Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
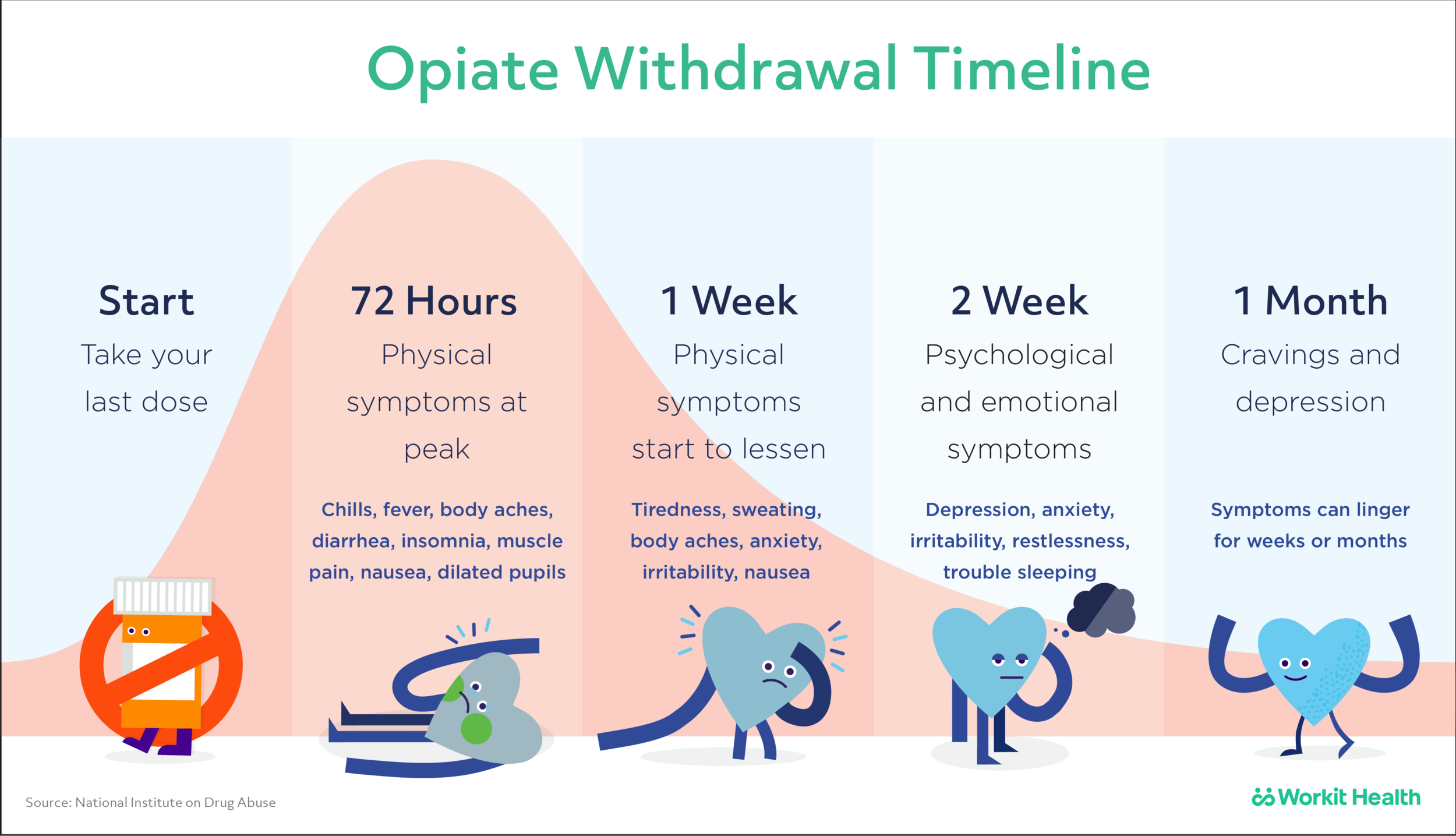
Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms occur when the body adjusts to the absence of the medication after stopping or reducing the dose. These symptoms can include anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and physical discomfort. In contrast, side effects are unintended reactions to gabapentin, such as dizziness, drowsiness, or difficulty concentrating. Tapering off gabapentin involves gradually reducing your dose by 10-20% every one to two weeks, allowing your body to adjust and minimizing uncomfortable symptoms. Even in cases of high doses, such as 1800 mg and above—where the worst withdrawal symptoms are more likely—a carefully planned gabapentin taper chart can make the process manageable. What is Gabapentin Withdrawal? Withdrawal occurs when someone dependent on gabapentin abruptly stops or significantly reduces their dose. Since gabapentin interacts with the nervous system, discontinuing use can cause various physical and emotional symptoms. How Common is Withdrawal with Gabapentin? Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers. Key Takeaways Gabapentin is used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain but requires careful medical supervision due to potential misuse and side effects. Gradual tapering off Gabapentin is necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Withdrawal symptoms can vary in onset and duration, typically peaking around the third day after the last dose. A standard The risks of withdrawal are higher if you’re taking high doses or have been on gabapentin for longer than 6 weeks. Withdrawal symptoms can start from 12 hours to 7 days after stopping the Gabapentin withdrawal isn’t always easy. Here is everything you need to know about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, your timeline, and how to get help. A comprehensive guide to safely stopping gabapentin, managing withdrawal symptoms, and addressing withdrawal-induced depression. Seek professional help throughout the process. Gabapentin Withdrawal Timeline The withdrawal timeline of gabapentin can depend on a number of factors. Factors that may influence the withdrawal timeline of gabapentin include: Dosage Duration of use Current medication Psychiatric conditions You should talk with your healthcare provider about the potential of withdrawal and to make a plan to safely go off of your medication. How Long Does it Does gabapentin cause withdrawal? Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, when they occur, and what can help. How can I avoid gabapentin withdrawal? The best way to avoid gabapentin withdrawal is to only take the dose prescribed by your doctor, for the shortest time possible. When it comes time to stop it, talk to your healthcare provider about a tapering schedule. Do not misuse substances or alcohol while you are taking gabapentin. What is gabapentin used for? Gabapentin is a prescription medication Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentin, marketed under brand names like Neurontin, is a medication widely indicated to manage nerve pain, seizures, and mental health conditions. While it can offer relief and improve quality of life, prolonged or high-dose use of the medication can provoke physical dependence. When someone who is dependent moderates or discontinues use, they experience gabapentin withdrawal. This guide to When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Gabapentin gabapentin 1200mg three times daily is included below. If the patient is taking a lower dose than 1200mg TDS then start the process further down the table and follow the suggested tapering guidance. Gabepentin for Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms - An epilepsy and nerve pain medication, studies show Gabapentin for Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms is very effective. Neurontin (Gabapentin) Tapering Recommendations Potential gabapentin withdrawal symptoms include: Anxiety Insomnia Nausea Sweating Pain Agitation Palpitations GI symptoms Flu-like symptoms The above symptoms are simply potential side effects. If they do occur, they are often mild and transient, typically resolving on their own within a few days. Why Gabapentin Must Be Carefully Weaned Off The cessation of Gabapentin requires a carefully managed tapering process to prevent withdrawal symptoms and potential health risks. Tapering refers to the gradual reduction of dosage, allowing the body to adjust to lower levels of the medication without triggering adverse reactions. How To Stop Gabapentin Withdrawal In our latest question and answer, we discuss how to safely stop taking gabapentin, by slowly lowering your dose to prevent withdrawal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |