Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 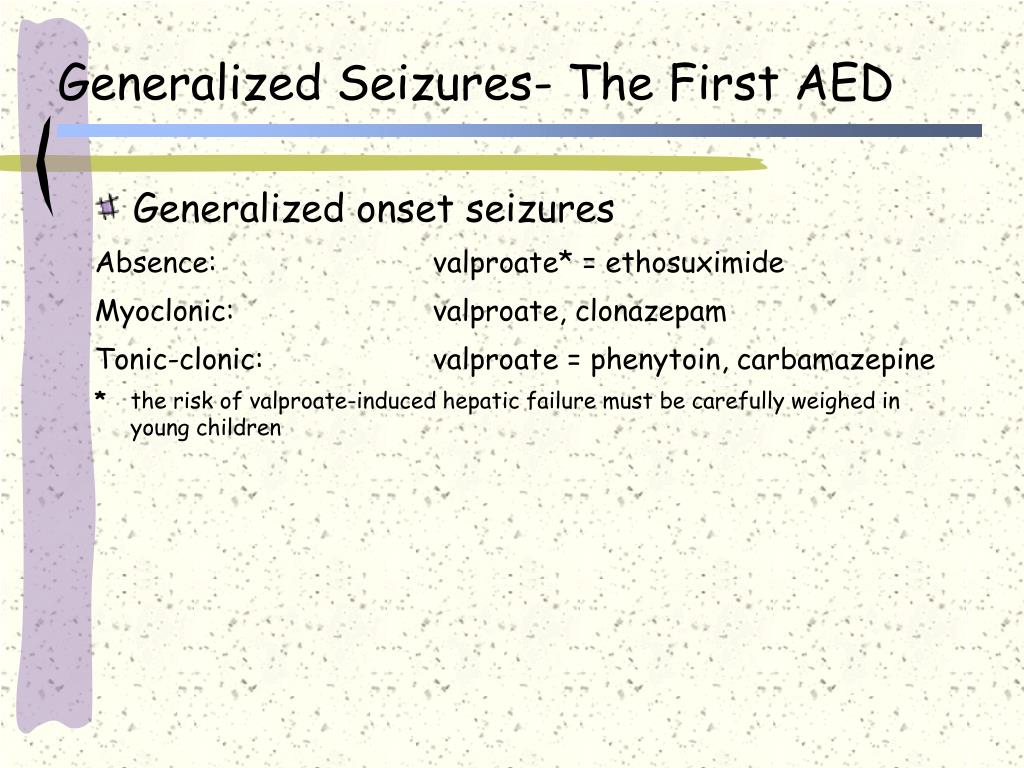 |
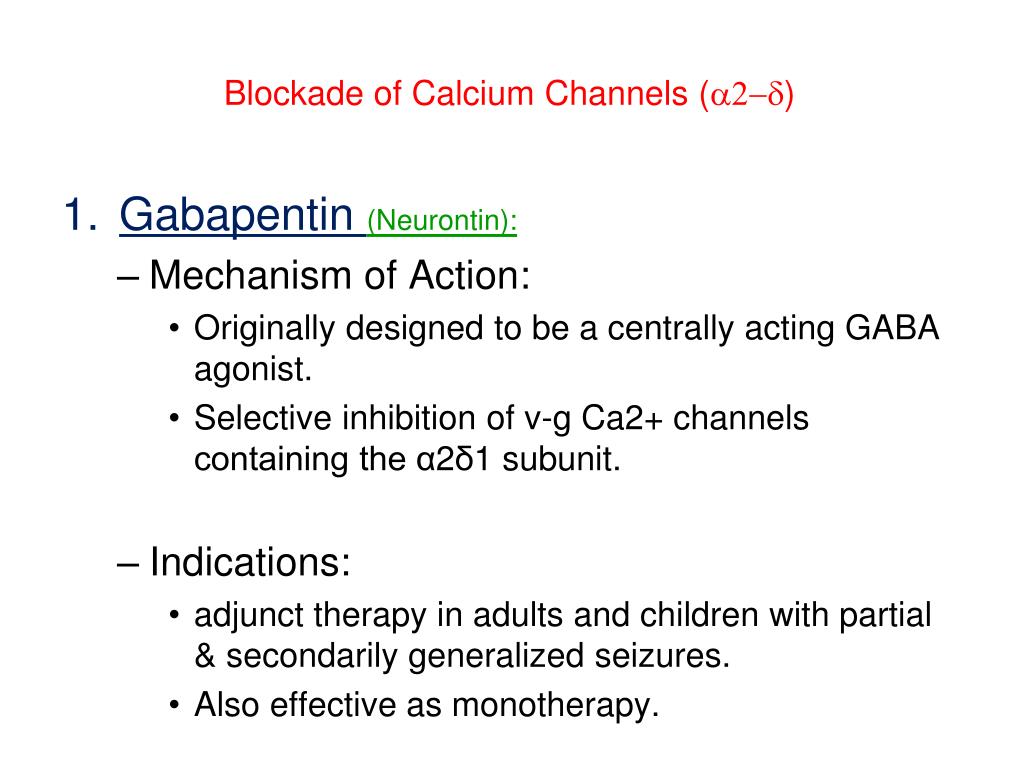
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client who has absence seizures. Which of the following medications are appropriate for the nurse to administer? (Select all that apply.) Question 1 options: Phenytoin (Dilantin) Ethosuximide (Zarontin) Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Valproic acid (Depakote) F Gabapentin for Seizures: Drugs [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2024 Oct. Table 9, Summary of Recommendations in Included Guidelines. Atypical absence seizures are distinct from typical absence seizures and generally result in changes in postural tone. 4 These seizures, primarily seen in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, are outside the scope of this article. 4 Absence seizures typically present during childhood—the peak age for diagnosis of childhood absence epilepsy is 5 to 7 The efficacy of gabapentin (Neurontin), in generalized seizures was evaluated in this 14 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on, multicenter study. A total of 129 patients with refractory generalized seizures were randomized to receive either placebo or 1200 mg/day gabapentin Absence seizures are brief seizures characterized by a behavioral arrest correlating with generalized 3-Hz spike and wave discharges on electroencephalogram (EEG).[1] Absence seizures occur in multiple genetic generalized epilepsies, including childhood absence epilepsy (CAE), juvenile absence epilepsy (JAE), and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME).[2] Genetic generalized epilepsies comprise What is an absence seizure? Absence seizures, formerly known as petit mal seizures, are short seizures that cause you to stare and lose awareness of your surroundings. They typically start without warning and last between three and 15 seconds. Absence seizures are common in children but also happen in adults. Gabapentin is available in Canada by prescription only. Known as Neurontin Uses Effective against partial seizures (including secondary generalized tonic-clonic). Somewhat effective against primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Ineffective or worsens absence, myoclonic or tonic / atonic type seizures. How to Use Do not increase or decrease the dose without your doctor’s approval. Do not Ethosuximide, valproate, and lamotrigine each have a role as treatments for childhood absence epilepsy. Care of children with childhood absence epilepsy should go beyond drug treatment and address associated behavioral and psychosocial conditions as well. Gabapentin (NEURONTIN®) Used for: Partial seizures. Tonic clonic (grand mal) seizures following partial seizures. Not effective for absence seizures. Add-on to current anti-epileptic drug therapy. An absence seizure is specifically caused by multifactorial inheritance. The voltage-gated T-type calcium channel is regulated by Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2 (GABRG2), GABRG3, and CACNA1A2 genes. [2] Inheritance of these genes is involved in the etiology (cause) of absence seizure. [2] The commonly held belief is that the genetic factor is the primary cause of childhood The efficacy of gabapentin (Neurontin ®) in generalized seizures was evaluated in this 14 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on, multicenter study. A total of 129 patients with refractory generalized seizures were randomized to receive either placebo or 1200 mg/day gabapentin as add-on therapy. Patients received their standard regimens of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of gabapentin as an adjunctive treatment for various types of seizures, including partial onset seizures and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. ANS: D Absence seizures and tonic-clonic seizures are considered to be generalized seizures. Consciousness is lost in both types. Whereas little movement occurs in absence seizures, major movement of large muscle groups occurs in tonic-clonic seizures. Simple (Jacksonian) seizures are considered partial seizures. Partial epilepsies involve activation of only part of the brain, and the location Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. Ethosuximide is the first choice in absence epilepsy without GTC (ILAE level A). Conclusions Lamotrigine and levetiracetam can be used as first choice for focal seizures and generalized epilepsy with GTC, suitable in all age-groups and for both men and women. Recommendations for GTC seizures have lower evidence than those for focal seizures. This is a protocol for a Cochrane Review (Intervention). The objectives are as follows: To assess the effects of gabapentin monotherapy for people with epileptic partial seizures with and without secondary generalisation. Abstract Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as an add-on treatment for focal-onset seizures, helping improve seizure control alongside other therapies. Learn about the use of gabapentin in the treatment of absence seizures, a type of epilepsy characterized by brief episodes of unconsciousness and staring spells. Gabapentin (gab-ah-PEN-tin) is the generic name (non-brand name) of the seizure medicine Neurontin (nur-ON-tin) used in the United States, Canada, the UK, and some other countries. Another commonly used name for gabapentin is GBP.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |