Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
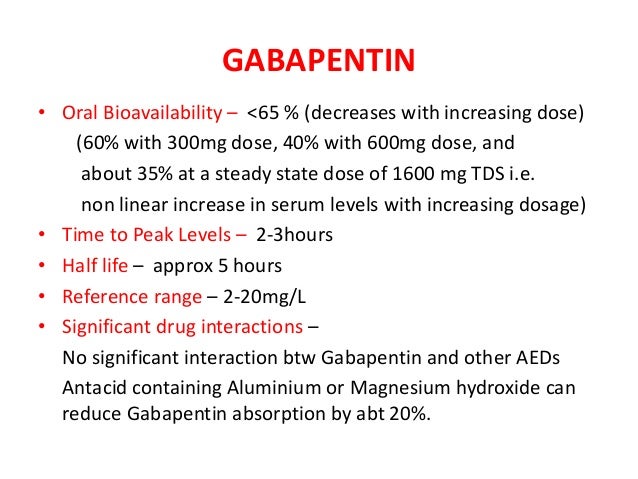
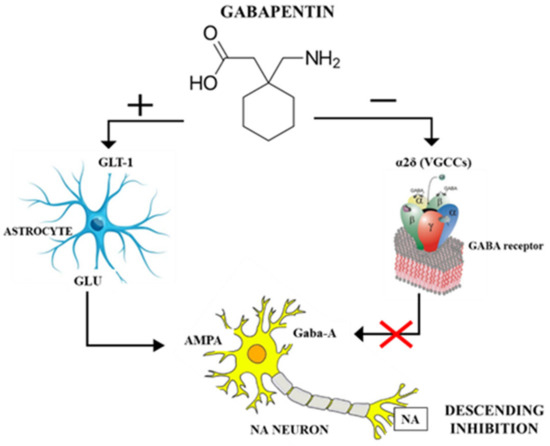
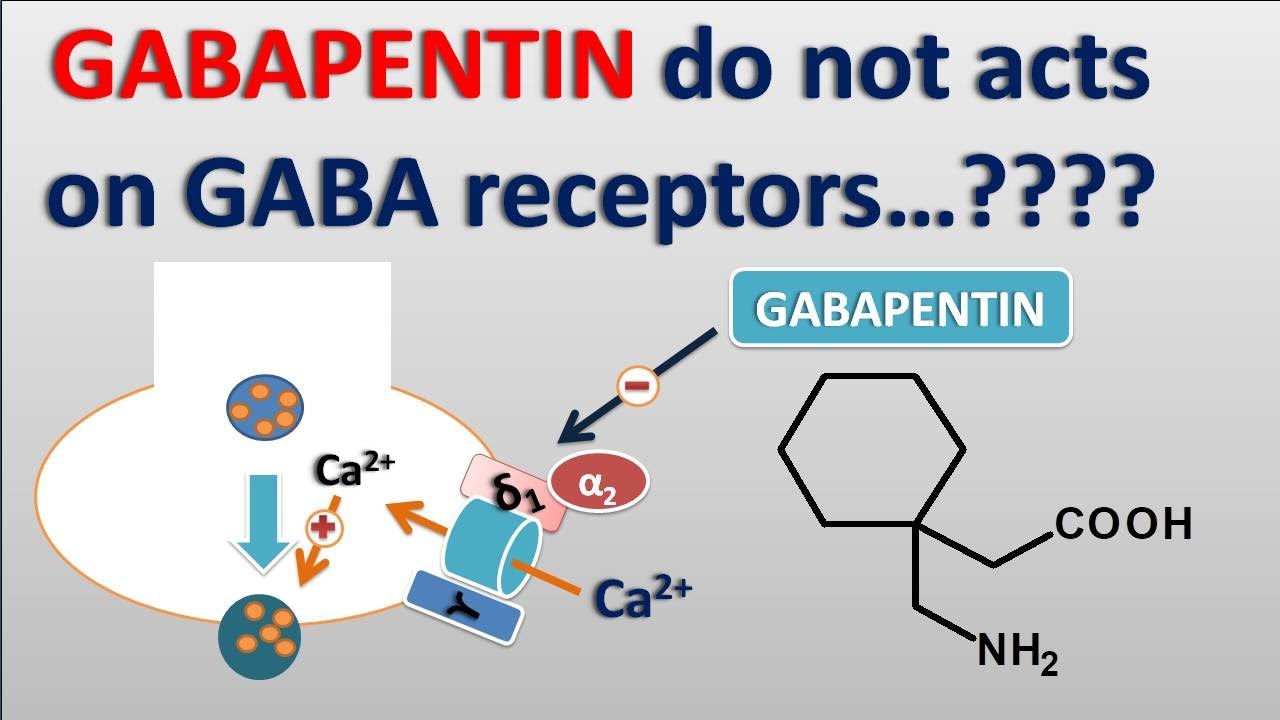
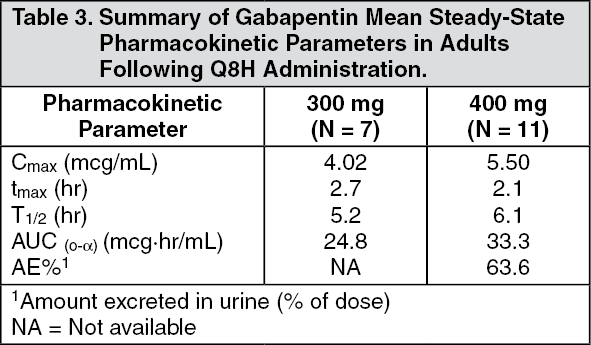
Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Learn how gabapentin works by binding calcium channel subunits. Full MOA, uses, MCQs, FAQs, and pharmacology inside. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Gabapentin is available in two extended-release formulations in addition to the immediate release: a gastric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn how gabapentin works by binding calcium channel subunits. Full MOA, uses, MCQs, FAQs, and pharmacology inside. Gabapentin is available in two extended-release formulations in addition to the immediate release: a gastric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin is an approved treatment as an adjunctive therapy in the management of epilepsy. However, it is most commonly prescribed off-label for other conditions, including anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and chronic pain. Gabapentin is especially effective at relieving allodynia and hyperalgesia in animal models. It has been shown to be efficacious in numerous small clinical studies and case reports in a wide variety of pain syndromes. However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is an approved treatment as an adjunctive therapy in the management of epilepsy. However, it is most commonly prescribed off-label for other conditions, including anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and chronic pain. However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Gabapentin is especially effective at relieving allodynia and hyperalgesia in animal models. It has been shown to be efficacious in numerous small clinical studies and case reports in a wide variety of pain syndromes. Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |