Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
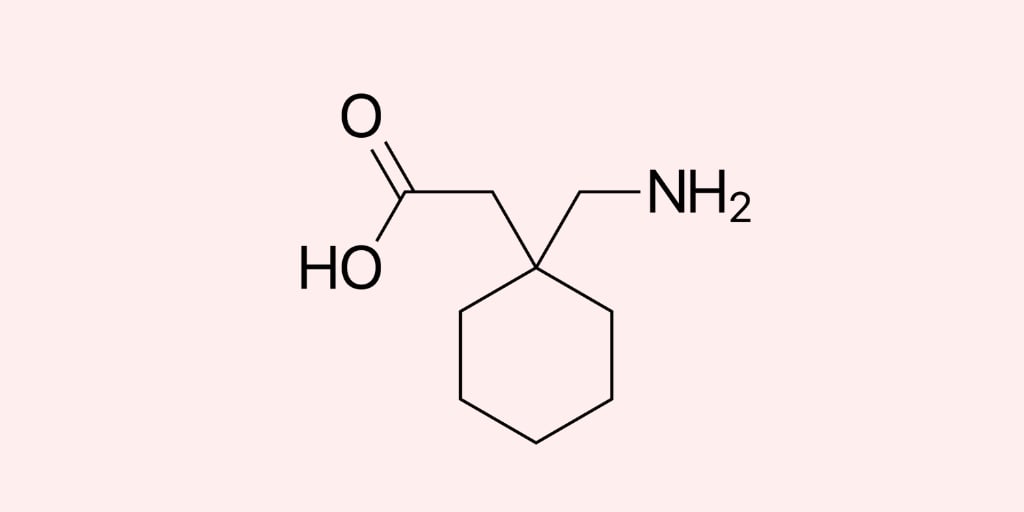
Gabapentin, a commonly prescribed anticonvulsant medication, is used to treat a variety of conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. While generally well-tolerated, nurses must be aware of potential adverse effects and implement appropriate nursing considerations to ensure patient safety and optimal therapeutic outcomes. Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes The information contained in Peak Development for Medication Administration is intended only as a guide for the practice of licensed nursing personnel who administer medications. Every effort has been made to verify the accuracy of the information herein. I don’t claim any copyright licensure home notes nursing pharmacology gabapentin considerations and patient teaching gabapentin considerations and patient Gabapentin nursing considerations involve monitoring seizure control, managing side effects, and educating patients on dosage, potential interactions, and withdrawal symptoms, ensuring safe administration and optimal therapeutic outcomes for neuropathic pain and epilepsy management. Bristol Community College NUR 101 Medication Sheet 1**. Generic** : Gabapentin : Neurontin Dosage : 600mg PO TID Route of Administration :PO Scheduled times : 0900, 1700, 0100 Classifications : Therapeutic - analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Safe dose : PO (Adults and Children >12 yr): 300 mg 3 times daily initially. Titration may be continued until desired Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Nurses vigilantly monitor patients for respiratory depression, especially when gabapentin is used with other Nursing Considerations Nursing considerations for gabapentin encompass thorough assessment, precise administration, vigilant monitoring, and comprehensive patient education to ensure safe and effective therapy. Assessment Medical History: Review for renal impairment, history of seizures, mental health disorders, or substance abuse. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin Related Nursing Diagnoses Acute pain Risk for injury Risk for infection (related to decreased white blood count) Risk for suicide, impaired oral mucous membrane, constipation as potential side effects of gabapentin Nursing Assessment Assess for allergies to gabapentin Monitor for changes in neurological status, changes in mood, or thoughts of suicide Gabapentin and Nursing: Key Considerations for Safe and Effective Patient Care Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic medication commonly encountered in various clinical settings. Nurses play a vital role in ensuring its safe and effective use. It's crucial for nurses to have a comprehensive understanding of gabapentin's pharmacology, administration guidelines, potential adverse effects Gabapentin Nursing Considerations and implications. Learn monitoring, administration, and patient education for safe and effective therapy. Neurontin Pre-Administration Assessment: Post Administration Evaluation: Nursing Considerations: You’ve learned about gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications (aka nursing considerations) and patient teachings in this article. In addition, you’ve learned about gabapentin’s mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, dosage, indications, contraindications, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Find detailed information on Gabapentin including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half-life, administration, and more. Drug Name Generic Name : gabapentin Brand Name: Apo-Gabapentin (CAN), Gen-Gabapentin (CAN), Neurontin Classification: Antiepileptic Pregnancy Category C Dosage & Route Available forms : Capsules—100, 300, 400 mg; tablets—100, 300, 400, 600, 800 mg; oral solution—250 mg/5 mL ADULTS Epilepsy: Starting dose is 300 mg PO tid, then titrated up as needed. Maintenance: 900–1,800 mg/day PO in Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more As needed, open gabapentin capsules and mx contents with water, fruit juice, apple sauce or pudding before administration. Give drug at least 2 hours after an antacid. Be aware that routine monitoring of blood gabapentin level isn't needed. Monitor renal function test results, and expect to adjust dosage, if needed. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |