Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
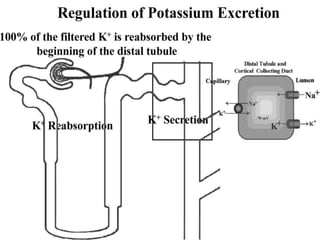 | 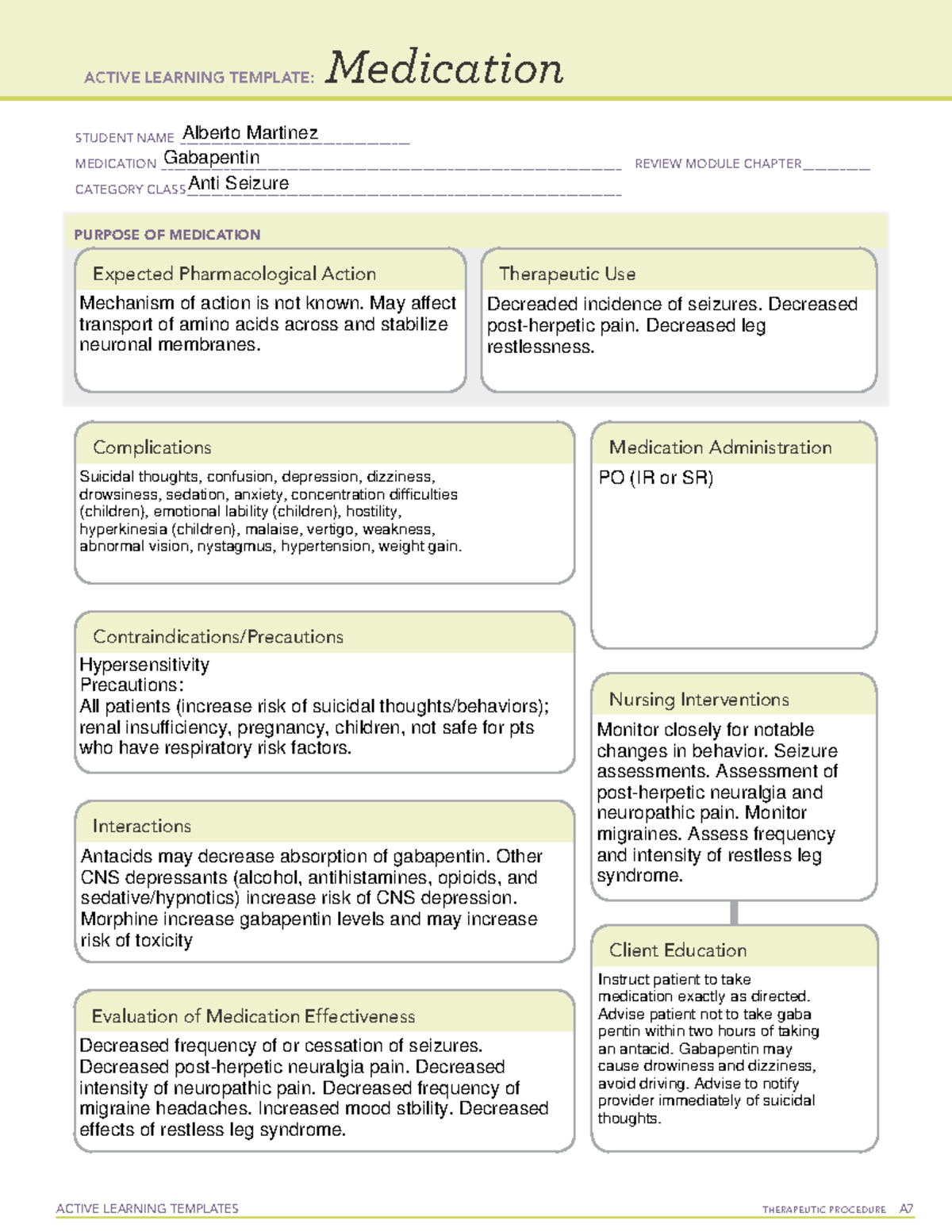 |
Hypokalaemia is one of the most commonly encountered fluid and electrolyte abnormalities in clinical medicine. It can be an asymptomatic finding, identified only on routine electrolyte screening, or it can be associated with symptoms ranging from mild weakness to sudden death. 1. Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, is a commonly used drug in the treatment of partial epilepsy and peripheral neuropathic pain. Although the exact mechanism of action has not been elucidated, the binding site has been identified as the alpha 2 -delta subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channels in the neocortex and Gabapentin, a newer antiepileptic drug commonly used in cancer and palliative medicine for neuropathic pain management, produces a blockade of neural calcium channels and increases release of GABA, which might modulate diaphragmatic excitability. Gabapentin has no known serious drug interactions and is not hepatically metabolized. Gabapentin withdrawal has been reported infrequently, suggesting there may be predisposing conditions for a withdrawal syndrome. AB and an older adult in a previous case report experienced withdrawal despite gabapentin taper. Premorbid psychiatric illness may be a risk factor for gabapentin withdrawal. Result of checking the interaction of drug Gabapentin and disease Hypokalemia/hypomagnesemia for contraindications and side effects when used together. Some medications may cause your blood level of potassium to decrease, which is known as hypokalemia. The following drugs may cause low potassium: Diuretics, such as: Medications to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or other breathing problems: Other drugs that may decrease potassium include: Unlike hypokalemia, hyponatremia is dose-independent [68]. Hypertensive old women are particularly at risk of hyponatremia; the major risk factors for TIH are old age, female gender, low body mass, hypokalemia, and concurrent use of other medications that impair free water excretion [69]. Here, we report that gabapentin is a potent activator of the heteromeric KCNQ2/3 voltage-gated potassium channel, the primary molecular correlate of the neuronal M-current, and also homomeric KCNQ3 and KCNQ5 channels. Hypokalemia is a common electrolyte disturbance not given as much attention as hyperkalemia. Hypokalemia has associations with cardiac disease, renal failure, malnutrition, and shock. Additional risk factors, such as hypothermia and increased blood cell production, contribute to this condition's complexity. Purpose: Gabapentin is an analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), but its complete mechanism is not well understood. Common adverse effects from gabapentin include somnolence, sedation, and dizziness. Hyperglycemia is listed as a possible adverse drug reaction in the labeling. Case reports describe hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes, peritoneal dialysis, and/or incomplete medication Editor's note: A previous version of this article incorrectly listed hyperkalemic periodic paralysis in Burmese cats as a differential diagnosis. This has been corrected as of February 2020. Following are differential diagnoses, listed in order of likelihood, for patients presented with hypokalemia. Drug interactions are reported among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) and Potassium (potassium). Common drug interactions include arthralgia among females and fatigue among males. The phase IV clinical study analyzes what interactions people have when they take Gabapentin and Potassium. The gabapentinoids are often recommended as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. The differing pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic prof Hypokalemia is a common serum electrolyte abnormality affecting both young and old cats. Causes include dietary deficiency, chronic renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, and just about any condition involving metabolic alkalosis. Rare causes include aldosteronoma or other reasons for hyperaldosteronism. The most common clinical signs, as shown in the accompanying large photograph, are Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Of the severe potassium disturbances, 32.3 % were drug-induced, and 23 % were lethal. We identified previously undescribed pharmacological causes of hyperkalemia (risedronate, doxazosin) and hypokalemia (acyclovir, teicoplanin, cefepime, meropenem, dexketoprofen colistimethate). Kidneys play a pivotal role in maintaining the acid-base balance of body along with lungs, and they do so by reabsorbing filtered bicarbonate and removing excess hydrogen ions. Renal disorders due to the removal of HCO3 or acid handling in the presence of relatively preserved GFR are collectively referred to as renal tubular acidosis. It is a non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Medications cause hypokalemia through a variety of mechanisms, including intracellular potassium shifting, increased renal loss, and/or stool loss. Table 2 highlights selected medications associated with hypokalemia. Some published cases have reported an association between antidepressant use and the risk for hypokalemia. Hypokalemia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Lasix, and have Depression. The use of antineoplastic drugs has a central role in treatment of patients affected by cancer but is often associated with numerous electrolyte derangements which, in many cases, could represent life-threatening conditions. In fact, while several anti-cancer agents can interfere with kidney
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |