Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 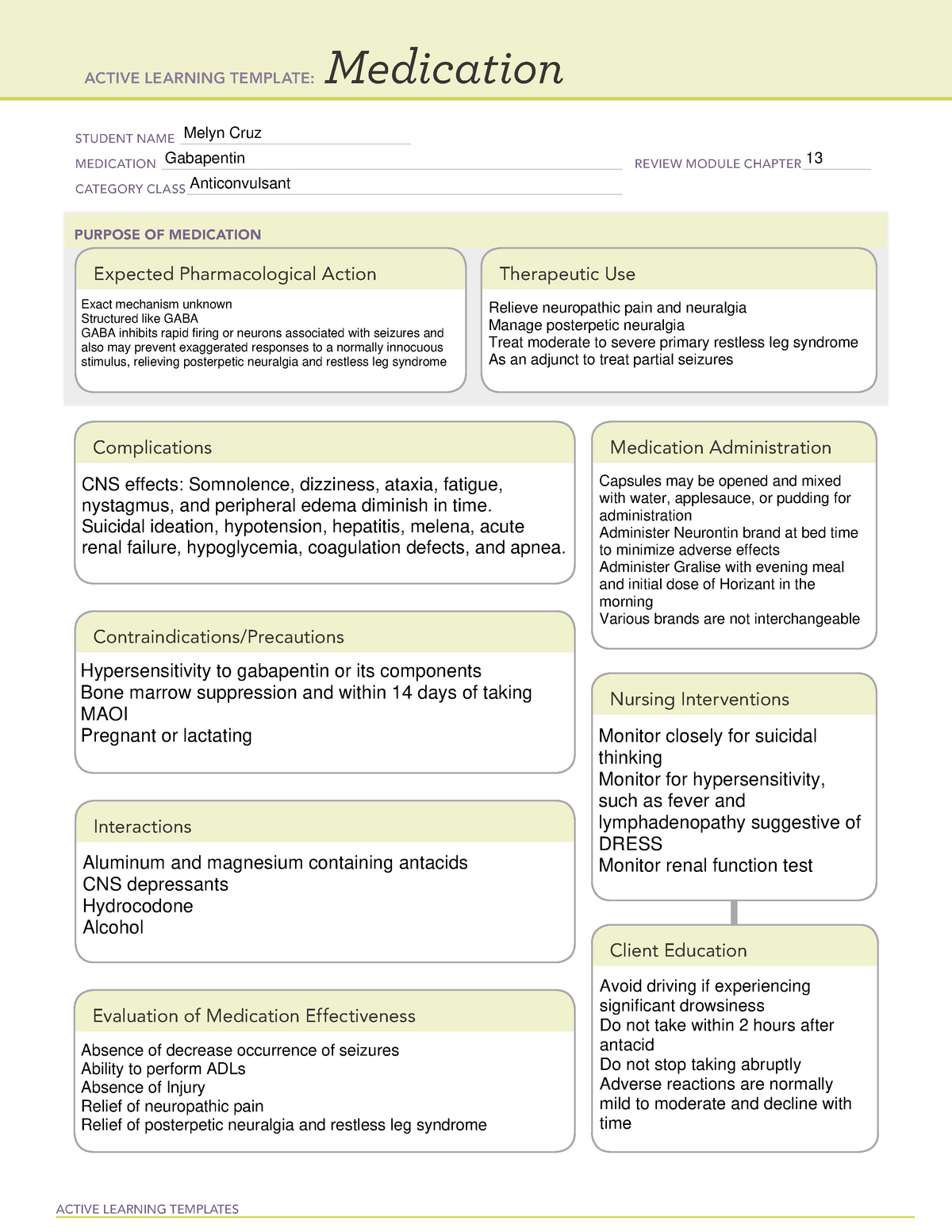 |
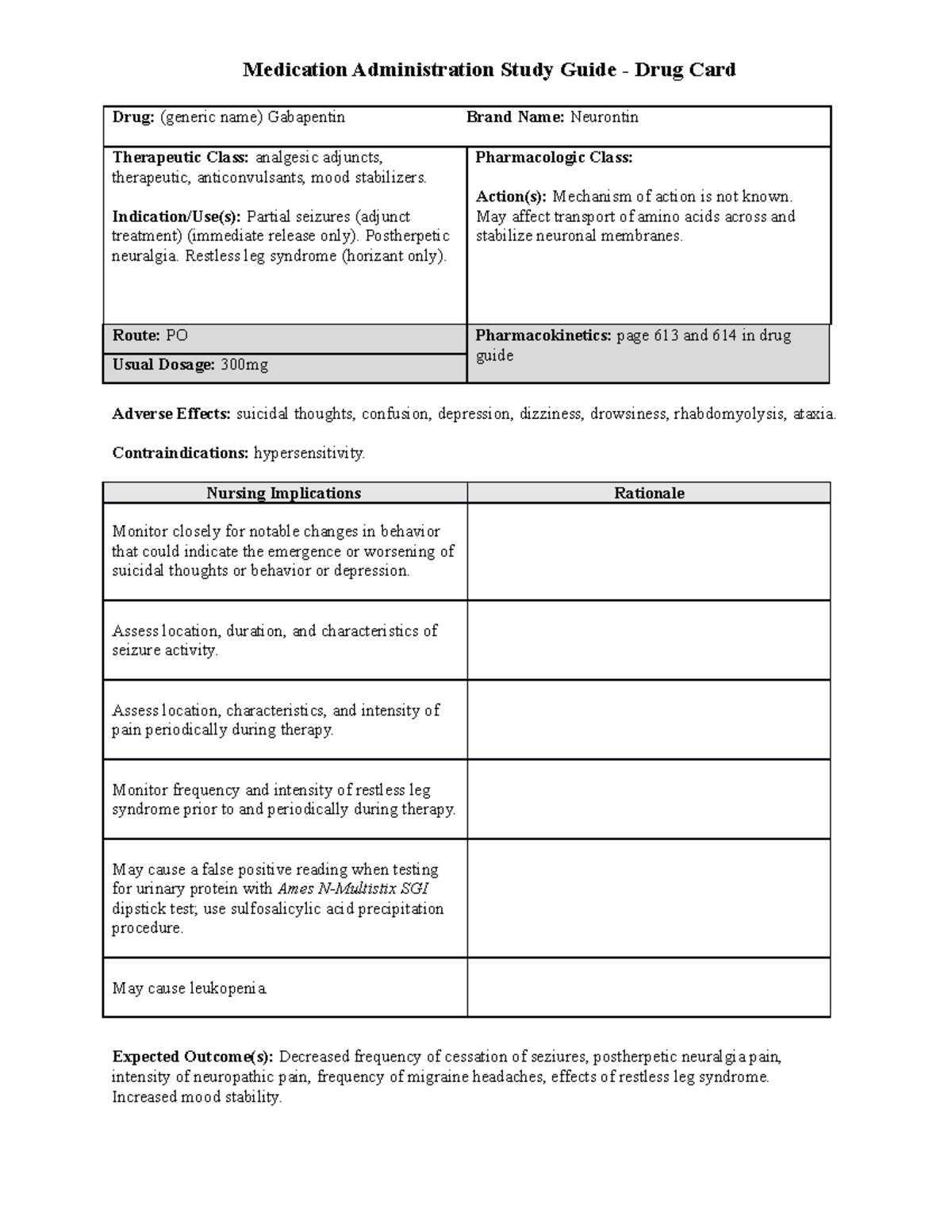
This is not an all-inclusive list of possible drug interactions, adverse effects, precautions, nursing considerations, or patient instructions. Please consult further with a pharmacist for complete information. Gabarone package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. If you are taking gabapentin to treat seizures and you suddenly stop taking the medication, you may experience seizures more often. Check with your medical doctor or dentist before taking any of the above while you or your child are using gabapentin. This medicine may cause respiratory depression, a serious breathing problem that can be life-threatening, when used together with narcotic pain medicines. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Intervention Medication administration: Neurontin is administered orally as capsules, tablets, or oral solution. It is usually taken in three divided doses daily, and may be taken with or without food. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Coadministration of NEURONTIN (125 to 500 mg; N=48) decreases hydrocodone (10 mg; N=50) Cmax and AUC values in a dose-dependent manner relative to administration of hydrocodone alone; Cmax and AUC values are 3% to 4% lower, respectively, after administration of 125 mg NEURONTIN and 21% to 22% lower, respectively, after administration of 500 mg Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. When prescribing gabapentin carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and observe them for signs and symptoms of gabapentin misuse or abuse (e.g., development of tolerance, self-dose escalation, and drug-seeking behavior). Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes 2.5 Administration Information Administer gabapentin orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with water. Inform patients that, should they divide the scored 600 mg or 800 mg gabapentin tablet in order to administer a half-tablet, they should take the unused half-tablet as the next dose. Half-tablets not used within 28 days of dividing the scored tablet should Background Gabapentin is a safe and well-tolerated anticonvulsant with a wide therapeutic index, and it is used for neuropathic pain. The aim of this study was to compare previous dosing methods with the administration of four different doses of gabapentin while maintaining the same maximum daily dose for the safe administration of high doses of the medication. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more In these instances, the useofalternative routes can be quite beneficial. Both nutrition and medication administration can be improved or maintained through the appropriate use of enteral alternatives such as gastrostomy tubes (GT), nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy buttons(G-Buttons; GB), jejunostomy tubes (JT), and nasojejunal tubes (NJ). Gabapentin capsules are contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |