Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
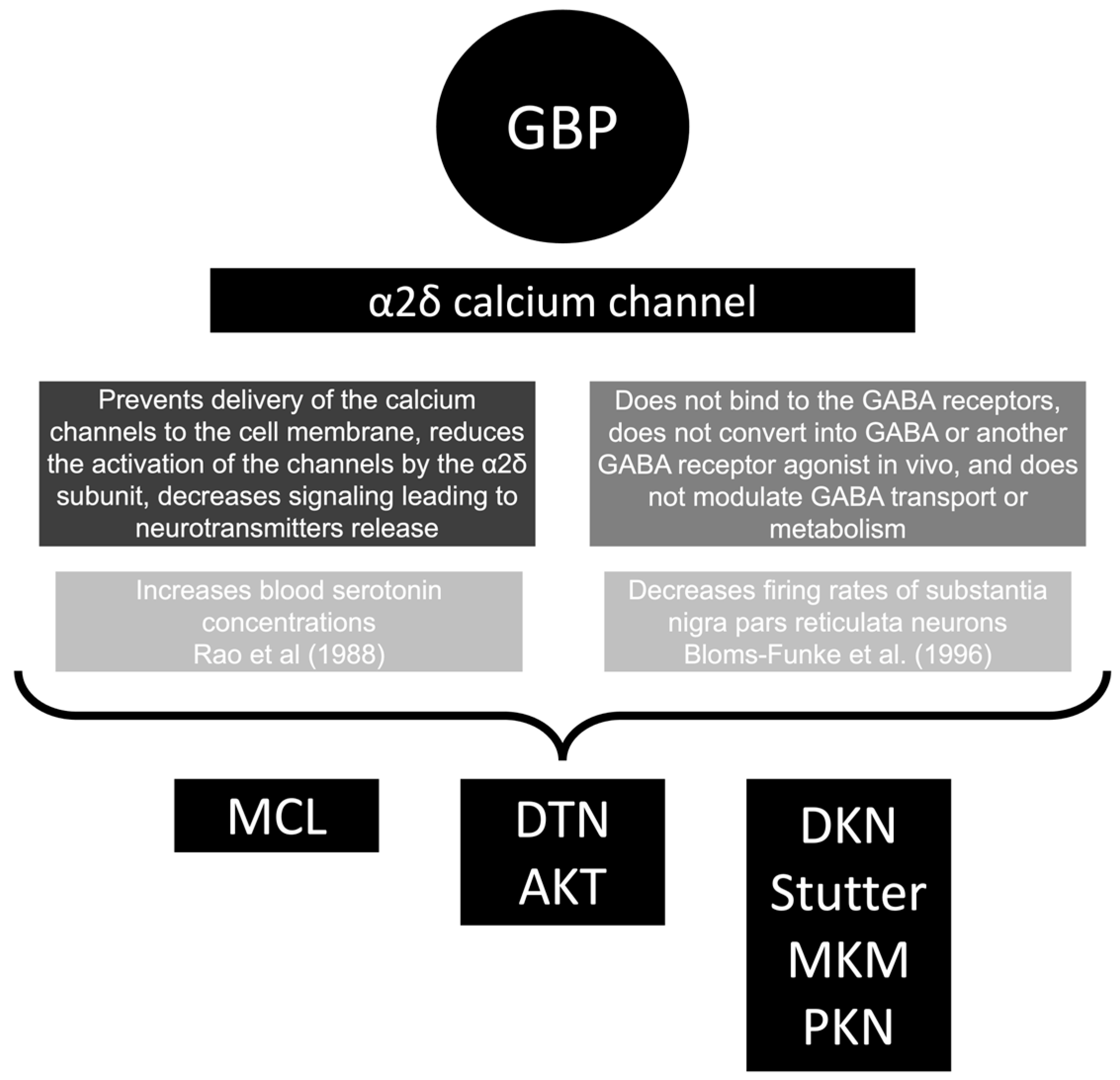
Gabapentin is a prescription medication primarily used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain. It works by altering electrical activity in the brain and nerves. While gabapentin can be an effective treatment option for many, it does come with potential side effects like any medication. One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is its impact on the gastrointestinal (GI) system and bowels. As I have GI issues, it is hard for me to tell if any symptoms are from the Gabapentin decrease! Also, I have developed neuropathy and numb big toes still being tested for and Dictirs admit they usually prescribe Gabapentin for this! Key Points Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat certain types of seizures and nerve pain, but it has some common side effects. People taking gabapentin most often experience dizziness, drowsiness, and swelling of the legs and feet. Constipation can occur with gabapentin, but it’s relatively rare. Other GI symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, are more likely. Key findings This retrospective, open-label study evaluated the efficacy of low-dose gabapentin in 62 adults with functional dyspepsia and normal gastric emptying Gabapentin resulted in significant improvements in dyspeptic symptoms as measured by change in total score and most subscale scores on the Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders–Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM) The Chronic abdominal pain is a common gastrointestinal (GI) symptom that characterizes many functional GI disorders/disorders of gut-brain interaction, including irritable bowel syndrome, functional dyspepsia, and centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome. The symptoms of abdominal pain in these highly prevalent disorders are often treated with antispasmodic agents. Antispasmodic treatment Dyspepsia is one of the most common gastrointestinal (GI) problems and is more prevalent in adults. Environmental hypersensitivity and anxiety and depression are among the factors that can cause this disease. In this regard, gabapentin as a Conclusion: Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). Keywords: Functional dyspepsia; gabapentin; gastrointestinal disorders. Gastrointestinal Issues Related to High Gabapentin Doses High doses of gabapentin can lead to various gastrointestinal complaints. Nausea, vomiting, and constipation These symptoms can be troubling and often occur in about 25% of patients taking high doses. Managing these effects often requires additional medications, complicating treatment. I have gastroparesis and taking Gabapentin how long does it take to get used to symptoms especially fatigue? Do you eventually adjust? Gastrointestinal issues are less frequently reported but can occur. Some patients experience nausea or vomiting when taking Gabapentin, raising concerns about its potential link to gastritis. In a retrospective, open-label cohort of patients treated with gabapentin for functional dyspepsia, there were significant improvements in dyspeptic symptoms interpreted within the limitations of an open-label study design. Further studies are needed to place gabapentin in the functional dyspepsia t Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and seizures. While it's effective for these conditions, many users report various side effects, including changes in bowel habits. One of the most common questions surrounding gabapentin is whether it makes users poop more frequently. Understanding the connection between gabapentin and gastrointestinal health is crucial for Being aware of the potential gastrointestinal side effects of gabapentin, such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, can help individuals taking this medication take proactive steps to manage these symptoms. If you experience persistent or severe gastrointestinal issues while on gabapentin, it is recommended to consult your healthcare provider for guidance on proper management Understanding the physical side effects of gabapentin, such as weight changes, swelling or edema, gastrointestinal issues, dizziness, and fatigue, is crucial for individuals who are prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that is also used for post-herpetic neuralgia and neuropathic pain. Recently, gabapentin showed anti-inflammatory effect. Nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) is a regulator of the inflammatory process, and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) is an important receptor involved in NFκB regulation. The aim of the present work was to study Table of Contents Gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication used to treat conditions like nerve pain and seizures. With over 64 million prescriptions written each year in the United States, many people have experienced gabapentin side effects. Whether you’re wondering, “does gabapentin make you sleepy?” or concerned about weight gain and coordination problems, understanding what is Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. For patients with existing liver issues or those taking multiple medications metabolized by the liver, consulting a healthcare provider about potential interactions is essential. Effects on the Gastrointestinal Tract Gastrointestinal side effects are common among gabapentin users.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |