Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |
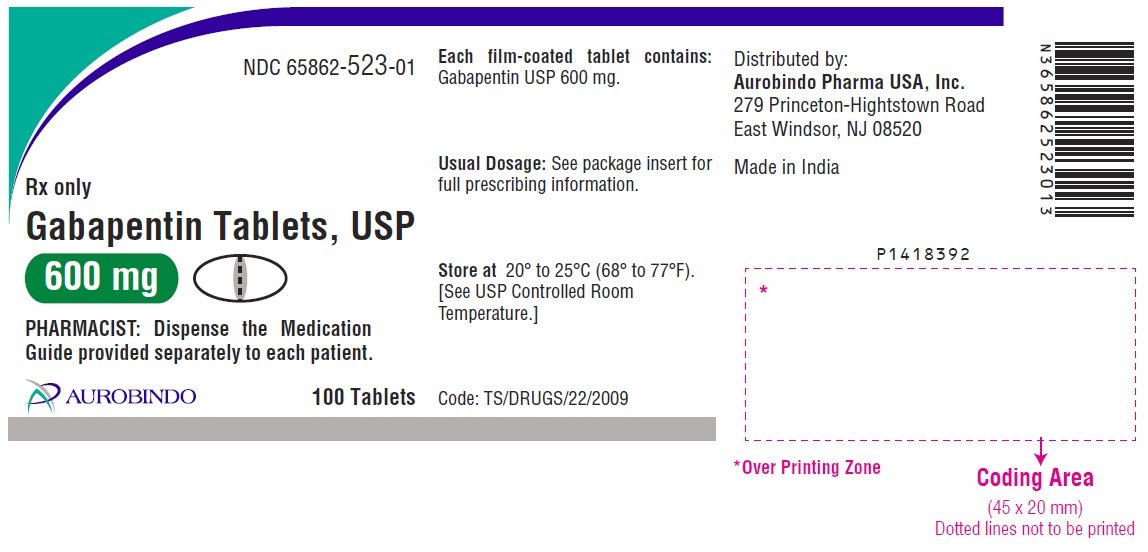
There are rare postmarketing reports of individuals experiencing withdrawal symptoms shortly after discontinuing higher than recommended doses of gabapentin used to treat illnesses for which the drug is not approved. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA-approved to treat specific types of nerve pain and seizures. It’s also sometimes used to treat other health conditions. These include restless leg syndrome, anxiety, and alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance according to the federal government. But several states have passed their own laws classifying gabapentin a schedule Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved for a variety of uses include fibromyalgia and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and pregabalin was Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant (antiseizure) medication approved by the FDA to treat several conditions. Doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin "off-label" to treat other conditions as well. A 2022 report stated that gabapentin was among the 10 most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve Gabapentin is a popular medication used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. The drug is prescribed to millions of patients annually, and it has also been used off-label to treat other conditions such as anxiety disorders, migraines, and bipolar disorder. Despite its widespread use, gabapentin has not been approved by the FDA for these off-label uses. In this blog post, we will Gabapentin gained FDA approval in 1993 under the brand name Neurontin as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, and subsequently for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults in 2002. It became available as a generic in 2004. There are rare postmarketing reports of individuals experiencing withdrawal symptoms shortly after discontinuing higher than recommended doses of gabapentin used to treat illnesses for which the drug is not approved. The uses of Gabapentin are primarily for treating seizures and nerve pain, with additional off-label applications for anxiety, insomnia, and withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is an FDA-approved drug for epilepsy and postherpetic neuralgia. It helps regulate nerve activity to prevent seizures and relieve chronic pain caused by nerve damage. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of seizures in 1993 and was subsequently approved for one pain indication, postherpetic neuralgia. However, gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant), a proprietary prodrug of gabapentin that produces extended release of gabapentin and is FDA-approved for pain and restless leg syndrome, is currently being evaluated as a treatment for alcohol use disorder in a Phase II multi-center trial (1200mg/d) conducted by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), restless legs syndrome (RLS), a painful movement disorder in the legs partial seizures in adults and children Gabapentin is not currently recognized as an FDA-approved drug for the prevention of alcohol relapse or as treatment for AUD. However, literature clearly indicates its strong role in treating AUD and symptoms associated with alcohol cravings. DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. Important Limitation: GRALISE is not interchangeable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration (See Warnings and Precautions) ^Gabapentin enacarbil doses up to 1200 mg daily have been used in clinical trials with no additional benefit and increased adverse reactions. While not FDA-approved, gabapentin has also been evaluated in adult clinical trials for use in neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and vasomotor symptoms with favorable results.1,2 1.2 Pediatrics FDA warns about serious breathing problems with seizure and nerve pain medicines gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR) When used with CNS depressants or in In December 1993, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted approval for gabapentin, under the brand name Neurontin, for adjunctive therapy of partial seizures. Subsequently, the FDA approved gabapentin in 2000 for treatment of partial seizures in children aged 3 years or older and in 2002
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | +and+Gabapentin+(Neurontin).jpg) |
 |  |