Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
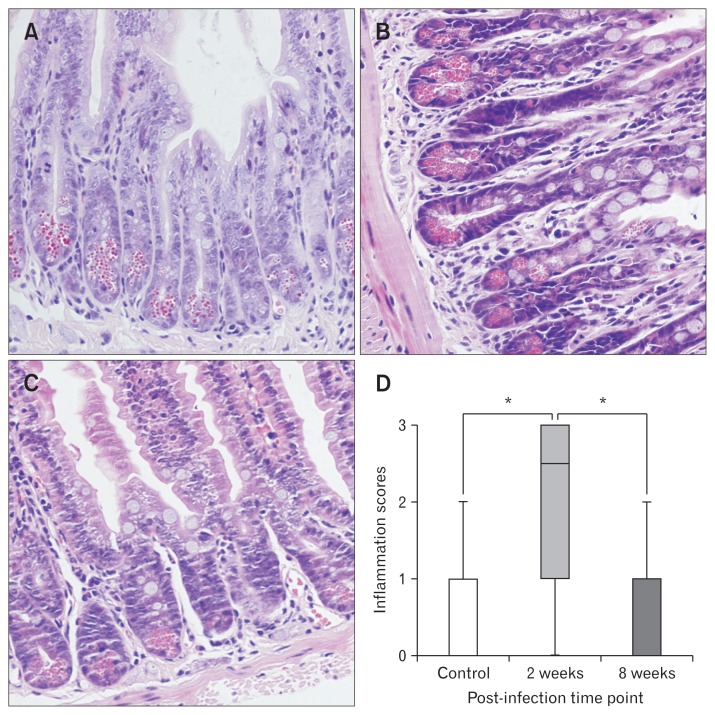
This study suggested a centrally acting mechanism for pregabalin for ameliorating or preventing visceral hypersensitivity. In molecular studies, gabapentin and pregabalin have been shown to inhibit the substance P mediated activation of transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NFκB) [Park et al. 2008]. Gabapentin for irritable bowel syndrome In conclusion, gabapentin presents a potentially valuable option for managing IBS-related pain, particularly in patients with prominent visceral hypersensitivity. So my plan to address hypersensitivity is as follows: Get on mast cell stabilizer (ketotifen reduces visceral sensitivity) Treat SIBO (currently on Rifaximin) Heal gut lining (eating low fodmap for six weeks w/ l-glutamine and other gut healing supplements after treatment) I also have been doing CBT for the last five years. Visceral Hypersensitivity: As we’ve discussed, visceral hypersensitivity can amplify the perception of pain in GERD patients. If a patient exhibits signs of heightened esophageal sensitivity, Gabapentin’s nerve-modulating effects could potentially help reduce their discomfort. Visceral hyperalgesia refers to increased pain sensation in response to gastrointestinal sensory stimulus. In neonates with neurological impairments, gabapentin has been successfully used as a treatment for visceral hyperalgesia in neonates. The authors describe a preterm infant with myelomeningocel Pregabalin or gabapentin may reduce visceral hypersensitivity. 63,84,85 Theoretically, in clinical practice these agents might also be helpful for abdominal wall pain, although no studies to assess this effect are available. The introduction of gabapentin, based on emerging evidence, played a crucial role in improving oral tolerance and addressing suspected visceral hyperalgesia. The patient's gradual recovery and eventual discharge with GJ-tube feeds highlight the utility of gabapentin in managing complex feeding disorders in neurologically intact patients. Visceral hyperalgesia causes increased sensitivity to pain in the internal organs. Learn about causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment in kids. Gabapentin was used for the treatment of term and preterm infants with suspected visceral hyperalgesia caused by a variety of neurologic and gastrointestinal morbidities. Improved feeding tolerance and decreased irritability were seen, as well as decreased usage of opioids and benzodiazepines. Adverse events occurred with abrupt discontinuation of this medication. What is visceral hypersensitivity syndrome? Visceral hypersensitivity refers to your experience of pain or discomfort in your visceral organs — the soft, internal organs that live in your chest, abdomen and pelvic cavity. If you have visceral hypersensitivity, your threshold for pain in these organs is lower than normal. Background: Gabapentin has been shown to reduce elements of central sensitization in human experimental hyperalgesia. It remains uninvestigated whether gab-apentin has beneficial effects for irritable bowel syn-drome associated with visceral hypersensitivity. These data demonstrate that gabapentin effectively inhibits acetic acid-induced nociception, and the antinociceptive effect of gabapentin correlates with the suppression of noxious-evoked release of excitatory amino acids in the spinal cord. GABAPENTIN is a novel, well-tolerated, anticonvulsant drug structurally related to γ-aminobutyric acid. In this case, we highlight the utility of a gabapentin trial in an otherwise healthy patient. This case underscores the complexities of managing severe feeding disorders in infants, particularly the role of gabapentin in addressing suspected visceral hyperalgesia and failure to thrive in a patient without previous neurological or cardiac surgery. Inflammatory bowel disease causes visceral hypersensitivity, intestinal stenosis, anorectal urgency, fistula, and abscess. One-third to half of individuals with inflammatory bowel will have disabling visceral symptoms such as pain or colic or symptoms that resemble the irritable bowel syndrome [4, 5]. Gastroenterologists at Massachusetts General Hospital have begun prescribing low-dose gabapentin for patients with functional dyspepsia because it is thought to be capable of relieving visceral pain. Gabapentin was used for the treatment of term and preterm infants with suspected visceral hyperalgesia caused by a variety of neurologic and gastrointestinal morbidities. Improved feeding tolerance and decreased irritability were seen, as well as Background: Gabapentin has an established role in the treatment of neuropathic pain, with evidence supporting a benefit in visceral hypersensitivity. There is currently no data on the use of gabapentin for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Visceral hyperalgesia refers to increased pain sensation in response to gastrointestinal sensory stimulus. In neonates with neurological impairments, gabapentin has been successfully used as a treatment for visceral hyperalgesia in neonates. The It remains uninvestigated whether gabapentin has beneficial effects for irritable bowel syndrome associated with visceral hypersensitivity. Aims : To evaluate the effects of gabapentin on sensory and motor function of the rectum in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Gabapentin has been successfully used as a treatment for visceral hyperalgesia in neonates with gastrointestinal and neurological comorbidities.2-6This is the 17th case to describe a neonate, preterm (n 1⁄4 11) or term (n 1⁄4 5), with neuropathic pain treated with gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |