Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
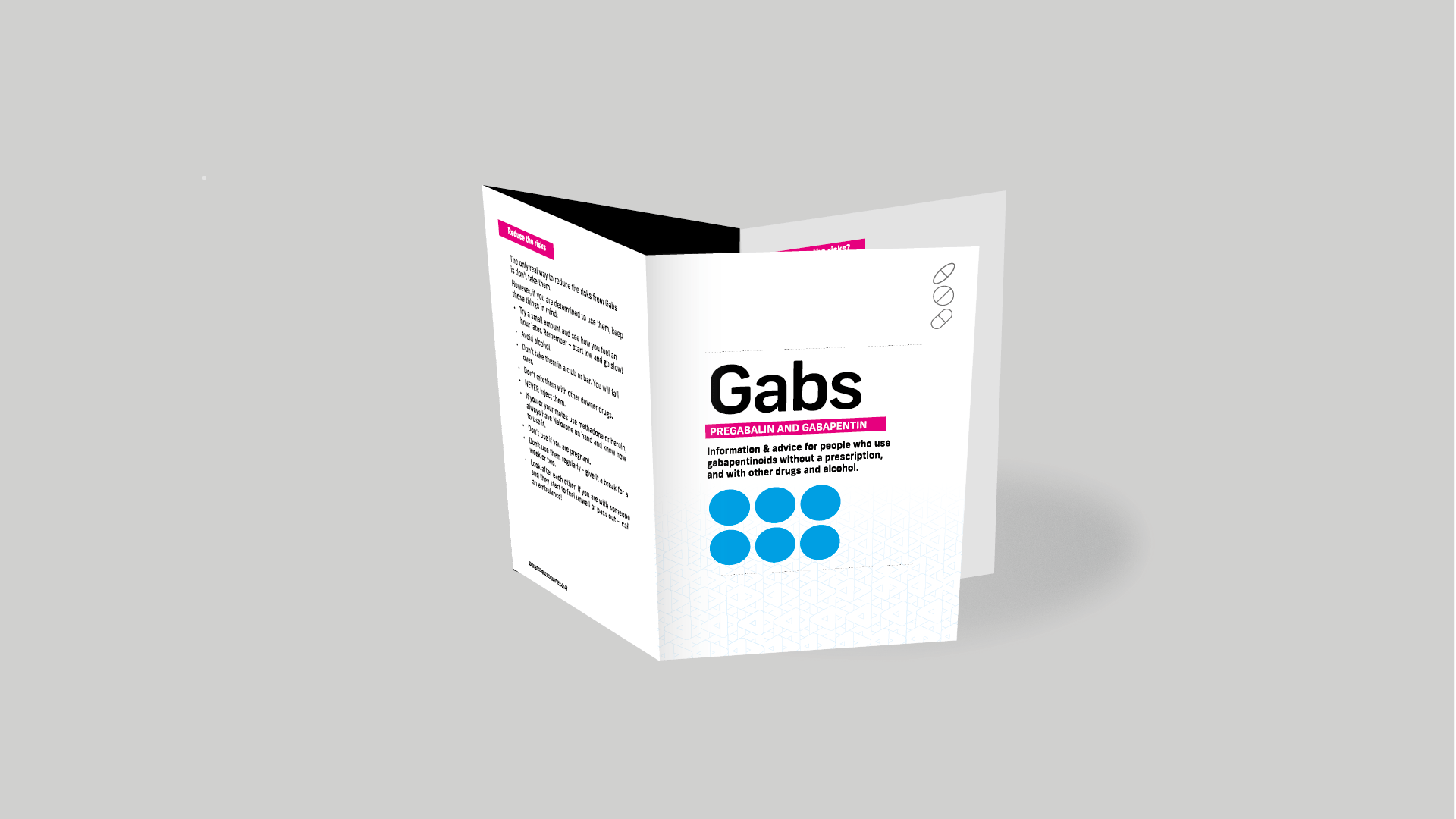 |  |
Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Licit Uses: According to the FDA-approved product label, gabapentin is used clinically for the management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults and as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Gabapentin tablets are indicated for: • Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy Where pregabalin and gabapentin are being prescribed outside their licensed indication for indications other than neuropathic pain, review the need to continue treatment. Unlicensed uses of gabapentin include use as a first line option for treatment of oscillopsia and second line antispasmodic medication (NICE NG220 Guidance for Multiple sclerosis in adults: management (June 2022). Both Pregabalin and Gabapentin were reclassified as Schedule 3 controlled drugs due to concerns of potential for abuse and dependence: Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Figure 1 Stacked bar chart illustrating the dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin categorized as therapeutic and sub-therapeutic. Table 4 presents the distribution of gabapentinoid prescriptions across FDA-approved indications, BNF indications for neuropathic pain, and off-label uses without documented neuropathic symptoms. In the UK, gabapentin and pregabalin are licensed for epilepsy and neuropathic pain, and pregabalin also for generalised anxiety disorder 7. They have been recommended as first-line treatments for neuropathic pain since 2013, although evidence of efficacy is based largely on trials in post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy 8, 9. Uses Warnings Before taking Dosage Side effects Interactions FAQ What is gabapentin? Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Before taking gabapentin, tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to gabapentin, any other medications, or any of the inactive ingredients in the type of gabapentin you plan to take. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the inactive ingredients. you should know that gabapentin is available in different forms that may be prescribed for different uses. Ask your doctor to be sure that Clinical indications for gabapentin and pregabalin The drugs are licensed in the UK for treating focal seizures and managing neuropathic pain; pregabalin is licensed for treating generalised anxiety disorder. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States (US) first licensed gabapentin (GBP) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures. In 2000, GBP was approved for treatment of partial seizures in children aged 3 years or older. The UK government reclassified gabapentin and pregabalin as ‘controlled drugs’ from April 2019. This study aimed to describe the trends in gabapentinoid prescribing before and immediately after reclassification, in the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink, an electronic primary care health record broadly representative of the UK. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are approved treatments for focal seizures and neuropathic pain, and were licensed in the UK in 1993 and 2004, respectively. Gabapentin is also licenced for the treatment of migraine in adults, while pregabalin is approved for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Recent data in the UK and elsewhere indicate that gabapentinoid Gabapentin and pregabalin should usually be prescribed for their licensed indications (epilepsy and neuropathic pain), and generalised anxiety disorder (only pregabalin). Prescription writing, dispensing and storage requirements for Schedule 3 and Schedule 4 Part 1 drugs
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |