Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
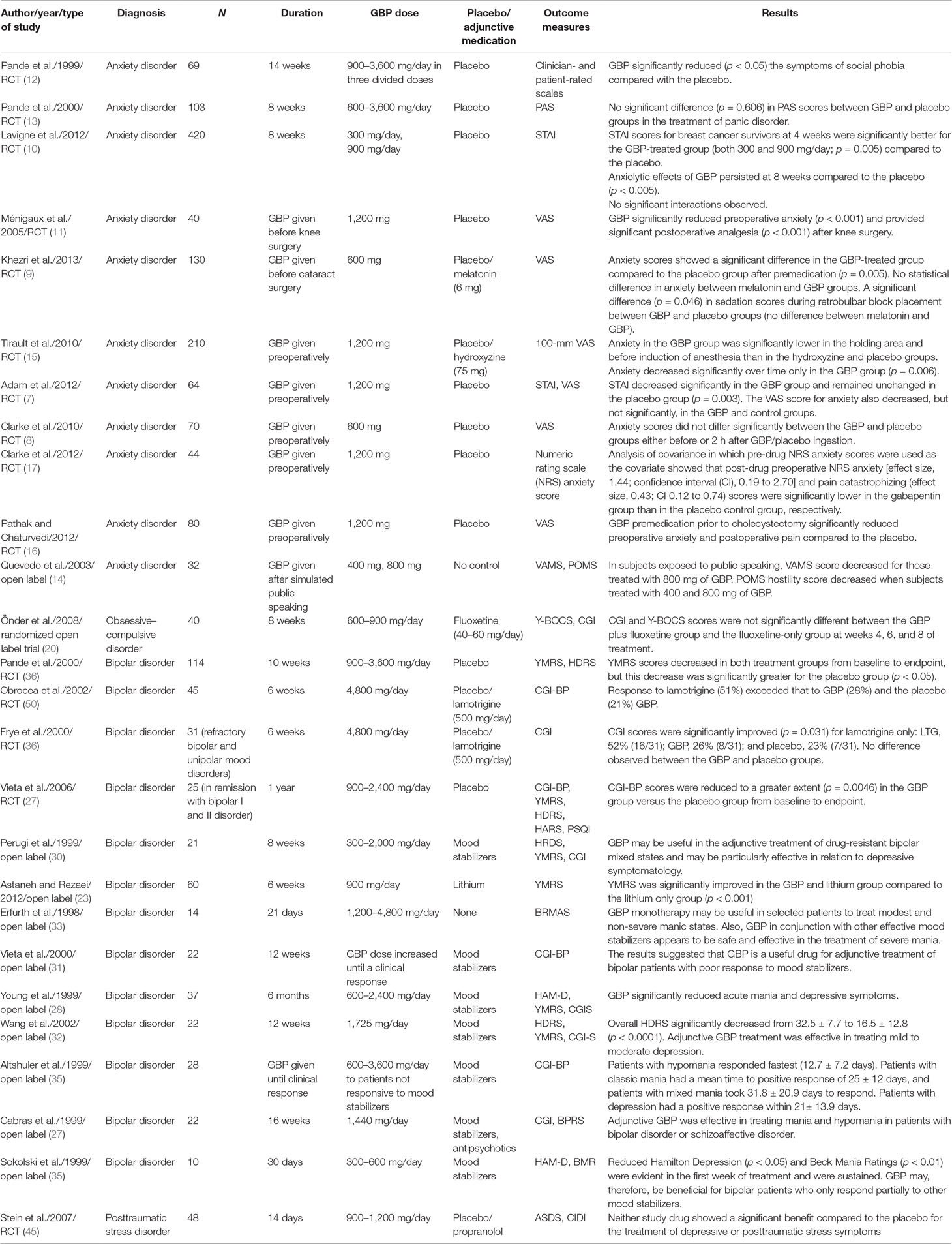
Anxiety disorder affects about one in five American adults, with 40 million struggling with this mental health challenge per year. Traditional treatment of anxiety involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and holistic interventions. One medication that is being used off-label for anxiety is called gabapentin. Here we’ll look at the use of gabapentin for anxiety, and explore the Whether you’re already taking gabapentin for an anxiety disorder or are curious if you might benefit from it, you may be wondering how effective it is, how it works, and if there are side effects. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about gabapentin for anxiety. What is Gabapentin? While gabapentin is increasingly being used to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), little is known about its effectiveness on GAD symptoms. The patient presented here has a relatively straightforward psychiatric history, with GAD playing a prominent role. Although evidence is limited, some studies show gabapentin can help with anxiety symptoms. One 2020 review suggests gabapentin may help with different types of situational anxiety, Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric To many medications are available to alleviate anxiety. Recent research indicates that gabapentin has proven to be an effective treatment for anxiety sufferers. Nevertheless, there are few case reports and no randomized controlled trials regarding this medication’s efficacy in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Gabapentin users with GAD have been demonstrated to have fewer Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly Results Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Preclinical data suggest the potential anxiolytic effect of gabapentin (6). Recently, Beauclair et al. (7) reported reduction in anxiety symptoms and syndromes in 18 patients with primary psychotic disorders and in one patient with generalized anxiety disorder treated adjunctively with gabapentin, 200–1800 mg/day. We report here on four patients with primary anxiety disorders refractory to Gabapentin may be an effective adjunct to anxiety therapy, according to a review published in the American Journal of Psychiatry. (7) Some characteristics imply it might be used as a stand-alone treatment, but additional study is needed because there is not sufficient empirical data. Gabapentin’s effective dose for anxiety ranges from 300 mg to 3,600 mg daily. Improvement in anxiety symptoms can typically be observed after 4-8 weeks of treatment. Gabapentin may be beneficial for individuals with a history of ineffectiveness from other anti-anxiety treatments. Gabapentin for anxiety is an off-label use, often applied when first-line anxiety medications are ineffective. It has been studied for generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and anxiety in breast cancer patients. Gabapentin is also used to support alcohol-dependent patients in managing anxiety symptoms during alcohol withdrawals. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Surgery: Those getting surgery may benefit from Gabapentin as a pre-surgical treatment to help decrease preoperative anxiety and reduce post-surgical pain. There is mounting evidence to substantiate claims that Gabapentin is an effective drug to be used on a short-term basis for patients getting surgery. Have you used Gabapentin for anxiety? Gabapentin may offer several benefits for individuals managing anxiety, particularly when traditional treatments aren’t effective or well-tolerated. Though it’s prescribed off-label, gabapentin helps anxiety by: Reduced symptoms of social anxiety and phobias: Research has shown Gabapentin can help ease symptoms in people with social phobia. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Other medications have been studied more for anxiety, and they’re typically tried first. The recommended gabapentin dosage for anxiety and other conditions can range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg per day. There are several ways to save on gabapentin. Gabapentin is pharmacodynamically close or identical to pregabalin, and is available at low cost in the United States. Gabapentin could theoretically represent a reasonable alternative to pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, but available evidence does not fully support this hypothesis. Preclinical data suggest the potential anxiolytic effect of gabapentin (6). Recently, Beauclair et al. (7) reported reduction in anxiety symptoms and syndromes in 18 patients with primary psychotic disorders and in one patient with generalized anxiety disorder treated adjunctively with gabapentin, 200–1800 mg/day. We report here on four patients with primary anxiety disorders refractory to In recent years, gabapentin has gained attention for its potential role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly for individuals who do not respond well to traditional anxiety medications like SSRIs or benzodiazepines. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |