Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/close-up-of-a-senior-woman-with-her-eyes-closed-56385149-5a58e97847c2660037700b80.jpg) | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-170616346-56ce25663df78cfb37a3a415.jpg) |
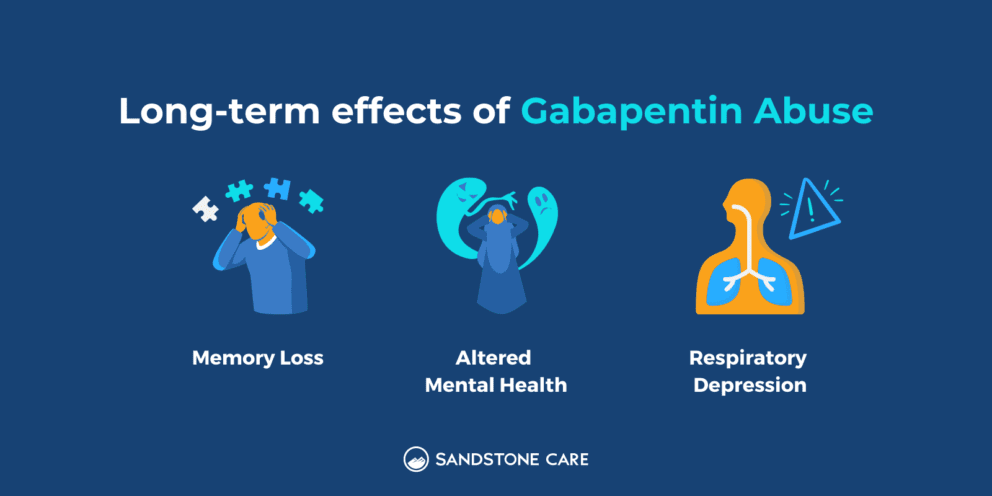
Our study aims to assess whether gabapentin use in chronic pain patients either increases dementia risk or offers protective benefits, using a population-based nested case-control approach. The novel antiepileptic agent gabapentin is being increasingly considered for use in the geriatric population because of its relatively favourable safety profile compared with other classes of psychiatric medications. Gabapentin has been administered to several geriatric patients with bipolar disorder and patients with dementia. Research shows that patients with six or more prescriptions for gabapentin, commonly used to treat lower back pain, were 29% more likely to be diagnosed with dementia and 85% more likely to be diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment within 10 years of their initial pain diagnosis. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin, a medication often prescribed for nerve pain and seizures, has raised concerns about its potential link to cognitive decline. While it helps many manage their symptoms, research suggests that prolonged or improper use might negatively impact brain function. Moreover, the stratification analysis revealed that the risk of dementia associated with gabapentin or pregabalin exposure was significant in all age subgroups; however, it was higher in younger patients (age <50) than in the older patients (hazard ratio, 3.16; 95% CI, 2.23–4.47). Gabapentin, which is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. Gabapentin use was significantly associated with decline in cognitive and functional status among older adults with initially normal cognition. Further studies are needed to examine the association. The adverse events from gabapentin could be higher in older adults who have more polypharmacy, higher comorbidities, and decreased renal functions. Since gabapentin is also prescribed to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) 19, gabapentin could be widely prescribed in patients with dementia. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has gained popularity in recent years for treating various conditions in elderly patients, including neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and behavioral symptoms associated with dementia. Complementing this formal systematic review, an illustrative case of a patient with BPSD in mixed Alzheimer's/vascular dementia, who appeared to derive benefits in terms of symptom control and functioning from the introduction of gabapentin titrated up to 3600 mg day -1 alongside other interventions, is presented. The clinic's database was searched to identify patients diagnosed with dementia (all types) and agitation, and treated with either gabapentin or pregabalin between January 2019 and April 2023. Medical records, brain images, and laboratory findings were reviewed retrospectively. Abstract Risk of dementia following gabapentin prescription in chronic low back pain patients Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Three of 4 patients were successfully titrated to a full dose of 2,400mg/day. These findings suggest a possible role for gabapentin in the behavioral Gabapentin prescription in adults with chronic low back pain is associated with increased risk of dementia and cognitive impairment, particularly in non-elderly adults. Physicians should monitor cognitive outcomes in patients prescribed gabapentin. Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. What’s more, the risk was more than doubled in people normally considered too young to suffer from brain aging, those 18 to 64, results show. As we mentioned above, in most of the reviewed cases gabapentin is reported to be a well-tolerated and effective treatment for dementia-associated agitation. However, several case reports in which gabapentin was used for agitation in dementia with Lewy bodies question its appropriateness for all types of dementia-related agitation [14 – 16]. A new study warns that gabapentin can significantly increase the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in people taking it for chronic low back pain. ryanking999 – stock.adobe.com We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin prescriptions for chronic back pain were linked to higher dementia and cognitive impairment risk. Risks were especially high for chronic back pain patients ages 35 to 64. The study
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/close-up-of-a-senior-woman-with-her-eyes-closed-56385149-5a58e97847c2660037700b80.jpg) | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-170616346-56ce25663df78cfb37a3a415.jpg) |