Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
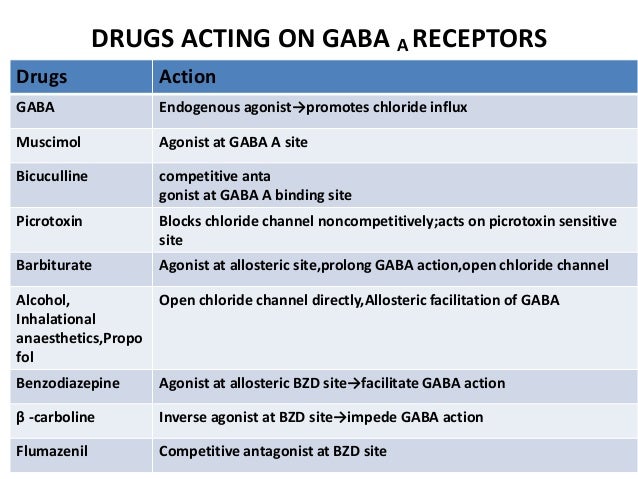
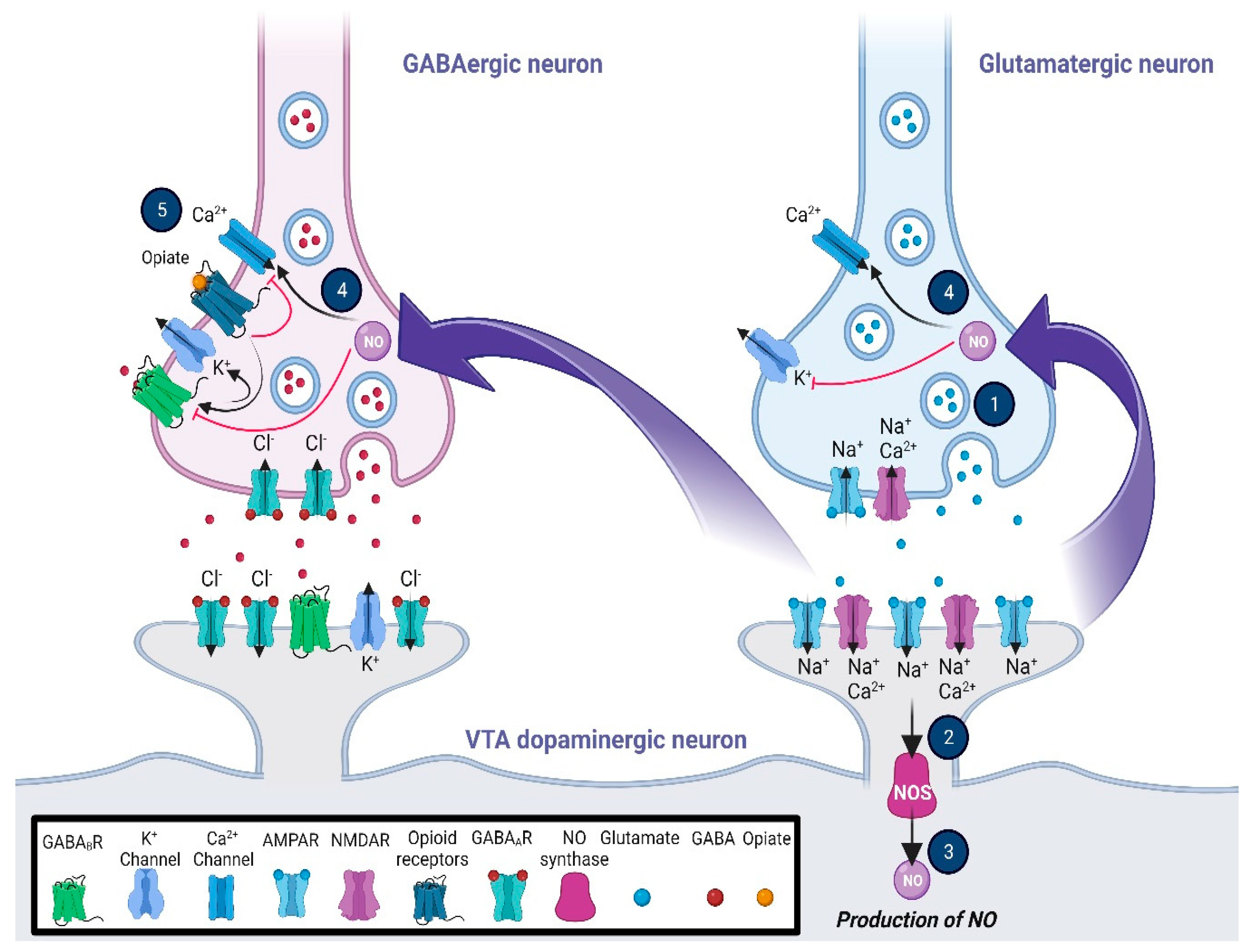
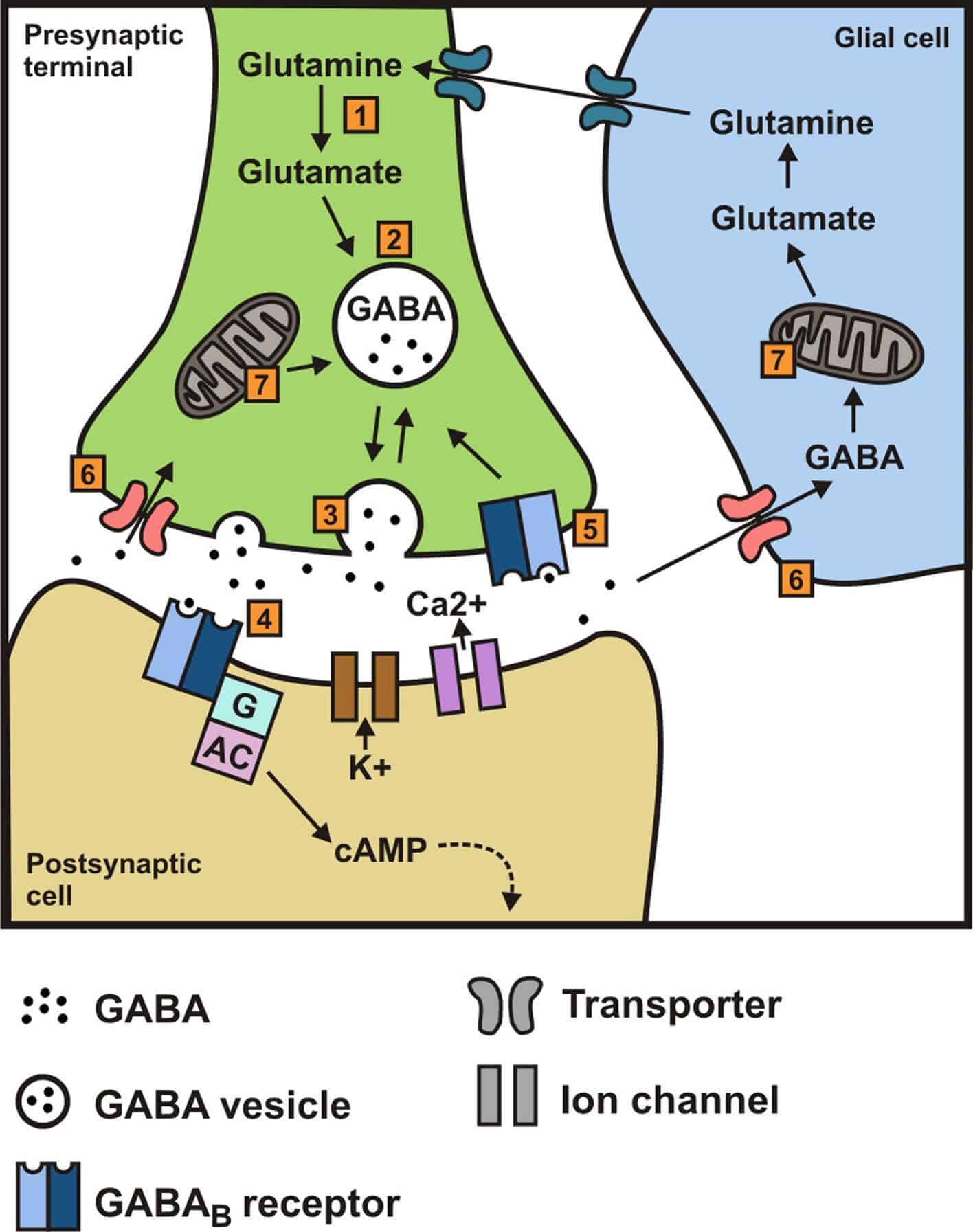
Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. In contrast, the antinociceptive properties of gabapentin were observed in both genotypes. Levels of GABA A receptor What brain chemicals does gabapentin affect? Gabapentin increases the concentration and probably the rate of synthesis of GABA in brain, which may enhance non-vesicular GABA release during seizures. 3. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to a novel binding site in brain tissues that is associated with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it modulates the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as glutamate, to reduce nerve excitability and alleviate pain or seizures. Gabapentin (3-cyclohexyl-GABA) is designed as a lipophilic analogue of GABA for blood-brain barrier penetration and closely resembles pregabalin. Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions 2. Gabapentin increases the concentration and probably the rate of synthesis of GABA in brain, which may enhance non-vesicular GABA release during seizures. 3. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to a novel binding site in brain tissues that is associated with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca 2+ channels. In conclusion, the mechanism of gabapentin is multifaceted, involving its interaction with VGCCs, modulation of GABA synthesis and release, and potential effects on other neurotransmitter systems and receptors. These actions collectively help reduce neuronal excitability and relieve symptoms associated with neuropathic pain and partial seizures. Introduction Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug and one of the most widely prescribed medications for neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial seizures. Originally developed as a GABA analog, it surprisingly does not act directly on GABA receptors. Instead, it binds to voltage-gated calcium channels, altering neurotransmitter release. It is also used off-label for conditions like Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from neuronal tissues in vitro. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Generic name : Gabapentin Brand names: Neurontin® Gralise® (gabapentin extended release) Horizant® (gabapentin enacarbil) Therapeutic class: Anti-epileptic, Anticonvulsant Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid, Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue FDA Approved: December 30, 1993 Chemical Formula: C9H17NO2 Pregnancy Category: C Habit forming? No Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) is an extended release tablet used to treat restless legs syndrome and for the pain from having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older Warnings Gabapentin enacarbil extended-release tablets: Initially, 600 mg once daily in the morning for 3 days, then increase to recommended maintenance dosage of 600 mg twice daily. Dosages >1.2 g daily provide no additional benefit and are associated with an increased incidence of adverse effects. via HealthDay FRIDAY, July 11, 2025 — A drug used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. Regular gabapentin use appeared to increase risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by 85%, researchers reported July 10 in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. What’s more, the risk was Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse Gabapentin Extended-Release Tablets What is this medication? GABAPENTIN (GA ba pen tin) treats nerve pain. It works by calming overactive nerves in your body. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, primarily responsible for inhibiting nerve transmission, which helps to reduce neuronal excitability. In contrast, gabapentin is a medication designed to mimic the effects of GABA, used primarily to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Understanding the differences between these two can help in making informed Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |