Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
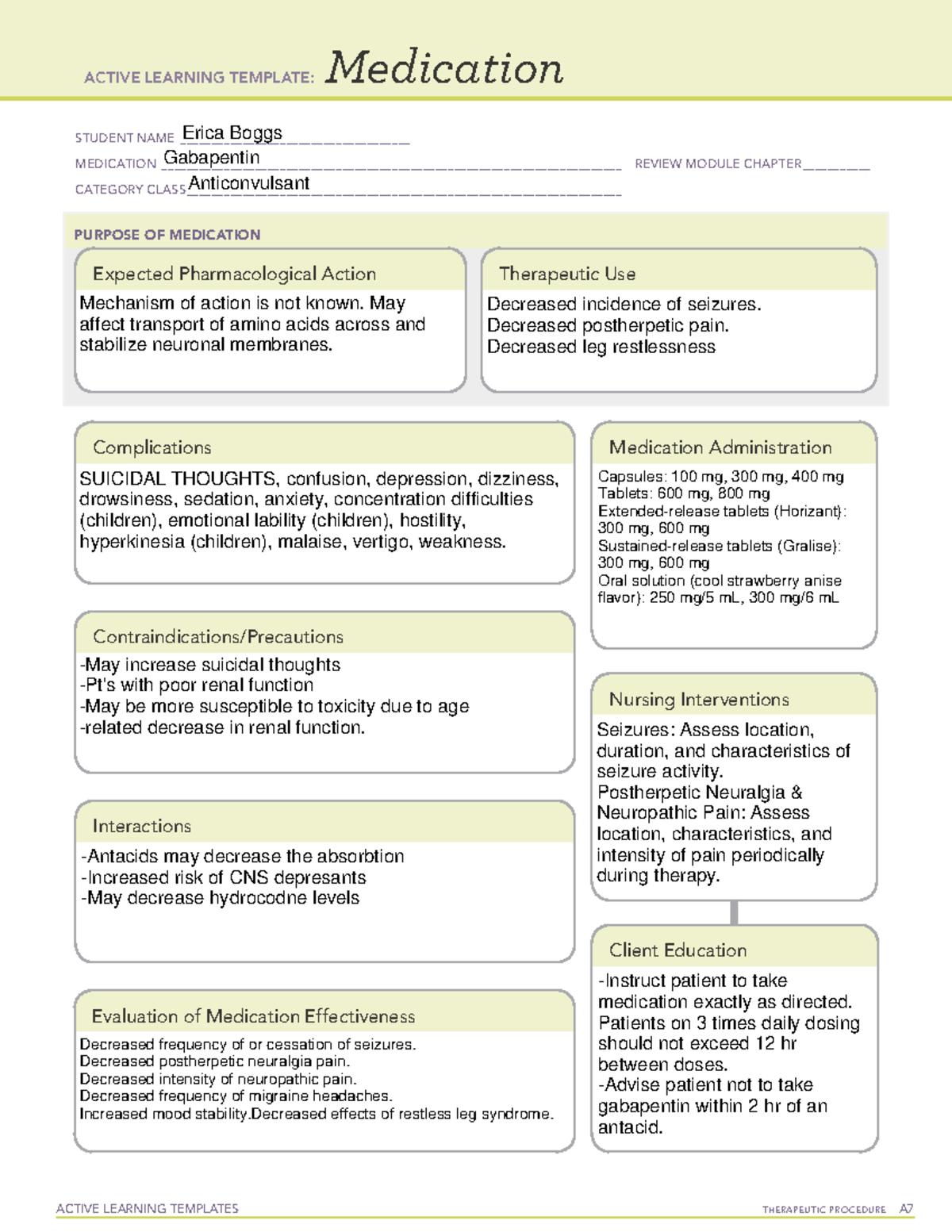 |  |
A nurse is teaching a client who has postherpetic neuralgia and a new prescription for gabapentin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Gabapentin is used to relieve pain from the nerves, from the spinal cord, or from the brain. Nerve pain may be associated with shingles (herpes zoster), diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, sciatica, trigeminal neuralgia and other conditions. Gabapentin is also used in the management of certain types of seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. How do I take this medicine? Written by Kathleen Salvador, MSN, RN Gabapentin Nursing Considerations & Patient Teachings Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Gabapentin Teaching 1979 SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. It is a first line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain arising from diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. Most common side effects of gabapentin in Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Amiodarone Teaching 2680 Instructed patient on medication Amiodarone. This medication is used to stabilize the rhythm of your heart. Amiodarone is used to treat ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Take this medication at the same time daily as directed. May take with or without food. Avoid grapefruit, St. John's wort, & sunlight or tanning beds. common side effects include Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Generic Name Gabapentin Trade Name Neurontin Indication Seizures, peripheral neuropathy, neuropathic pain, prevention of migraines Action Exact method of action unknown, may play a role in stabilizing neural membranes Therapeutic Class Analgesic adjuncts, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Pharmacologic Class None Nursing Considerations • May cause suicidal thoughts, confusion, depression You’ve learned about gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications (aka nursing considerations) and patient teachings in this article. In addition, you’ve learned about gabapentin’s mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, dosage, indications, contraindications, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. May cause suicidal thoughts, confusion, depression, drowsiness, ataxia, facial edema, hypertension Nurse Teachings on Side Effects of Gabapentin. Gabapentin can be used as an antineuropathy agent to control nerve pain. Gabapentin is evaluated based on its ability to release neuropathic pain relief and alleviate neuralgia symptoms. The effectiveness of gabapentin in managing neuropathic pain is assessed by monitoring the reduction in pain intensity and frequency reported by the patient. Hypertension Teaching 2622 Instructed patient Rising slowly from a sitting or lying position may help ease symptoms. Avoiding alcohol, drinking plenty of water, and eating small, low-carbohydrate meals along with fruits and vegetables may also help. See a doctor immediately if you Faint, Break out in cold sweats, breathe rapidly and shallowly, Notice blood in your stool. Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output Interventions Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. I don’t claim any copyright licensure home notes nursing pharmacology gabapentin considerations and patient teaching gabapentin considerations and patient What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. It is also known under the brand names Neurontin and Gralise. As a nurse, understanding the uses, dosages, side effects, and patient education related to gabapentin is crucial for providing optimal care. Evaluation The nurse promotes safe and effective relief of pain through assessment, patient education, and monitoring for therapeutic and adverse effects of gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |