Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
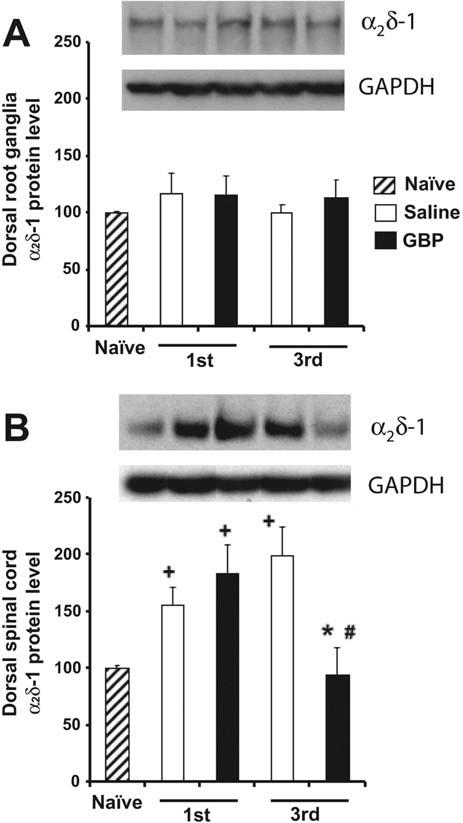
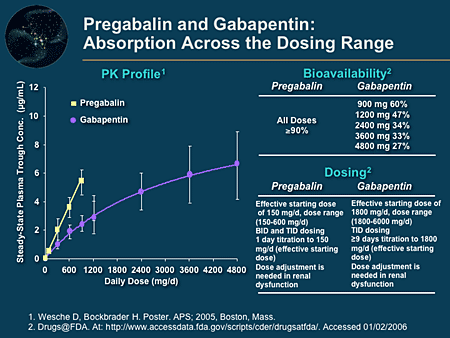
Introduction Chemotherapy- induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) affects patients’ quality of life and treatment effectiveness. Gabapentinoids, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are often used for CIPN treatment, but their efficacy and safety remain uncertain. Efficacy and safety of oxycodone/naloxone as add-on therapy to gabapentin or pregabalin for the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in Korea. KEYWORDS: gabapentin, peripheral neuropathy, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, taxanes, paclitaxel, cisplatin, carboplatin, vinca alkaloids, neurotoxi-city, pain. P eripheral neuropathy is a common complication of several classes of chemotherapeutic agents including taxanes (paclitaxel A new NDC code for gabapentin, pregabalin, or duloxetine was used to identify new pharmacy dispensings of these drugs since initiation of chemotherapy. Gabapentin and pregabalin were investigated because gabapentin is prescribed frequently for CIPN [9] and pregabalin is in the same drug family as gabapentin. Introduction Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) affects patients’ quality of life and treatment effectiveness. Gabapentinoids, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are often used for CIPN treatment, but their efficacy and safety remain uncertain. This study reviews and analyses randomised controlled trial data on this topic. Chemotherapy substantially deteriorates the neurologic condition of the patients and the quality of life. Paclitaxel and carboplatin treated patients may benefit from gabapentin therapy in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. We review here the recommendations of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, as well as some new and promising approaches to neuropathy, including new neuromodulation techniques. Gabapentin monotherapy seems to be well tolerated and useful for the management of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. With the 1 older placebo-controlled clinical trial that showed no benefit for gabapentin for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, 66 2 subsequent trials investigating pregabalin as an agent to prevent chemotherapy-induced neuropathy (1 for paclitaxel 43 and 1 for oxaliplatin [ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00380874 Is gabapentin considered a painkiller? Can Neuropathy from Chemo Be Reversed? While some patients experience partial or complete recovery after stopping chemotherapy, a significant proportion continue to have persistent symptoms. The likelihood of reversal depends on the chemotherapy agent, dose, duration, and individual patient factors. The effects of Gabapentin are well-known in conditions such as post-herpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuropathy, spinal cord injury pain, and neuropathic cancer pain. More common cancer-related neuropathic pain syndromes are listed in Table 1. The use of Gabapentin in patients with neuropathic pain can alleviate pain and increase daily Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common dose-limiting side effect experienced by patients receiving treatment for cancer. Approximately 30–40% of patients treated with neurotoxic chemotherapy will develop CIPN and there is Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common toxicity associated with treatment with platinum-based agents, taxanes, vinca alkaloids, and other specific agents. The long-term consequences of this condition can result in decreased Background: The antiepileptic agent, gabapentin, has been demonstrated to relieve symptoms of peripheral neuropathy due to various etiologies. On the basis of these data, a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, randomized trial was conducted to evaluate the effect of gabapentin on symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral INTRODUCTION Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common adverse effect of cancer therapy that can have a profound impact on quality of life and survivorship [1]. Introduction: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) affects patients' quality of life and treatment effectiveness. Gabapentinoids, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are often used for CIPN treatment, but their efficacy and safety remain uncertain. Abstract When peripheral neuropathy occurs due to chemotherapy treatment, it is referred to as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Typically, symptoms are sensory rather than motor and include reduced feeling and heightened sensitivity to pressure, pain, temperature, and touch. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a progressive, enduring, and often irre-versible adverse effect of many antineoplastic agents, among which sensory abnormities are common and the most suffering issues. The pathogenesis of CIPN A randomized, multicenter, blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover, clinical trial was conducted to evaluate the role of gabapentin in patients with symptomatic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurop When peripheral neuropathy occurs due to chemotherapy treatment, it is referred to as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Typically, symptoms are sensory rather than motor and include reduced feeling and heightened sensitivity to
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |