Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
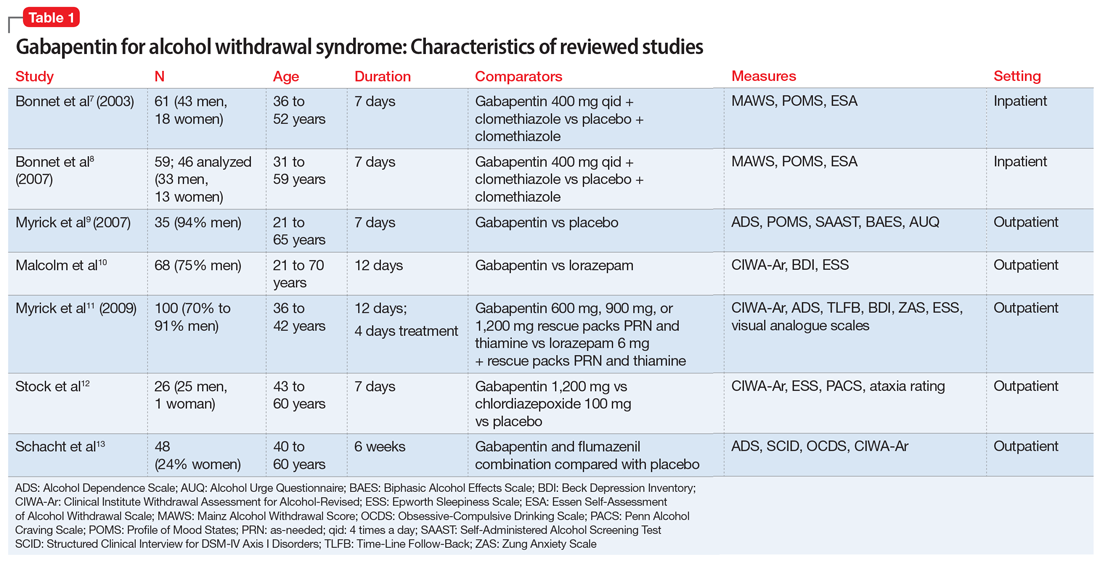
Clinical question Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Results are statistically A new study reports the nerve pain reliever gabapentin may be helpful in treating people with serious alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Some experts say gabapentin is most effective if used in Doctors don’t recommend drinking alcohol while taking gabapentin, especially for those who have just started taking it. However, you may talk to your doctor about drinking in moderation after you’ve reached a stable dose. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol intensifies central nervous system depression, increasing risks of drowsiness, dizziness, and respiratory depression. Consuming alcohol while on gabapentin can lead to severe side effects, including increased risk of seizures, overdose, and death. Gabapentin specifically has been shown to decrease rates of relapse in patients with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Why should hepatologists be involved in treating alcohol use disorder? The burden of alcohol-related liver disease is increasing. These findings were similar for other drinking variables, where gabapentin was more efficacious than placebo in the high-alcohol withdrawal group only. Gabapentin caused more dizziness, but this did not affect efficacy. While benzodiazepines are considered the standard of care for alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin is a valuable alternative that can also help with cravings and abstinence long term. Read on to find out more. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Gabapentin is an off-label medication for alcohol use disorder, sold under the brand names Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant, among others. The medication was originally developed to treat epilepsy and is now FDA-indicated for a variety of additional uses, including the treatment of conditions like postherpetic neuralgia and restless leg syndrome. According to double-blind evaluations, gabapentin appears generally safe when used alongside alcohol consumption in alcoholic individuals—though we’d never recommend mixing the two. The research shows no significant harmful interactions between gabapentin and alcohol in controlled settings. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. It may have some efficacy and safety for mild withdrawal and early abstinence, but it also has potential for abuse and misuse. Gabapentin is a potentially efficacious treatment for reducing the risk of relapse to harmful drinking patterns in outpatient management of alcoholism. Gabapentin's ease of use, rapid titration, good tolerability, and efficacy in both the withdrawal and chronic phases of treatment make it particularly appealing. Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02349477. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Gabapentin can reduce your desire to drink and can help you stop drinking. Gabapentin may also help improve symptoms of anxiety and dificulty sleeping that may occur when stopping alcohol use. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or naltrex
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |