Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 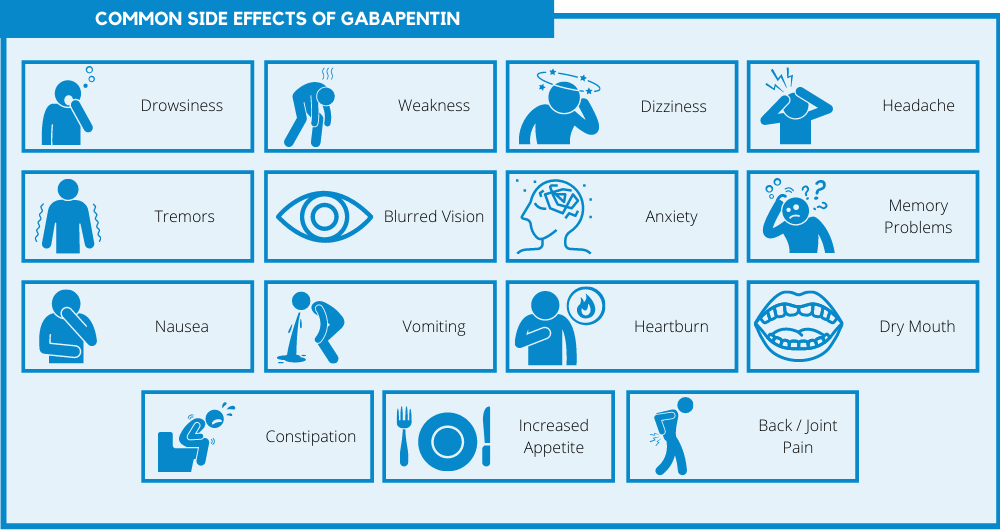 |
Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. We delineate its pharmacological, laboratory and clinical profiles, with a review of the world literature. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Abstract Risk of dementia following gabapentin prescription in chronic low back pain patients Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Off-label, gabapentin has been used in the treatment of migraine and other types of headache, including cluster and tension headaches. It shows potential as an option for those living with migraine and other headache disorders. Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Neuropathy caused by other etiologies such as chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS), cancer, multiple sclerosis, phantom limb pain, HIV Vasomotor symptoms (i.e. hot flashes Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1, 2. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain following shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. Tension-type, migraine, and cluster headaches are the most common primary headaches. Primary headaches are differentiated by clinical criteria from the International Classification of Headache Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Headache is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Vitamin D3, and have Multiple sclerosis. Understanding the relationship between gabapentin and migraines involves delving into how the medication works, its side effects, and anecdotal evidence from users. The primary concern is whether gabapentin can trigger migraines or exacerbate headache disorders in susceptible individuals. What Is Gabapentin? Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. A 2016 study showed evidence that gabapentin benefits headache syndromes, but it still wasn’t recommended as a primary therapy. If you’re experiencing migraine attacks or your current
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |