Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
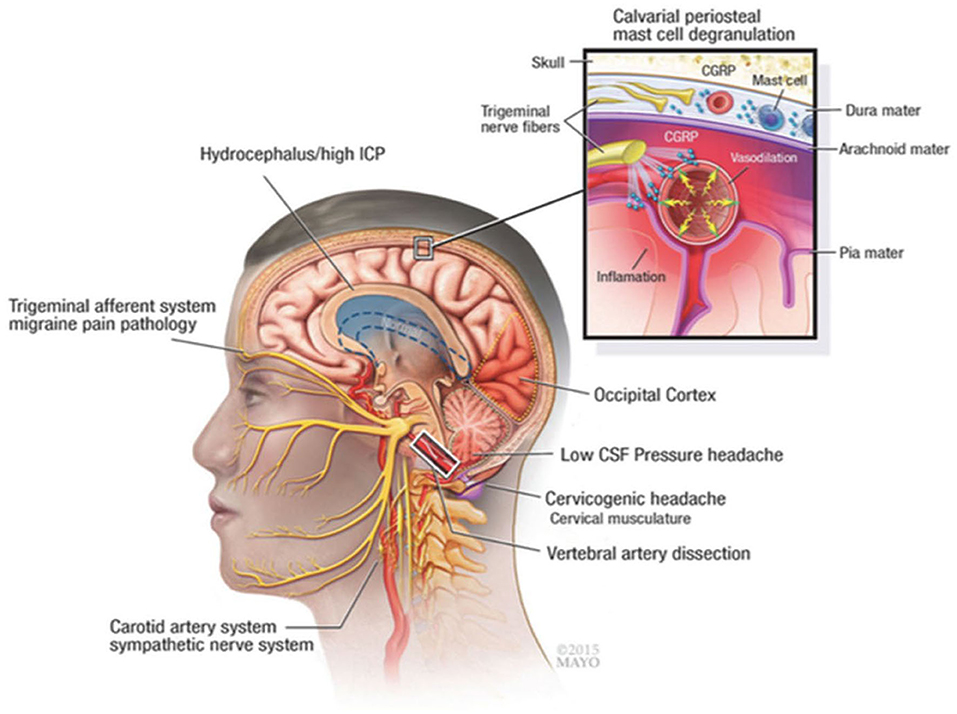
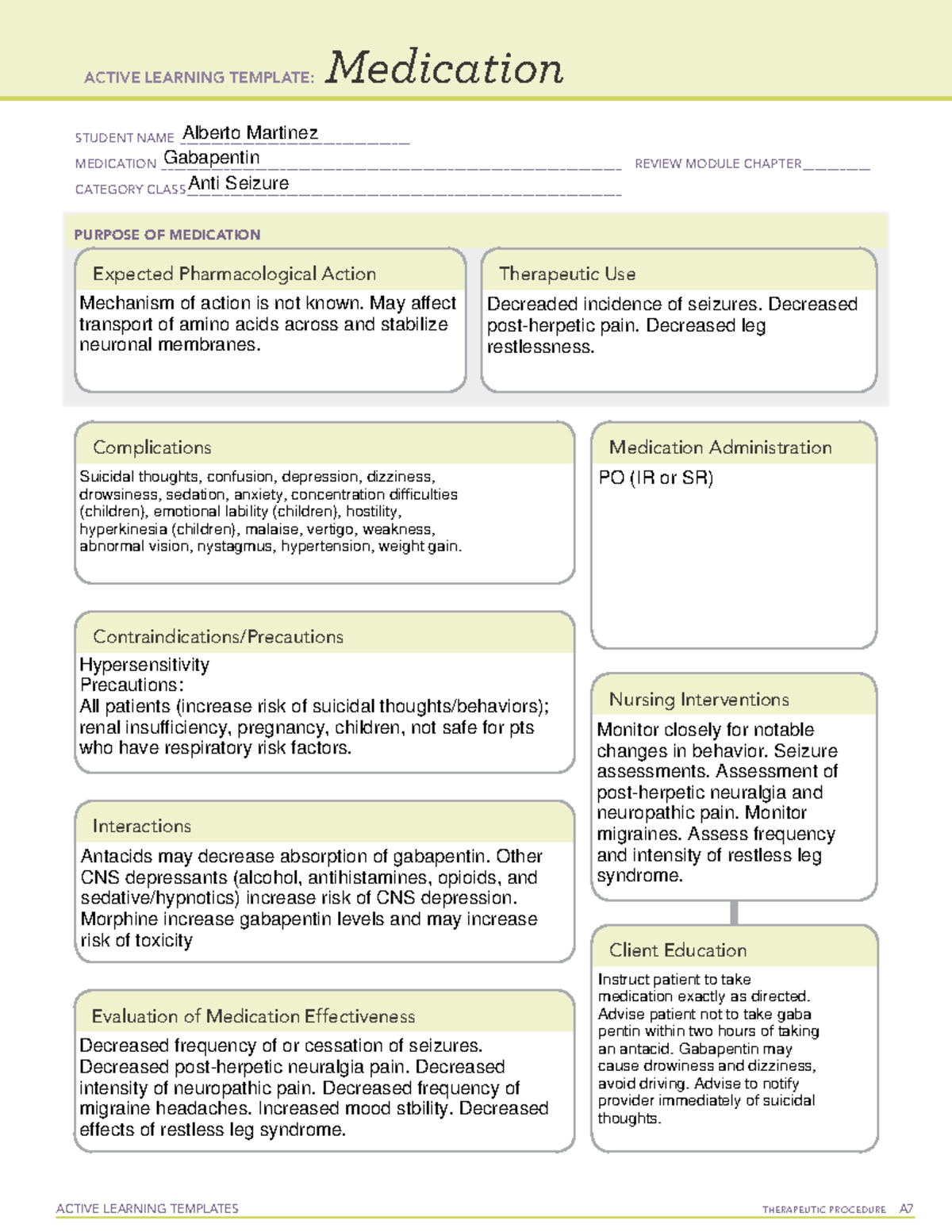
Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Chronic daily headache is defined as the presence of a headache on 15 days or more per month for at least three months. The most common types of chronic daily headache are chronic migraines and Understanding the relationship between gabapentin and migraines involves delving into how the medication works, its side effects, and anecdotal evidence from users. The primary concern is whether gabapentin can trigger migraines or exacerbate headache disorders in susceptible individuals. What Is Gabapentin? A 2016 study showed evidence that gabapentin benefits headache syndromes, but it still wasn’t recommended as a primary therapy. If you’re experiencing migraine attacks or your current Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. (Strength of Recommendation: B, based on inconsistent or limited-quality patient Gabapentin is one such drug. It's an anti-seizure drug sometimes used to prevent migraines, though there is conflicting scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness in this regard. We offer a panoramic view of nociception, from a central perspective, and discuss various pharmacological options available to treat headache and neck pain. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. Gabapentin is used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type nerve pain that can occur due to an outbreak of shingles, and restless legs syndrome (RLS), an uncomfortable urge to move your legs around, often at night. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Tension-type, migraine, and cluster headaches are the most common primary headaches. Primary headaches are differentiated by clinical criteria from the International Classification of Headache Gabapentin is a medication that may help prevent or treat some types of headaches, including migraine, cluster, and chronic daily headaches. Learn about the evidence, dosage, mechanism, and references for gabapentin in headache management. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |