Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
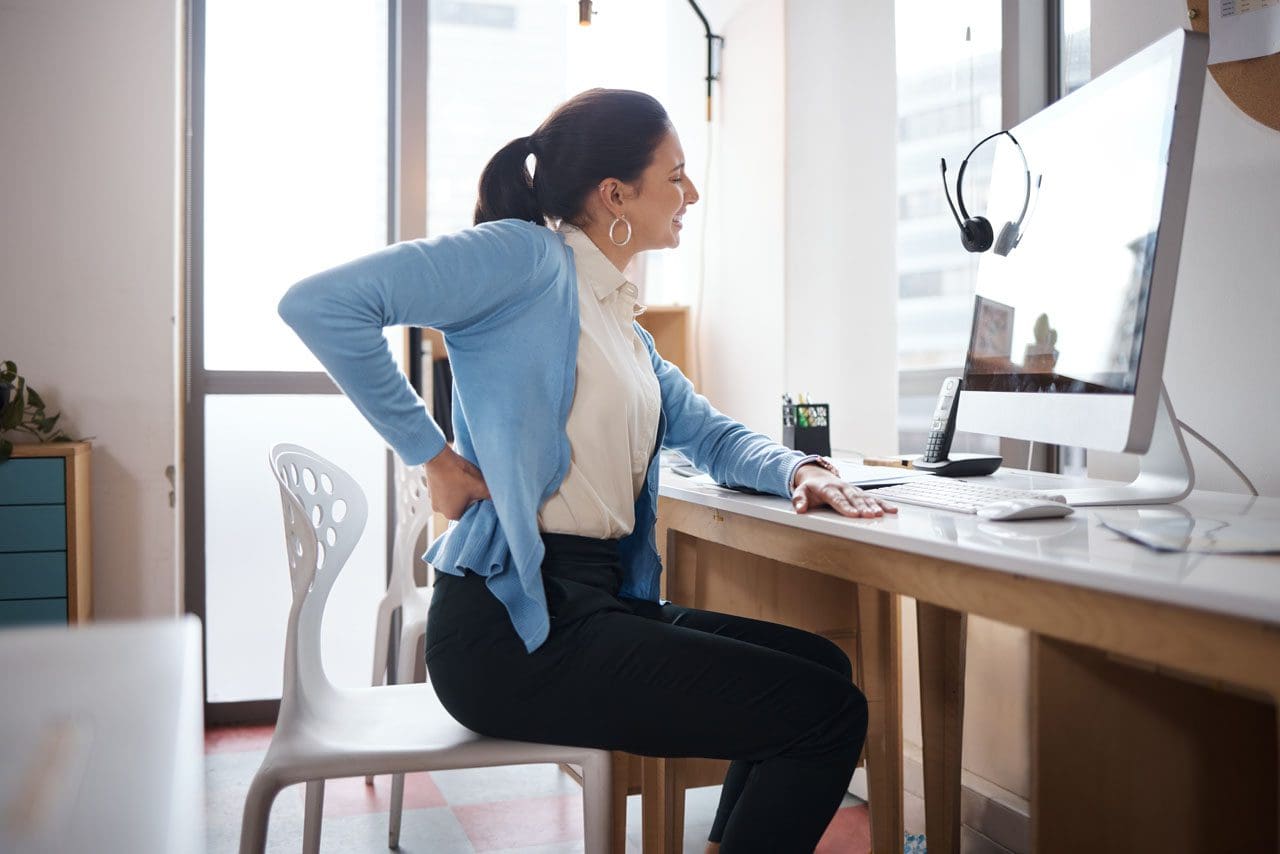
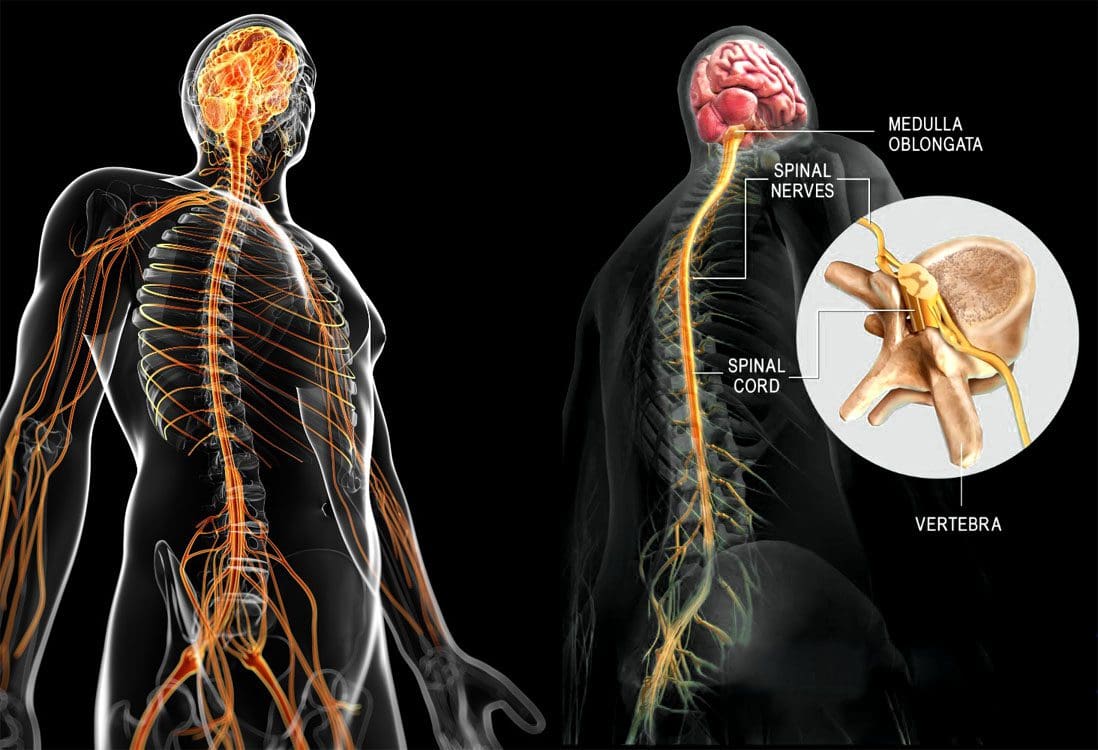
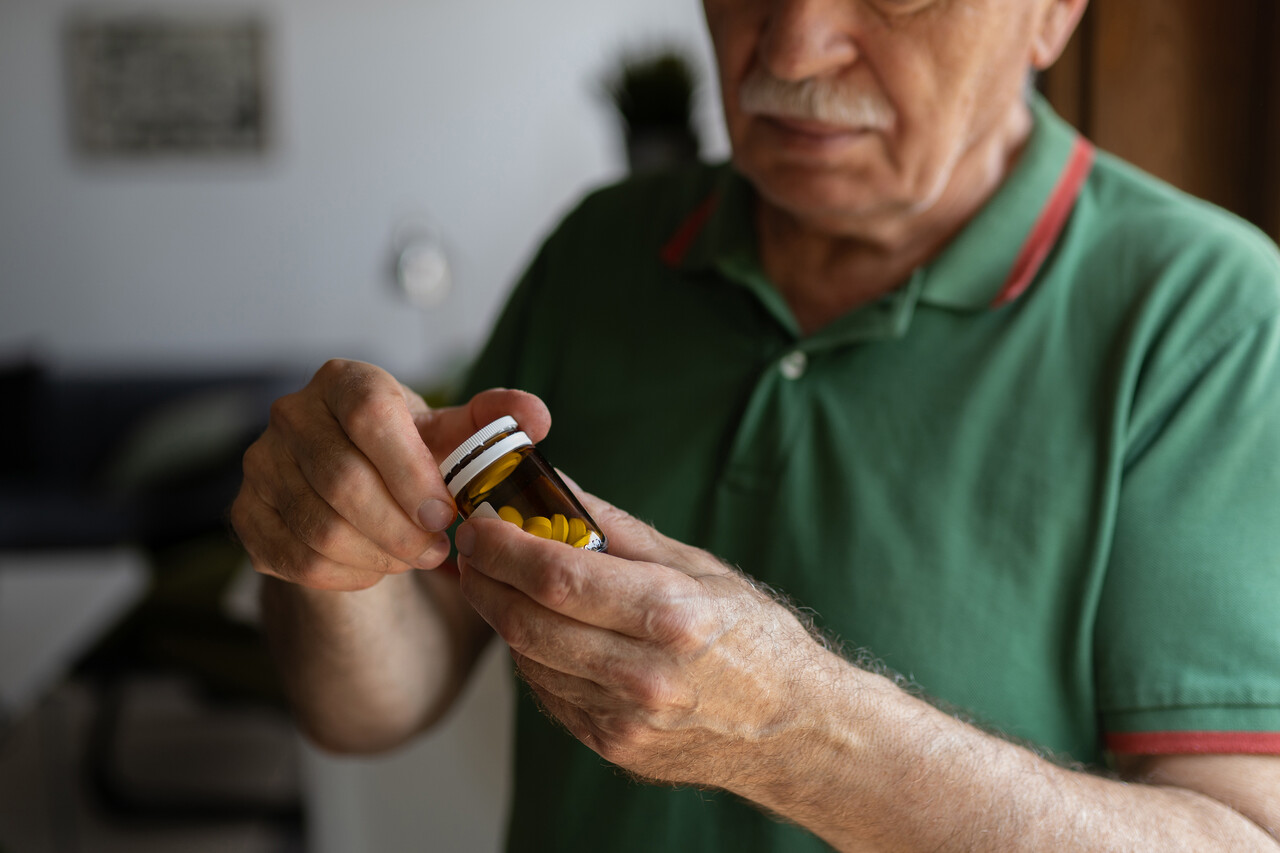
Gabapentin works best for patients with diabetic neuropathy or sciatica, which causes nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs. It can reduce pain signals to the nerves. Available Dosage Forms Gabapentin can be purchased in various forms, including pills, oral solutions, capsules, and extended-release tablets. Gabapentin for sciatica is considered alongside NSAIDs including naproxen or ibuprofen, corticosteroids and physical therapy to help in the pain management caused by this condition. To address the following questions keep reading this article: Does Gabapentin help with sciatica nerve pain? What is the Gabapentin dosage for sciatica nerve pain? Read on to learn more about which sciatic medications may help to alleviate nerve pain, including medications like Lyrica and gabapentin. Both gabapentin (GBP, Neurontin) and pregabalin (PGB, Lyrica) are used to treat chronic sciatica (CS). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an important pain-related neurotransmitter, although neither GBP nor PGB affect the GABA receptor. Sciatica pain is often a dull pain, but it also can be sharp and, at times, you may feel the pain travel or “shoot” down your leg. Symptoms of sciatica may include numbness, tingling or weakness along with the pain. Sciatica develops due to a change in one of the cartilage pads in your spine, called discs. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Gabapentin has been approved in the United States for the treatment of epilepsy and postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin has also demonstrated proven efficacy for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and trigeminal neuralgia, although these represent off-label uses of the drug. However, to Sciatica is a symptom rather than a specific diagnosis 4 and is used broadly to refer to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve. 5 The commonest cause of sciatica is impingement of lumbosacral nerve roots, as they emerge from the spinal canal, by a herniated intervertebral disc (fig 1). This SR aims to assess the effectiveness of pregabalin and gabapentin on pain and disability caused by acute sciatica and the adverse events associated with their clinical use. Systematic review. Electronic databases of Cochrane Central Register of Is Gabapentin Good For Sciatica Pain? Gabapentin has earlier shown potential in providing relief for chronic sciatica; however, recent studies indicate its ineffectiveness in reducing pain and disability associated with low back pain and sciatica. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. The pooled results of two trials of corticosteroids (mean difference in overall and leg pain −12.2, 95% confidence interval −20.9 to −3.4) and a single trial of the anticonvulsant gabapentin for chronic sciatica (mean difference in overall pain relief −26.6, −38.3 to −14.9) showed some benefits but only in the short term. Sciatica is a condition that causes pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back down each leg. The pain can be debilitating and impact daily activities, making it essential to find effective treatment options. One such option is the use of Gabapentin, a medication that has shown promise in providing relief for sciatica pain. In this article, we will explore the Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant medication that’s FDA-approved to treat nerve pain caused by shingles and certain types of seizures. It’s also used off-label for various conditions, such as nerve pain and sciatica. Sciatica is a condition characterized by nerve pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling along the sciatic nerve. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug originally intended for seizures. It’s most effective for treating neuropathic back pain caused by disk herniation and consequent sciatica, as well as spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin has not been directly compared with other medications or treatments for sciatica, and there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against other antiepileptic drugs for back pain with or without radiculopathy. Pressure on the sciatic nerve can cause pain and often numbness down a leg. Self-care measures might help. There is currently an absence of high-grade evidence regarding the treatment of chronic sciatica (CS). Whilst gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are both currently used to treat CS, equipoise exists regarding their individual use. In particular, While gabapentin is not a cure for sciatica, it can provide a 1-2 point average reduction in pain scores, allowing better mobility and function. Its favorable side effect profile, lack of drug interactions, and reduced risks of dependency make gabapentin a potentially useful part of a comprehensive sciatica treatment plan. Surgical diskectomy can be offered to patients with refractory sciatica, but there is only modest, short-term improvement in leg pain and disability scores. Epidural steroid injections may be
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |