Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 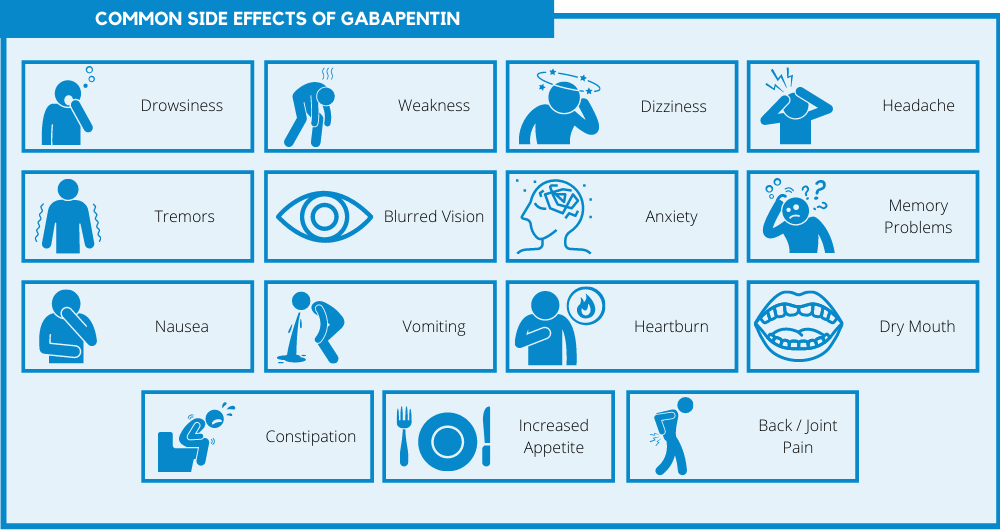 |
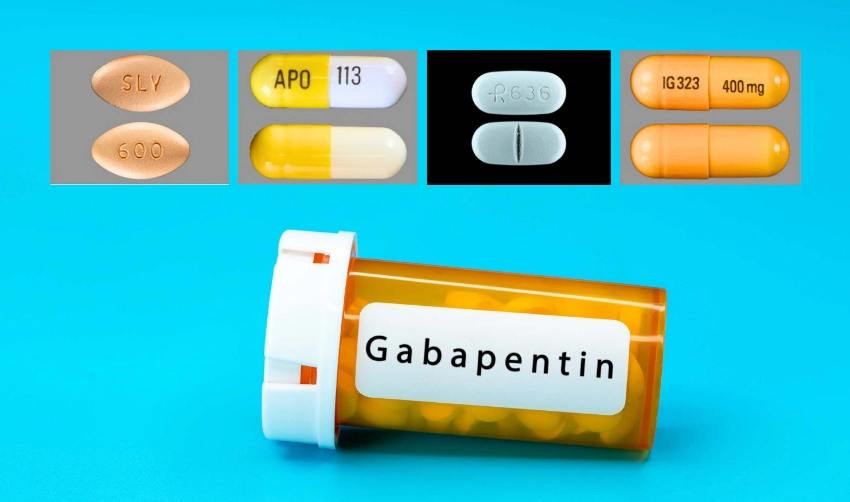
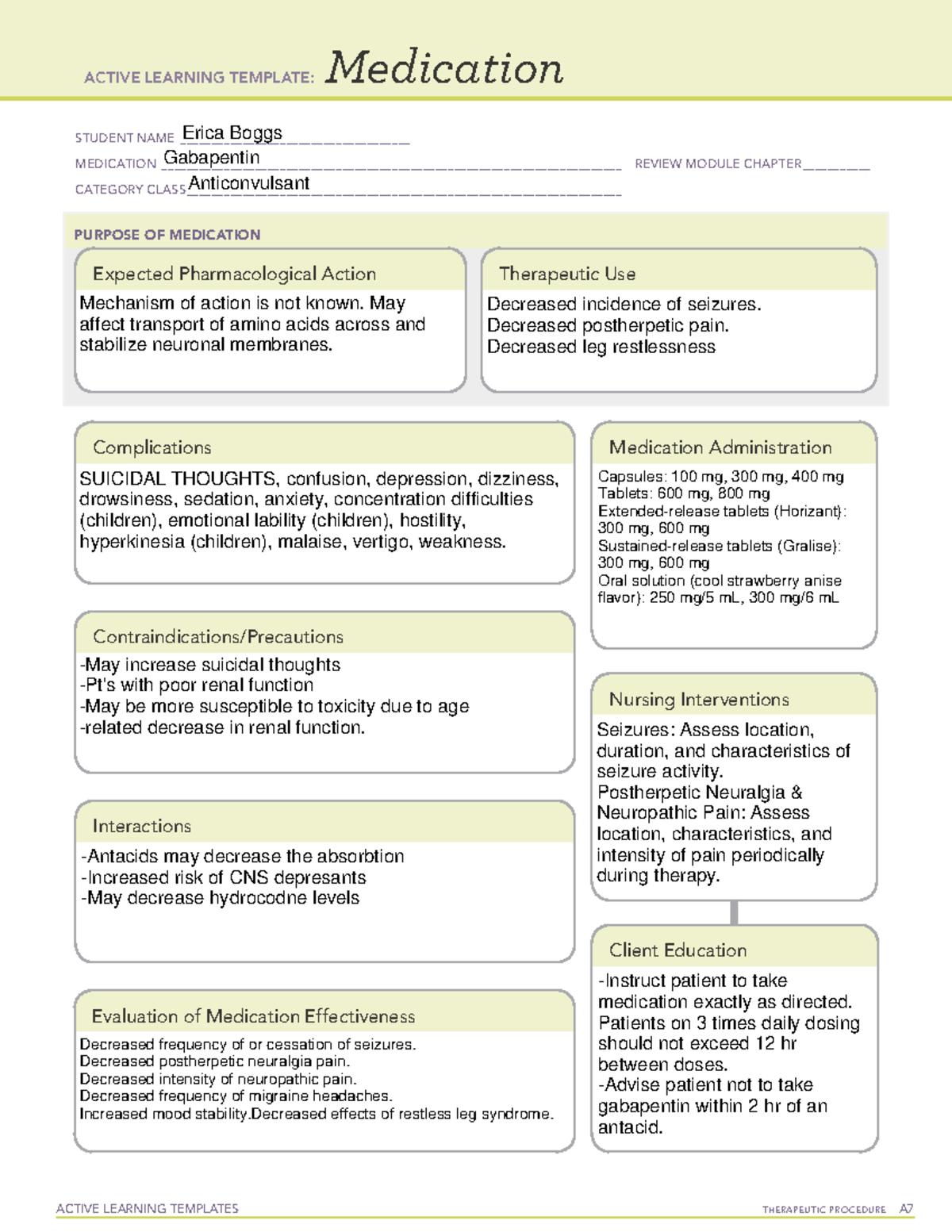
Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Gabapentin FAQs: Experts answer common questions about taking gabapentin, from if you should take it with food to what to do if you miss your dose. Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor, even if you experience side effects such as unusual changes in behavior or mood. If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. A study published in 2015 showed evidence for gabapentin use in treating alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Gabapentin works by changing neurotransmitters in the brain and is utilized in treating nerve pain and convulsions. The gabapentin (horizant brand) is also effective in treatment of restless leg syndrome. Common side effects of gabapentin includes: headache, dizziness and drowsiness. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Document the number, duration, and severity of seizures to help determine if this drug is effective in reducing seizure activity. Monitor drowsiness, anxiety, confusion, and other changes in mood or behavior (hostility, emotional lability, concentration difficulties). Repeated or excessive symptoms may require change in dose or medication. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX national database of de-identified patient records from 2004 to 2024 Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug currently licensed to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain but has been used off-label to treat acute postoperative pain. The GAP study will compare the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and safety of gabapentin as Gabapentin can interact with other medications, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or reducing the effectiveness of either drug. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Gabapentin works by changing neurotransmitters in the brain and is utilized in treating nerve pain and convulsions. The gabapentin (horizant brand) is also effective in treatment of restless leg syndrome. Common side effects of gabapentin includes: headache, dizziness and drowsiness. In the United Kingdom (UK), gabapentin and pregabalin are approved for the treatment of peripheral (both) and central (pregabalin only) neuropathic pain in adults [3, 4]. Gabapentinoids, a collective term for these drugs, have a similar structure and mechanism of action.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |