Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
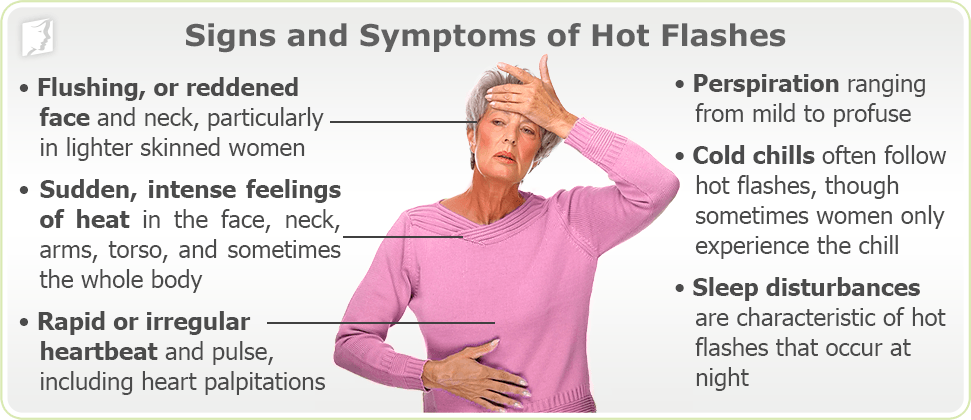 |  |
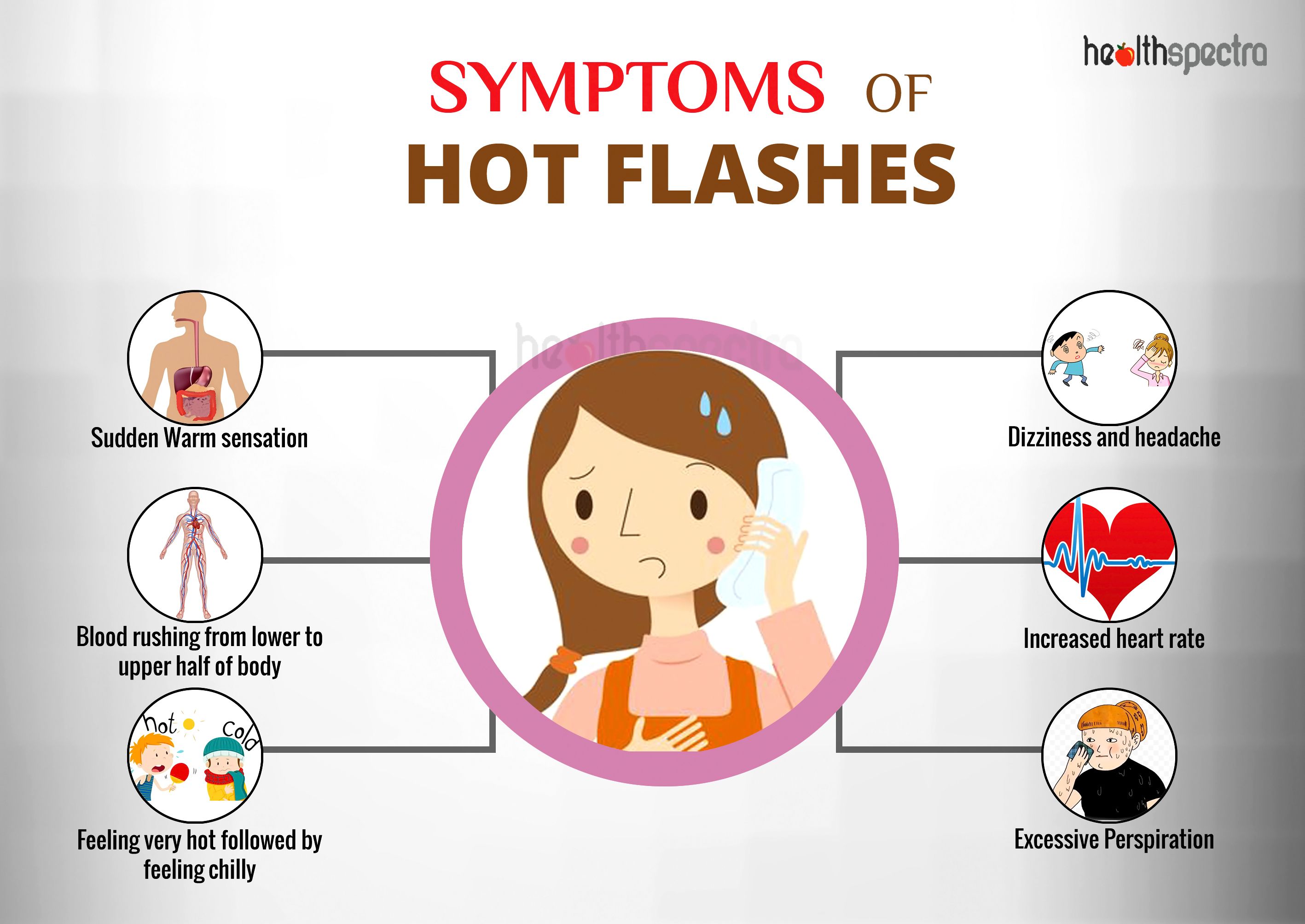
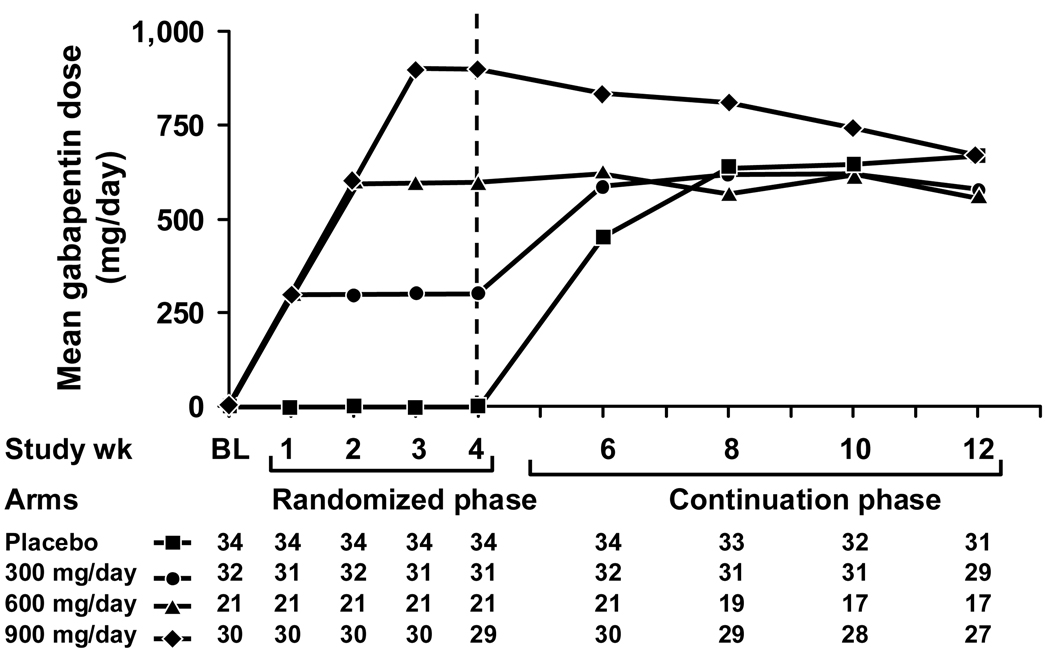
Side effects include belly pain, diarrhea, trouble sleeping, back pain, hot flashes and higher liver enzymes, which can be a sign of liver damage. Most healthcare professionals don't prescribe this medicine to people with liver disease. Medications that cause hot flashes: Learn about common drugs that may trigger hot flashes and how to manage this side effect effectively. Gabapentin, traditionally used for nerve pain, has emerged as a promising option for managing menopausal symptoms. Gabapentin belongs to a class of medications called anticonvulsants. While initially developed to treat epilepsy, research has shown promising results in managing various menopausal symptoms, particularly hot flashes and night sweats. There is more on how to manage hot flashes, including other prescription drugs that are sometimes used for this purpose, in our Guide to Menopause. It makes sense to know about the potential side effects of any medication and how easy or difficult it may be to discontinue before starting it. Various non-hormonal agents have been used for the treatment of hot flashes in women with menopause. Some studies have reported that gabapentin appears to be an effective and well-tolerated treatment modality. The aim of this study was to evaluate Gabapentin is a GABA analogue used in the treatment of epilepsy, neurogenic pain, restless-leg syndrome, essential tremor, bipolar disorder, and migraine prophylaxis; it was first reported for its effects on hot flashes in five women and one man. 19 A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled trial has shown that gabapentin is effective in Hot flashes are a common and often distressing symptom experienced by many women during menopause. These sudden feelings of warmth, usually accompanied by sweating and discomfort, can disrupt daily life and sleep patterns. While hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has long been a go-to treatment for managing hot flashes, not all women can or want to use hormones due to potential side effects or There may be different gabapentin side effects in women than in men. Learn why dizziness, tiredness, and other side effects may occur and how to prevent them. Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve (neuropathic) pain. It is also a non-hormonal medicine that has been shown to be effective in reducing menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin appears to be comparable with low dose oestrogen in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flushes.3 What is the usual dosage? Discover if gabapentin can help alleviate hot flashes. Learn about its effectiveness, potential benefits, and side effects for menopausal symptom relief. Several studies have shown that gabapentin (Neurontin) at 600-2400 mg/day in divided doses is effective for treating hot flashes in menopausal women. Research presented at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) indicates that an investigational extended release (ER) formulation of gabapentin (Serada, Depomed) is effective for the treatment of hot flashes and sleep Discover how gabapentin helps reduce hot flashes. Learn about its effectiveness, dosage, and whether it's the right choice for managing symptoms. In rare cases, gabapentin can have more severe side effects, such as swelling of the extremities and increased suicide risk. It may also cause sexual dysfunction, which is already common among postmenopausal women. On the whole, gabapentin is a perfectly safe, non-hormonal intervention for reducing hot flash frequency. Gabapentin, a medication widely prescribed for various conditions, has garnered attention for its potential side effects. Among these, hot flashes have emerged as a point of concern for many. Understanding the relationship between gabapentin and hot flashes is essential for anyone considering or currently using this medication. hot flashes, which are sudden feelings of heat and sweating that can happen in women after menopause and in those being treated for breast cancer mood disorders such as anxiety alcohol addiction. How gabapentin works In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Gabapentin for Hot Flashes: Learn how this medication can help manage menopausal symptoms, including efficacy, dosage, and side effects. The most pertinent side effects of gabapentin to consider before initiation include dizziness or coordination difficulties (thus, possible increase in fall risk), edema, drowsiness, lethargy, weight gain, nausea, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Side effects can include drowsiness, dizziness, and water retention. In conclusion, gabapentin is a non-hormonal treatment that may be prescribed for women who need to or want to avoid MHT or who prefer alternatives to hormonal therapy. It is generally used to control epilepsy, chronic nerve pain, and reduce menopausal hot flushes.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |