Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | %3B+open+bars%2C+placebo%3B+colored+bars%2C+therapies%3B+length+of+bars%2C+ranges+in+studies%3B+horizontal+bar%2C+means.+All+of+these+agents+are+generally+well+tolerated+(226).+Hypersensitivity+or+prior+adverse+drug+reactions+to+each+of+these+agents+represent+contraindications.+For+the+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+prior+neuroleptic+syndrome%2C+serotonin+syndrome%2C+and+concurrent+use+of+monoamine+oxidase+inhibitors+are+also+contraindications.+SSRI/SNRIs+should+be+used+with+caution+in+patients+with+bipolar+disease%2C+uncontrolled+seizures%2C+hepatic+or+renal+insufficiency%2C+uncontrolled+hyponatremia%2C+concurrent+use+of+other+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+or+poorly+controlled+hypertension.+These+agents+uncommonly+induce+suicidal+thoughts+within+the+first+few+months+of+treatment.+Preliminary+evidence+suggests+a+possible+increase+in+risk+of+bone+fracture.+Gabapentin+and+pregabalin+may+increase+suicidal+thoughts+and+behaviors%2C+cause+drowsiness+or+dizziness%2C+and+impair+balance+and+coordination.+Pregabalin+may+impair+memory+and+concentration.+Clonidine+is+contraindicated+in+patients+with+low+blood+pressure+and+may+cause+lightheadedness%2C+hypotension%2C+headache%2C+and+constipation%3B+sudden+cessation+of+treatment+can+be+associated+with+significant+increments+in+blood+pressure+(63)..jpg) |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
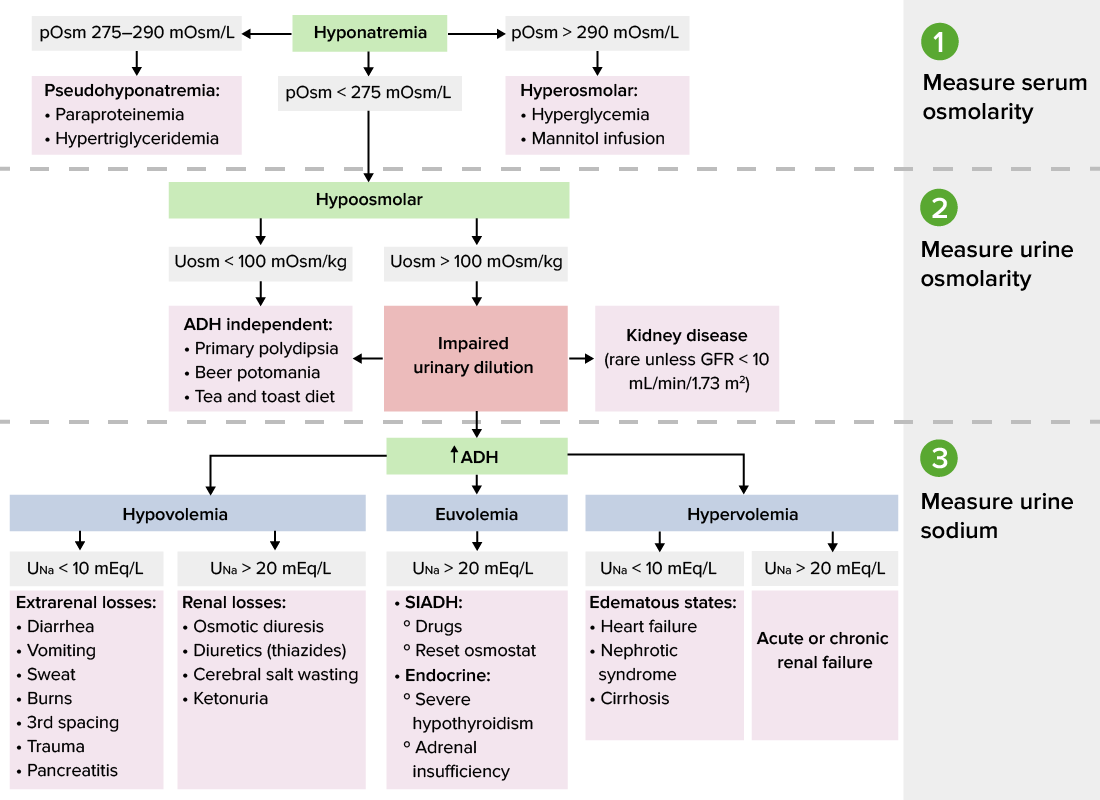
Gabapentin Hyponatremia Risk & Management Tips Understanding Gabapentin: Uses and Applications Gabapentin Hyponatremia Risk & Management Tips Gabapentin is a drug that doctors often prescribe. It has many uses and plays a big role in treating health issues. It’s mainly an anticonvulsant, but it helps with more than just seizures. Hyponatremia (defined as a serum sodium level < 134 mmol/L) is a common electrolyte disturbance in clinical practice that is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. 1,2 Drugs are a common cause of electrolyte abnormalities, and a careful drug history is essential in patients with electrolyte abnormalities. One of the more common electrolyte abnormalities that may be drug induced Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the anticonvulsants most commonly reported to be associated with hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy, although other anticonvulsants, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and gabapentin, have also been reported to cause hyponatremia [56]. In patients experiencing clinically significant hyponatremia, i.e. symptomatic hyponatremia leading to hospitalization, after recent initiation of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, valproate or levetiracetam, an alternative treatment could be lamotrigine or gabapentin. The objective of this article is to summarize current literature regarding gabapentin-induced hyponatremia, discuss possible pathophysiologic mechanisms, and consider clinical implications based on current epidemiological and pharmacological research. In the case described above, peripheral edema secondary to hyponatremia was first thought to be the potential cause prior to gabapentin identification by the resident pharmacist. Abstract Purpose: Hyponatremia induced by antiepileptic drugs is common, but detailed evidence is lacking. This can be problematic for the treating neurologist confronted with a patient with severe hyponatremia in need of an alternative drug. The objective of this study was to examine the association between individual antiepileptic drugs and hospitalization due to hyponatremia. Expert opinion: Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the most common AEDs which induce hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy. Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. In acute symptomatic hyponatremia, hypertonic saline solution (3%) is commonly used to acutely increase serum sodium levels and prevent severe neurologic symptoms (eg, seizures). Hypovolemic hyponatremia is treated with adequate fluid resuscitation to decrease the stimulus for ADH secretion. The corresponding association for phenytoin and valproate was moderate. The risk for hyponatremia was lower during ongoing treatment. Lamotrigine and gabapentin had the lowest risk both during initiation and ongoing treatment and may be advantageous in patients at risk of developing hyponatremia. In the excellent review of drug-induced hyponatremia, Liamis et al1 gave clinical information about the incidence of hyponatremia associated with specific drug treatment and discussed the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. To evaluate the risk factors and prevalence of hyponatremia among epilepsy patients in relation to use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).We retrospectivel Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the anticonvulsants most commonly reported to be associated with hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy, although other anticonvulsants, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and gabapentin, have also been reported to cause hyponatremia [56]. Studies have shown a potential association between gabapentin use and an increased risk of developing hyponatremia. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, it is believed that gabapentin may affect the regulation of sodium levels in the body. In this review, we will discuss common ASMs associated with hyponatremia, the mechanism of action of various ASMs, clinical symptoms, the presentation of hyponatremia, and treatment strategies for hyponatremia in patients using ASMs. Learn how gabapentin can lower sodium levels and cause hyponatremia, a serious condition that affects electrolyte balance. Find out the symptoms, causes, treatments, and precautions for gabapentin users and hyponatremia. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is the most common cause of euvolemic hyponatremia, and many medications have been associated with SIADH. Pregabalin is a drug used for the treatment of neuropathic pain, though Patients on gabapentin should be monitored for symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headache, confusion, nausea, weakness, and in severe cases, seizures or coma. The risk of hyponatremia appears to be higher during the first few weeks of treatment with gabapentin. Hyponatremia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Ondansetron, and have Stress and anxiety.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | %3B+open+bars%2C+placebo%3B+colored+bars%2C+therapies%3B+length+of+bars%2C+ranges+in+studies%3B+horizontal+bar%2C+means.+All+of+these+agents+are+generally+well+tolerated+(226).+Hypersensitivity+or+prior+adverse+drug+reactions+to+each+of+these+agents+represent+contraindications.+For+the+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+prior+neuroleptic+syndrome%2C+serotonin+syndrome%2C+and+concurrent+use+of+monoamine+oxidase+inhibitors+are+also+contraindications.+SSRI/SNRIs+should+be+used+with+caution+in+patients+with+bipolar+disease%2C+uncontrolled+seizures%2C+hepatic+or+renal+insufficiency%2C+uncontrolled+hyponatremia%2C+concurrent+use+of+other+SSRI/SNRIs%2C+or+poorly+controlled+hypertension.+These+agents+uncommonly+induce+suicidal+thoughts+within+the+first+few+months+of+treatment.+Preliminary+evidence+suggests+a+possible+increase+in+risk+of+bone+fracture.+Gabapentin+and+pregabalin+may+increase+suicidal+thoughts+and+behaviors%2C+cause+drowsiness+or+dizziness%2C+and+impair+balance+and+coordination.+Pregabalin+may+impair+memory+and+concentration.+Clonidine+is+contraindicated+in+patients+with+low+blood+pressure+and+may+cause+lightheadedness%2C+hypotension%2C+headache%2C+and+constipation%3B+sudden+cessation+of+treatment+can+be+associated+with+significant+increments+in+blood+pressure+(63)..jpg) |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |