dosing may need consideration and adjustment on a case by case basis. This study represents our early experience. A shift in the institutional mindset of pain control was necessary for adoption of the ERAS protocol. While the ERAS pathway functions to reduce stress and return patients to homeostasis following surgery, postoperative gabapentin resulted in the greatest These pills include: gabapentin, celecoxib (Celebrex) and acetaminophen (Tylenol). Each medication takes a different pathway to reduce pain. Additional pain control methods used preoperatively include non-steroidal medications, Ketamine and a Transverse-Abdominis Plane (TAP) Block using a local anesthetic that dulls the nerves to the abdominal This cohort study examines whether perioperative gabapentin use among older adults after major surgery is associated with in-hospital adverse clinical events. Regarding the dose of gabapentin, a low dose such as 300 mg, which is commonly used in ERAS guidelines, 41, 42, 43 should be evaluated in future studies as respiratory depression, sedation, and somnolence are dose-dependent side effects.36 The imprecision of the estimates, specifically the pain scores in the first 24 hours and the opioid SUMMARY Gabapentin (NeurontinTM) has gained significant interest as part of a multi-modal pain management strategy for the control of acute pain. There has been considerable variation in both the dose and the regimen used in recent clinical trials. Most have relied on pre-operative dosing and have utilized a single dose of 300 to 1200 mg. Higher doses seem to show a decrease in postoperative Postoperative medications may include acetaminophen and gabapentin, as well as the following, as needed: codeine, ketorolac, hydromorphone or morphine, ondansetron, dimenhydrinate, and metoclopramide; doses are provided in Table 2. Discharge instructions include wound observation, drain care, and dressing care. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. To minimize opioid demands, ERAS uses adjunct medications and a multi-modal approach. Acetaminophen (Tylenol), gabapentin (Neurontin), celecoxib (Celebrex) and regional nerve blocks have been found to synergistically reduce postoperative pain and thus opioid needs. The regional block provides a pre-analgesic effect and continues to provide anesthesia and control pain for hours following Preoperative Holding Identify ERAS patients, initiate ERAS protocol Reinforce NPO: can drink up to 2 hours before surgery Surgery team to order preop medications GABAPENTIN 600 mg po ACETAMINOPHEN 1 g po ENTEREG 12 mg po Except in patients taking opioids for >7days prior to surgery Recommendations and Conclusions The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists makes the following recommendations and conclusions regarding the implementation of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathways: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery pathways were developed with the goal of maintaining normal physiology in the perioperative period, thus optimizing patient outcomes without The present study examines maternal gabapentin pharmacokinetics, disposition into breast milk, and infant dose from breast milk in the immediate postpartum following CD in patients receiving gabapentin as part of a standard of care ERAS protocol. Pain control is an integral part of Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) protocols for colorectal surgery. While opioid therapy remains the mainstay of therapy for postsurgical pain, opioids have undesired side effects including delayed recovery ERAS is a multimodal perioperative care pathway designed to achieve early recovery for patients undergoing surgery and reduce post-op pain medication usage. ERAS represents a paradigm shift in perioperative care in two ways. First, it re-examines traditional practices, replacing them with evidence-based best practices when necessary. Second, it is comprehensive in its scope, covering all areas PHS Colorectal Collaborative Enhanced Recovery after Surgery & Surgical Site Infections Prevention Bundle Measure Name: Colorectal Pathway (Colorectal Surgical Site Infection & Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) Measure category: Hospital Quality Measure Who is at risk: Hospitals and Physicians Gabapentin plays a significant role in ERAS protocols due to its effectiveness in providing analgesia while simultaneously minimizing opioid usage and the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). MGH Bariatric Surgery (ERAmbS) Pathway Updated 11.21.2022 Fig. 1. Considerations of clinical scenarios for omission or dose reduction of ERAS® protocol premedications. Forpatientsundergoingminimallyinvasivesurgery,especiallywith-inthecontextofanticipateddischargeonthedayofsurgery,omissionof Tramadol ER and Gabapentin/Pregabalin as premedication is a reason-able consideration.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |